(Press-News.org) In the modern day, our interactions with voice-based devices and services continue to increase. In this light, researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology and RIKEN, Japan, have performed a meta-synthesis to understand how we perceive and interact with the voice (and the body) of various machines. Their findings have generated insights into human preferences, and can be used by engineers and designers to develop future vocal technologies.
As humans, we primarily communicate vocally and aurally. We convey not just linguistic information, but also the complexities of our emotional states and personalities. Aspects of our voice such as tone, rhythm, and pitch are vital to the way we are perceived. In other words, the way we say things matters.
With advances in technology and the introduction of social robots, conversational agents, and voice assistants into our lives, we are expanding our interactions to include computer agents, interfaces, and environments. Research on these technologies can be found across the fields of human-agent interaction (HAI), human-robot interaction (HRI), human-computer interaction (HCI), and human-machine communication (HMC), depending on the kind of technology under study. Many studies have analyzed the impact of computer voice on user perception and interaction. However, these studies are spread across different types of technologies and user groups and focus on different aspects of voice.
In this regard, a group of researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Japan, RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project (AIP), Japan, and gDial Inc., Canada, have now compiled findings from several studies in these fields with the intention to provide a framework that can guide future design and research on computer voice. As lead researcher Associate Professor Katie Seaborn from Tokyo Tech (Visiting Researcher and former Postdoctoral Researcher at RIKEN AIP) explains, "Voice assistants, smart speakers, vehicles that can speak to us, and social robots are already here. We need to know how best to design these technologies to work with us, live with us, and match our needs and desires. We also need to know how they have influenced our attitudes and behaviors, especially in subtle and unseen ways."
The team's survey considered peer-reviewed journal papers and proceedings-based conference papers where the focus was on the user perception of agent voice. The source materials encompassed a wide variety of agent, interface, and environment types and technologies, with the majority being "bodyless" computer voices, computer agents, and social robots. Most of the user responses documented were from university students and adults. From these papers, the researchers were able to observe and map patterns and draw conclusions regarding the perceptions of agent voice in a variety of interaction contexts.
The results showed that users anthropomorphized the agents that they interacted with and preferred interactions with agents that matched their personality and speaking style. There was a preference for human voices over synthetic ones. The inclusion of vocal fillers such as the use of pauses and terms like "I mean..." and "um" improved the interaction. In general, the survey found that people preferred human-like, happy, empathetic voices with higher pitches. However, these preferences were not static; for instance, user preference for voice gender changed over time from masculine voices to more feminine ones. Based on these findings, the researchers were able to formulate a high-level framework to classify different types of interactions across various computer-based technologies.
The researchers also considered the effect of the body, or morphology and form factor, of the agent, which could take the form of a virtual or physical character, display or interface, or even an object or environment. They found that users tended to perceive agents better when the agents were embodied and when the voice "matched" the body of the agent.
The field of human-computer interaction, particularly that of voice-based interaction, is a burgeoning one that continues to evolve almost daily. As such, the team's survey provides an essential starting point for the study and creation of new and existing technologies in voice-based human-agent interaction (vHAI). "The research agenda that emerged from this work is expected to guide how voice-based agents, interfaces, systems, spaces, and experiences are developed and studied in the years to come," Prof. Seaborn concludes, summing up the importance of their findings.
INFORMATION:
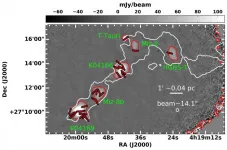
Magnetic fields are ubiquitous throughout our Milky Way Galaxy and play a crucial role in all dynamics of interstellar medium. However, questions like how Solar-type stars form out of magnetized molecular clouds, whether the role of magnetic fields changes at various scales and densities of molecular clouds, and what factors can change the morphology of magnetic fields in low-mass dense cores still remain unclear.
A new study led by Dr. Eswaraiah Chakali from Prof. LI Di's research group at the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC) has partially answered these questions. ...
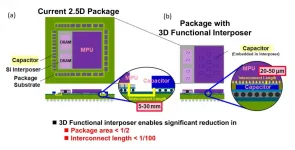
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology develop a 3D functional interposer--the interface between a chip and the package substrate--containing an embedded capacitor. This compact design saves a lot of package area and greatly reduces the wiring length between the chip's terminals and the capacitor, allowing for less noise and power consumption. Their approach paves the way to new semiconductor package structures with greater miniaturization.
Electronics started big size-wise but have only grown smaller and more compact over time. Today, even smartphones outperform the bulky computers from the 1980s by orders of magnitude. Unfortunately, ...
Up to three quarters of the biodiversity living on Western Australia's iconic ironstone mountains in the State's Mid West (known as Banded Iron Formations) could be difficult or impossible to return quickly to its previous state after the landscape has been mined, a Curtin University study has found.
The research published in Ecology and Evolution, discovered that the plant ecosystems are well-adapted to the characteristics of the region's ancient and nutrient-poor soils - and that the very different features of mined landscapes mean many native species are unlikely to be returned by rehabilitation.
Lead researcher Dr Adam Cross ...
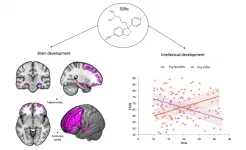
One person in 2000 suffers from a microdeletion of chromosome 22 that can lead to the development of psychotic disorders, such as schizophrenia, in adolescence. In addition to symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions, psychotic disorders also comes with a progressive decline in intelligence quotient (IQ). If current drug treatments are successful in containing psychotic symptoms, nothing can be done to prevent the deterioration of intellectual skills that leads to loss of autonomy. Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, have discovered that prescription of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) - a class of drugs used to treat anxiety and depression -in late childhood can reduce the deterioration ...
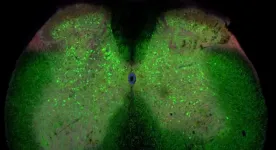
ALS is a very severe neurodegenerative disease in which nerve cells in the spinal cord controlling muscles and movement slowly die. There is no effective treatment and the average life expectancy after being diagnosed with ALS is usually short. Because of this, new knowledge about the disease is urgently needed.
Now, researchers from the University of Copenhagen have gained new insights about ALS, by investigating the early development of the disease in a mouse model.
"We have found that networks of nerve cells in the spinal cord called inhibitory interneurons lose connection to motor neurons, the nerve ...
Researchers have created a new nanometer-scale proximity labeling system that targets histidine residues quickly, providing a new chemical tool in protein chemical modification.
The results of their research were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on April 27, 2021.
Protein chemical modification, a technology that introduces functions into the chemical structure of proteins through irreversible strong bonds, is used for the creation of protein-based biomaterials and for drug delivery systems.
In order to carry out modification, protein labeling is necessary. Proximity labeling is one of those techniques. It labels biomolecules located close to a protein of interest which can then also be marked ...
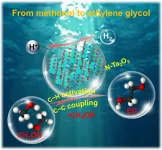
The photochemistry of the future will spring up human industry without smoke, and bring a brighter civilization based on the utilization of solar energy instead of fossil energy. Photochemistry has been used in controlling many reaction processes, especially for the challenging reactions containing selective C-H activation and C-C coupling in chemical synthesis. It is of great interests that a "dream catalytic reaction" of direct coupling of methanol to ethylene glycol (2CH3OH ? HOCH2CH2OH + H2, denoted as MTEG) could be achieved through the solar energy-driven C-H activation and C-C coupling processes, and this MTEG reaction has not been achieved through thermocatalysis yet.
Ethylene glycol (EG) is an important monomer for the manufacture of polymers (e.g., poly(ethylene ...
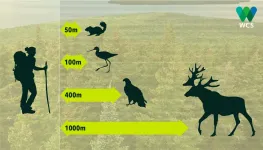
Spending time outdoors is good for a person's body and soul, but how good is it for the wildlife around us?
Outdoor recreation has become a popular activity, especially in the midst of a pandemic, where access to indoor activities might be limited. Long known to have negative behavioural and physiological effects on wildlife, outdoor recreation is one of the biggest threats to protected areas. Human disturbance to animal habitats can lower their survival and reproduction rates, and ultimately shrink populations or eradicate them from areas where they would ...
Researchers have identified the key factors that influence a vital pattern of ocean currents.
The Atlantic meridional overturning circulation (AMOC) carries warm water from the tropics northward.
Many scientists think that this heat transport makes areas including north-west Europe and the UK warmer than they would otherwise be.
Climate models suggest the AMOC is likely to weaken over the coming decades, with widespread implications for regional and global climate.
The new study - led by the universities of Exeter and Oxford, and published in Nature Geoscience - pinpoints the causes of monthly and annual AMOC variation and finds a differing picture at two key locations.
Observational data came from large ...
The Covid-19 pandemic has introduced us to expressions like 'lockdown', 'isolation' and 'social distancing', which became part of social conduct all over the world. Now it appears that bats also maintain social distancing which might help prevent the spread of contagious diseases in their colonies. In a new study published in Annals of the New York Academy of Science, researchers from Tel Aviv University demonstrate that sick bats, just like ill humans, prefer to stay away from their communities, probably as a means for recovery, and possibly also as a measure for protecting others. The study was conducted by postdoctoral researcher Dr. Kelsey Moreno and PhD candidate Maya Weinberg ...