(Press-News.org) Following an 18-month meditation programme can improve the wellbeing of older adults, finds a new randomised controlled trial by an international team co-led by UCL.
The findings, published in PLOS ONE, show that meditation can improve people’s awareness, connection to others, and insight.
While the meditation training did not confer significant benefits on two commonly used measures of psychological wellbeing and quality of life, the researchers say their findings may reveal limitations in existing methods of tracking wellbeing.
Lead author Marco Schlosser (UCL Psychiatry and University of Geneva) said: “As the global population ages, it is increasingly crucial to understand how we can support older adults in maintaining and deepening their psychological wellbeing. In our study, we tested whether long-term meditation training can enhance important dimensions of wellbeing. Our findings suggest that meditation is a promising non-pharmacological approach to support human flourishing in late life.”
The study is the longest randomised meditation training trial conducted to date, and explored the impact of an 18-month meditation programme on the psychological wellbeing of more than 130 healthy French-speaking people aged 65 to 84. The study, led by Principal Investigator Professor Gaël Chételat, took place in Caen, France. It was conducted by the European Union's Horizon 2020-funded Medit-Ageing (Silver Santé Study) research group which involves UCL, Inserm, University of Geneva, Université de Caen Normandy, Lyon Neuroscience Research Center, University of Liège, Technische Universität Dresden, and Friedrich Schiller University Jena.
The researchers compared a meditation programme, which included a nine-month mindfulness module followed by a nine-month loving kindness and compassion module, delivered by weekly group sessions (two hours long), daily home practice (at least 20 minutes), and one retreat day, with a group that did English language training (as a comparison group) and a no-intervention control group.
The team found that meditation training significantly impacted a global score that measures the wellbeing dimensions of awareness, connection, and insight. Awareness describes an undistracted and intimate attentiveness to one's thoughts, feelings, and surroundings, which can support a sense of calm and deep satisfaction. Connection captures feelings such as respect, gratitude, and kinship that can support more positive relationships with others. Insight refers to a self-knowledge and understanding of how thoughts and feelings participate in shaping our perception – and how to transform unhelpful patterns of thought relating to ourselves and the world.
The benefits of meditation training to an established measure of psychological quality of life were not superior to English language training, while neither intervention significantly impacted another widely used measure of psychological wellbeing. The researchers suggest this may be because these two established measures do not cover the qualities and depth of human flourishing that can potentially be cultivated by longer-term meditation training, so benefits to awareness, connection and insight are missed.
The programme did not benefit everyone equally, as participants who reported lower levels of psychological wellbeing at the start of the trial showed greater improvements compared to those who already had higher levels of wellbeing.
Co-author Dr Natalie Marchant (UCL Psychiatry) said: “We hope that further research will clarify which people are most likely to benefit from meditation training, as it may confer stronger benefits on some specific groups. Now that we have evidence that meditation training can help older adults, we hope that further refinements in partnership with colleagues from other research disciplines could make meditation programmes even more beneficial.”
Senior author Dr Antoine Lutz (Lyon Neuroscience Research Center, Inserm, France) said: “By showing the potential of meditation programmes, our findings pave the way for more targeted and effective programmes that can help older adults flourish, as we seek to go beyond simply preventing disease or ill-health, and instead take a holistic approach to helping people across the full spectrum of human wellbeing.”
END
Meditation training can support wellbeing in older adults
2023-12-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research shows human behavior guided by fast changes in dopamine levels
2023-12-01
What happens in the human brain when we learn from positive and negative experiences? To help answer that question and better understand decision-making and human behavior, scientists are studying dopamine.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter produced in the brain that serves as a chemical messenger, facilitating communication between nerve cells in the brain and the body. It is involved in functions such as movement, cognition and learning. While dopamine is most known for its association with positive emotions, scientists are also exploring ...
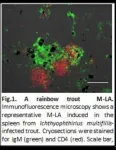
Scientists navigate uncharted waters in fish immunology research
2023-12-01
Upon infection or immunization, all jawed vertebrate species generate proteins called antibodies that bind and neutralize pathogens. Strong and long-lasting antibody responses in warm-blooded species such as mammals are produced in secondary lymphoid microstructures (SLMs) among which germinal centers (GCs) are the centerpiece. Despite the apparent absence of GCs or similar SLMs in cold-blooded vertebrates (e.g., fish), these species can mount significant antibody responses that can persist for several months. Thus, for decades, the outstanding question has remained as to how and where ...
Study explores how pre- and postnatal B-12 vitamins improve breast milk vitamin B-12 levels, which supports infant brain development
2023-12-01
Babies and children need vitamins, including vitamin B-12, to help their brains and bodies develop and grow. Babies get B-12 from their mothers and can have low levels of B-12 if their mothers had low vitamin levels during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The vitamin B-12 levels of infants strongly depend on maternal levels. Adequacy of vitamin B-12 in breast milk is particularly important for infants during the first six months of life when breastfeeding is highly recommended. Even after the first six months of life, breast milk may continue ...
Botany must feature more prominently on the school curriculum to promote awareness of climate change, study warns
2023-12-01
Children must be taught more about the importance of plants if education about climate change and sustainability is to be effective, experts have warned.
Botany should feature more heavily in the school curriculum, and be a greater focus of educational policy, the study says.
It warns neither the importance of plants for sustainability or the threats facing many of them are adequately represented in science education. While the problem has been identified for some time, attempts to address it have often struggled to gain a foothold in science education practice.
Dr Bethan Stagg from the University of Exeter and Professor Justin Dillon ...
ADA Forsyth scientists work to bring tissue regeneration to replace root canal treatment
2023-12-01
Cambridge, MA - Want to avoid a root canal? In the future, you might be able to opt for tissue regeneration instead. ADA Forsyth scientists are testing a novel technology to treat endodontic diseases (diseases of the soft tissue or pulp in your teeth) more effectively. The study, “RvE1 Promotes Axin2+Cell Regeneration and Reduces Bacterial Invasion,” which appeared in The Journal of Dental Research, demonstrates regenerative properties of resolvins, specifically Resolvin E1 (RvE1), when applied to dental pulp. Resolvins ...
University of Houston challenges students to solve plastic waste crisis
2023-12-01
Plastics are firmly entrenched in today’s world thanks to their cheap, light and versatile nature, but the downside is that plastic waste continues piling up. Earlier this year, United Nations Secretary-General Antonio Guterres said that every day, the equivalent of over 2,000 garbage trucks full of plastics is dumped into our oceans, rivers and lakes.
According to the World Economic Forum, the United States only recycled about 6% of the 40 million tons of plastic waste it generated in 2021. Around the world, about 400 million tons of plastic waste is produced each year. Much of it ends up in landfills, oceans and natural ...
Auburn University invites aspiring physicists to PhD program information meeting
2023-12-01
Auburn University's Department of Physics is hosting a special meeting targeting college students passionate about pursuing a PhD in Physics. This engaging event is set for December 8 at 2 PM Central Time. Interested individuals can join the session virtually via Zoom at https://aub.ie/faKH5W.
Studying Physics at Auburn University is an immersive journey into the universe's fundamental principles. Our PhD program offers a robust foundation in physics and promotes groundbreaking research and discovery. Known for small class sizes and personalized ...
Social media influencers may affect more than voter opinions
2023-12-01
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — If Thanksgiving dinner conversations have turned into heated political arguments over the past two decades, social media may be to blame. Popular social media figures — or influencers — who create or share distorted political messages may cause political parties to moderate their policies to win over independent voters in general elections but tend to polarize the rest of society, according to researchers who created a model to study how social media may affect election ...
1 in 8 older adults use cannabis products, suggesting need to screen for risks
2023-12-01
More older Americans use cannabis now than before the pandemic, with 12% saying they’ve consumed a THC-containing substance in the past year and 4% saying they do so multiple times a week, according to a new study of people aged 50 to 80. Those who drink alcohol at risky levels have a much higher rate of cannabis use.
The new findings, published in the journal Cannabis and Cannabinoids Research by a team from the University of Michigan’s Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation, suggest a need for more education and screening of older adults for cannabis-related ...
Study identifies peptide as key mediator in heavy alcohol drinking
2023-12-01
(Boston)—Alcohol is the most common addictive substance in the world. Every year in the U.S. excessive alcohol use costs $249 billion and causes approximately 88,000 deaths, as well as various chronic diseases and social issues. Alcohol use disorder, a highly prevalent, chronic, relapsing disorder, affects more than 14 million people in the U.S. alone, in addition to being severely under-treated, with only three modestly effective pharmacological therapies available.
Chronic exposure to alcohol has been shown to produce profound neuroadaptations in specific brain regions, including the recruitment of key stress neurotransmitters, ultimately ...