(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study of children and adolescents with acute concussion suggest that moderate-to-vigorous-intensity physical activity reduced symptoms up to a certain threshold but appeared to offer no further benefit in symptom reduction beyond that point.
Authors: Andrée-Anne Ledoux, Ph.D., of the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.56458)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.56458?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=021624
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Optimal volume of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity postconcussion in children and adolescents
JAMA Network Open
2024-02-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Projecting the future registered nurse workforce after the pandemic
2024-02-16
About The Study: The rebound in the total size of the U.S. registered nurse (RN) workforce during 2022 and 2023 indicates that the earlier drop in RN employment during the first 2 years of the COVID-19 pandemic was likely transitory. Updated forecasts of the future RN workforce are very close to those made before the pandemic.
Authors: David I. Auerbach, Ph.D., of Brandeis University in Waltham, Massachusetts, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.5389)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, ...
Lockdown skin cancer diagnosis delays linked to deaths and £6bn costs in Europe
2024-02-16
Delays in diagnosing melanoma due to Covid-19 lockdown may have contributed to over 100,000 years of life lost across Europe and over £6bn in costs, mainly indirectly due to loss of productivity, finds a new study led by UCL and University Hospital of Basel researchers.
The authors of the new JAMA Network Open paper say their findings show how vital early detection of cancer can be, while also highlighting the importance of considering unintended side effects in any future pandemic planning.
Co-lead ...
RNA interference with zilebesiran for mild to moderate hypertension
2024-02-16
About The Study: In adults with mild to moderate hypertension, treatment with zilebesiran, an investigational RNA interference therapeutic, across a range of subcutaneous doses at 3-month or 6-month intervals significantly reduced 24-hour mean ambulatory systolic blood pressure at month three in this phase 2, randomized clinical trial.
Authors: George L. Bakris, M.D., of University of Chicago Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.0728)
Editor’s ...
Electrification or hydrogen? Both have distinct roles in the European energy transition
2024-02-16
“Previous research has shown that our power system can be transformed to renewable sources like wind and solar at low cost and low environmental impact. However, the next question is how this renewable electricity can be used to substitute fossil fuel use in the buildings, industry and transport sectors. Our analysis shows that the direct use of electricity, for example, via electric cars and heat pumps, is critical for a broad range of sectors, while the conversion of electricity to hydrogen is important only for few applications,” ...
Toxoplasmosis: evolution of infection machinery
2024-02-16
Researchers have identified a protein that evolved concurrently with the emergence of cellular compartments crucial for the multiplication of the toxoplasmosis pathogen.
Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease found worldwide, caused by the single-celled parasite Toxoplasma gondii. In humans, infection poses a particular risk to pregnant woman, as it can lead to birth defects. Like the closely related malaria pathogen – Plasmodium falciparum – and other related species, T. gondii possesses special organelles, so-called rhoptries ...
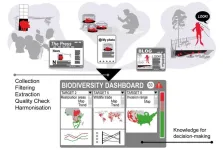
Online digital data and AI for monitoring biodiversity
2024-02-16
The random information posted online could be used to generate information about biodiversity and its conservation.
“I think it's quite amazing that images and comments that people post online can be used to infer changes on biodiversity”, says Dr. Andrea Soriano-Redondo, the lead-author of a new article published in the journal Plos Biology and a researcher at the Helsinki Lab of Interdisciplinary Conservation Science at the University of Helsinki.
Scientists from the University of Helsinki together with colleagues from other universities and institutions around the world propose a strategy for integrating online digital data from media platforms to complement ...
Heart attack significantly increases risk of other health conditions
2024-02-16
Having a heart attack significantly increases the risk of developing other serious long-term health conditions, a major new study shows.
Researchers at the University of Leeds have analysed more than 145 million records covering every adult patient admitted to hospital over a nine-year period to establish the risk of long-term health outcomes following a heart attack – in the largest study of its kind.
Whilst heart attacks are a serious and life-threatening condition, the British Heart Foundation estimates that nowadays more than seven in 10 people survive them, provided they receive quick and emergency treatment to get the blood flowing to the heart muscle again. Yet ...
Plasma technology for more effective lithium extraction
2024-02-16
New research suggesting a improved method for extracting lithium by applying plasma technology has been recently published.
On the 31st of January, the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy(KFE) announced revealed that their researchers have successfully increased the lithium extraction rate by three times compared to pre-existing methods by applying CO2 microwave plasma technology.
The most common method of extracting lithium is mixing sodium carbonate(Na2CO3) to saltwater that contains lithium and extracting lithium carbonate(Li2CO3)-which is a mixture of lithium and carbon dioxide. The downside to this method ...
Can astronomers use radar to spot a cataclysmic asteroid?
2024-02-16
How can humans protect the Earth from “devastating asteroid and comet impacts?” According to the National Academies and their 2023-2032 Planetary Science and Astrobiology Decadal Survey, ground based astronomical radar systems will have a “unique role” to play in planetary defense.
There is currently only one system in the world concentrating on these efforts, NASA’s Goldstone Solar System Radar, part of the Deep Space Network (DSN). However, a new instrument concept from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory ...
Self-monitoring improves physical activity of care-needing elderly
2024-02-16
Self-monitoring of physical activity with an accelerometer and feedback is an effective tool to improve physical activity in elderly people requiring long-term support. The Kobe University study is the first to show that with simple and safe means the physical activity of this demographic can be improved, which is expected to help prevent serious illness and reduce costs for long-term care.
Taking more steps and sitting less is well known as having a significant influence on a wide range of noncommunicable diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, orthopedic diseases and stroke. This is particularly problematic in senior citizens who depend on long-term care such as in day-care ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] Optimal volume of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity postconcussion in children and adolescentsJAMA Network Open