(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of pregnancy-associated homicide rates, barriers to divorce were associated with higher homicide rates and access to reproductive health care was associated with lower homicide rates. This study highlights the association between state legislation and pregnancy-associated homicide in the U.S., which is important information for policymakers.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kaitlin M. Boyle, PhD, email kb49@mailbox.sc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.44199)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.44199?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=110824
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
State divorce laws, reproductive care policies, and pregnancy-associated homicide rates
JAMA Network Open
2024-11-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
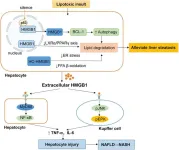
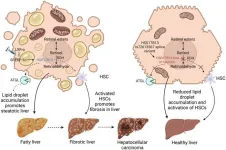
Emerging roles of high-mobility group box-1 in liver disease
2024-11-08
Liver diseases, both acute and chronic, continue to pose significant clinical challenges due to high morbidity and mortality rates. Acute liver injury (ALI) caused by acetaminophen (APAP) overdose, hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury (HIRI), and chronic conditions like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) are influenced by HMGB1-mediated pathways. HMGB1 is released from injured or necrotic liver cells and triggers inflammatory responses. Its circulating levels have been associated with disease severity in liver conditions, marking ...
Exploring the systematic anticancer mechanism in selected medicinal plants
2024-11-08
Cancer remains one of the leading global causes of mortality, with an estimated increase in cases due to lifestyle, environmental, and genetic factors. Despite advancements in treatment, cancer's complexity and the side effects of conventional therapies necessitate alternative approaches. Medicinal plants, long valued for their therapeutic properties, have shown promise in cancer treatment, attributed to their natural phytoconstituents. This review focuses on the anticancer mechanisms of specific medicinal plants and discusses their potential for future therapeutic development.
Anticancer Mechanisms of Selected Medicinal Plants
Medicinal plants exert anticancer ...
University of Cincinnati researchers pen editorial analyzing present, future of emergency consent in stroke trials
2024-11-08
The University of Cincinnati’s Yasmin Aziz, MD, and Joseph Broderick, MD, coauthored an editorial published Nov. 7 in the journal Neurology analyzing the current use and potential future of alternatives to traditional informed consent in acute stroke trials.
Patient informed consent is a crucial part of ethical clinical trial design and implementation, but time is of the essence for stroke trials. Approximately 2 million neurons die each minute they are deprived of oxygen, and patients are also sometimes incapacitated and therefore unable to consent ...
Scarlet Macaw parents ‘play favorites,’ purposefully neglect younger chicks
2024-11-08
Scarlet macaws are a symbol of fidelity and virtue to many people because they are thought to mate for life — but it turns out that they also “play favorites” when feeding their young, making them excellent mates, but neglectful parents.
Fortunately, Texas A&M scientists have developed a way to ensure the birds’ bad parenting results in fewer chick deaths.
Researchers at the College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences have discovered that scarlet macaws purposefully neglect feeding the youngest chicks ...
One gene provides diagnoses for 30 patients whose condition was unexplained for years
2024-11-08
An international team of researchers has provided a genetic diagnosis for 30 individuals whose condition was undiagnosed for years despite extensive clinical or genetic testing. The study, conducted by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, National University of Singapore and collaborating institutions worldwide, appeared in Genetics in Medicine, the official journal of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.
“The story of our findings began with one patient I saw in the clinic presenting an uncommon combination of problems,” said first and co-corresponding ...
Current practice and emerging endoscopic technology in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer
2024-11-08
The evolution of gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy has transformed CRC diagnostics since its early 20th-century origins. Initial rigid endoscopes provided limited visualization, were highly uncomfortable for patients, and only partially visualized the colon. With the introduction of fiber-optic technology in the 1950s, endoscopy began transmitting real-time images, greatly enhancing diagnostic applications for GI conditions. Today, CRC remains a primary target for endoscopic screening due to its high prevalence as the second leading cause of cancer ...
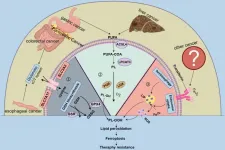
Decoding 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13: A multifaceted perspective on its role in hepatic steatosis and associated disorders
2024-11-08
Chronic liver disease (CLD) is a growing global health challenge, accounting for millions of deaths each year. Its major contributors include metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), alcoholic liver disease (ALD), and hepatitis C virus infection. These conditions are closely tied to hepatic steatosis, a condition characterized by the abnormal accumulation of fat in the liver. Recent genome-wide association studies have identified the 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 13 (HSD17B13) gene and its loss-of-function variant ...
Key pathway leading to neurodegeneration in early stages of ALS identified
2024-11-08
Approximately 5,000 people in the U.S. develop amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) each year. On average, they survive for only two to five years after being diagnosed, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rapidly progressing neurodegenerative disease causes the death of neurons in the brain and spinal cord, resulting in muscle weakness, respiratory failure and dementia. Despite the devastating nature of the disease, little is known about what first triggers the deterioration of motor neurons at the onset of ALS.
Now, researchers from University of California San Diego and their colleagues ...
Ferroptosis in regulating treatment tolerance of digestive system tumors
2024-11-08
The global burden of digestive tract tumors is profound, with these cancers accounting for nearly half of all malignant tumors worldwide. Despite advancements in endoscopic diagnostic methods, which enable earlier detection and treatment, a large portion of patients still receive diagnoses at later stages. For these patients, chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapies are often the only viable options, yet resistance to treatment remains common, leading to high recurrence and mortality rates. Research increasingly shows that ferroptosis may be a key mechanism to reverse treatment tolerance. Ferroptosis, characterized by ...
A promising future in pancreatic incidentaloma detection
2024-11-08
In recent research published in eGastroenterology, Dr. J-Matthias Löhr and colleagues provide an in-depth review of diagnostic methods for pancreatic incidentaloma—incidental findings often detected during imaging scans intended for other conditions. These pancreatic lesions, which vary in severity, can occasionally signal pancreatic cancer in its earliest stages. However, traditional methods, including MRI and CT scans, are limited by invasiveness, cost, and variable sensitivity to early pancreatic changes.
The research highlights ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does mental health affect mortality risk in adults with cancer?
EANM launches new award to accelerate alpha radioligand therapy research
Globe-trotting ancient ‘sea-salamander’ fossils rediscovered from Australia’s dawn of the Age of Dinosaurs
Roadmap for Europe’s biodiversity monitoring system
Novel camel antimicrobial peptides show promise against drug-resistant bacteria
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
[Press-News.org] State divorce laws, reproductive care policies, and pregnancy-associated homicide ratesJAMA Network Open