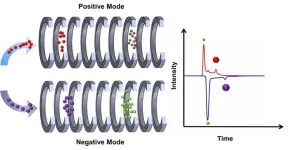
(Press-News.org) Recently, a research group led by Prof. HUANG Chaoqun from the Hefei lnstitutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed an innovative dual drift tube ion mobility spectrometry (DDT-IMS) technology. This novel approach has successfully facilitated the rapid detection of both positive and negative ions of four toxic metabolites derived from 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT), allowing for the detection of residual metabolites in the human body and providing valuable health warnings.
The research results were published in Talanta.
TNT undergoes biodegradation under the influence of fungi and bacteria, producing hazardous metabolites such as 2-amino-4,6-dinitrotoluene (2-ADNT), 4-amino-2,6-dinitrotoluene (4-ADNT), 2,4-diamino-6-nitrotoluene (2,4-DANT), and 2,6-diamino-4-nitrotoluene (2,6-DANT). These metabolites pose potential health risks, making their detection critical, especially among workers in TNT manufacturing facilities.
In this study, the self-developed DDT-IMS technology was used for the rapid detection of these four metabolites. The research team conducted dual-mode detection, calculating the ion mobilities of the metabolites and analyzing how drift tube temperature affected the results. Furthermore, they evaluated the instrument response times for both detection modes.
By applying this technology to urine samples, the researchers demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of DDT-IMS in detecting TNT metabolites within complex biological matrices.
“Our finding indicated that the developed DDT-IMS detection technology has significant potential in assessing the environmental and biological risks of TNT,” said Prof. HUANG Chaoqun.
END
Novel detection technology alerts health risks from TNT metabolites
2024-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
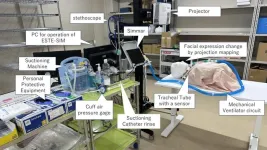
New XR simulator improves pediatric nursing education
2024-11-22
A new simulator gives nursing students hands-on practice with vital procedures like mechanical ventilation and tracheal suctioning in children.
Researchers at Hokkaido University in Japan have created a new training tool to equip nursing students with the skills needed in caring for children who require mechanical ventilation and tracheal suctioning. In a study published in the Journal of Nursing Care & Reports, the team highlighted the simulator's role in addressing the significant increase ...
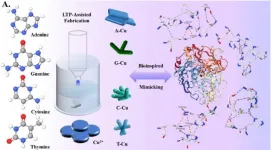
New copper metal-organic framework nanozymes enable intelligent food detection
2024-11-22
Recently, a team led by Prof. HUANG Qing from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, successfully used the gas-liquid interface dielectric barrier (DBD) low-temperature plasma (LTP) technology to prepare a series of Cu metal organic framework (MOF) nanozymes.
“These nanozymes have different base ligands and mimic the activity of laccase,” said Prof. HUANG. The team also developed encoded array sensors for intelligent sensing and identification of bioactive components in food.
The relevant research ...
The Lancet: Deeply entrenched racial and geographic health disparities in the USA have increased over the last two decades—as life expectancy gap widens to 20 years
2024-11-22
The differences in US health and life expectancy based on where an individual lives, the economic conditions in that location, and their racial and ethnic identity have increased over the last two decades, leading to substantial health disparities that divide the USA into ten mutually exclusive populations, which the study authors term “The ten Americas”.
The life expectancy gap—an important indicator of a population’s health— across these ten Americas increased from 12·6 years in 2000 to 20·4 years in 2021, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Between 2000 and 2010 life expectancy increased in nine out of ten Americas, but between 2010 ...
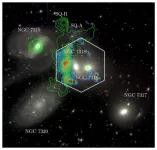
2 MILLION mph galaxy smash-up seen in unprecedented detail
2024-11-22
A massive collision of galaxies sparked by one travelling at a scarcely-believable 2 million mph (3.2 million km/h) has been seen in unprecedented detail by one of Earth's most powerful telescopes.
The dramatic impact was observed in Stephan's Quintet, a nearby galaxy group made up of five galaxies first sighted almost 150 years ago.
It sparked an immensely powerful shock akin to a "sonic boom from a jet fighter" – the likes of which are among the most striking phenomena in the Universe.
Stephan's Quintet represents "a galactic crossroad where past collisions between galaxies ...
Scientists find a region of the mouse gut tightly regulated by the immune system
2024-11-21
The intestine maintains a delicate balance in the body, absorbing nutrients and water while maintaining a healthy relationship with the gut microbiome, but this equilibrium is disrupted in parts of the intestine in conditions such as celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. Scientists don’t fully understand how different regions of the organ resist or adapt to changes in the environment and how that is disrupted in disease.
Now, researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital have analyzed the entire mouse intestine, mapping gene expression and cell states and location in the healthy gut and in response to ...
How school eligibility influences the spread of infectious diseases: Insights for future outbreaks
2024-11-21
A recent study in JAMA Network Open sheds light on how school attendance influences the spread of infectious diseases, using COVID-19 as a case study. Researchers analyzed the natural age cutoff for kindergarten eligibility in California to compare COVID-19 rates between children old enough to start school and those who were not. This approach, called regression discontinuity, offers a way to rapidly understand the role of schools in disease transmission and evaluate the effectiveness of within-school prevention measures without requiring additional data collection or school closures.
The study's findings underscore the complexity of school-based transmission ...
UM School of Medicine researchers link snoring to behavioral problems in adolescents without declines in cognition
2024-11-21
Adolescents who snore frequently were more likely to exhibit behavior problems such as inattention, rule-breaking, and aggression, but they do not have any decline in their cognitive abilities, according to a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). This is the largest study to date tracking snoring in children from elementary school through their mid-teen years and it provides an important update to parents struggling with what medical measures to take to help manage snoring in their children.
The findings were recently published in JAMA ...
The Parasaurolophus’ pipes: Modeling the dinosaur’s crest to study its sound #ASA187
2024-11-21
MELVILLE, N.Y., Nov. 21, 2024 – Fossils might give a good image of what dinosaurs looked like, but they can also teach scientists what they sounded like.
The Parasaurolophus is a duck-billed dinosaur with a unique crest that lived 70 million to 80 million years ago. It stood around 16 feet tall and is estimated to have weighed 6,000 to 8,000 pounds.
Hongjun Lin from New York University will present results on the acoustic characteristics of a physical model of the Parasaurolophus’ crest Thursday, Nov. 21, at 4:30 p.m. ET as part of the virtual 187th Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, running Nov. 18-22, 2024.
“I’ve ...
St. Jude appoints leading scientist to create groundbreaking Center of Excellence for Structural Cell Biology
2024-11-21
MEMPHIS, Tennessee – November 21, 2024 St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital today announced the addition of Georgios Skiniotis, PhD, as a faculty member in the Department of Structural Biology. Skiniotis will also develop and lead the newly created Center of Excellence for Structural Cell Biology.
In his role as director of the Center of Excellence, Skiniotis will develop a world-class technology center that will advance our understanding of cell biology from the atomic scale to the micron scale, including ...
Hear this! Transforming health care with speech-to-text technology #ASA187
2024-11-21
MELVILLE, N.Y., Nov. 21, 2024 – Speech-to-text programs are becoming more popular for everyday tasks like hands-free dictation, helping people who are visually impaired, and transcribing speech for those who are hard of hearing. These tools have many uses, and researcher Bożena Kostek from Gdańsk University of Technology is exploring how STT can be better used in the medical field. By studying how clear speech affects STT accuracy, she hopes to improve its usefulness for health care professionals.
“Automating note-taking for patient data ...