Astrophysics: Mystery of the ‘missing’ binary stars solved
2024-12-17
(Press-News.org)
An international team of researchers led by PD Dr Florian Peißker has found the first binary star in the immediate vicinity of the supermassive black hole Sgr A* (Sagittarius A star) at the centre of our galaxy. Although it is known that most stars in the universe do not form alone, so far there are only five confirmed binary stars at a greater distance from the black hole. None of the systems are so close. The researchers assume that the binary star system they found, named D9, will merge into a single star in the near future. The discovery was published in Nature Communications under the title ‘A binary system in the S cluster close to the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A*’. The work contributes to a better understanding of the centre of our galaxy and the conditions around the supermassive black hole.
For approximately thirty years it has been possible to observe individual stars in the vicinity of the black hole using infrared telescopy. So far, many of the observations have raised more questions. The central region around the supermassive black hole Sgr A* contains millions of stars and is divided into various sub-regions. A particularly interesting region of this so-called ‘inner parsec’ is the S star cluster, which contains Sgr A*. Due to its high density of stars, there should in theory be many binary stars. However, the five known binary stars are actually located in other, more distant regions, while none have yet been detected in this star cluster.
Researchers attributed this to gravitational forces: The stars in the S star cluster move in stable orbits around the black hole, similar to the Earth orbiting the Sun. However, the conditions there are much more extreme, as Sgr A* is four million times heavier than our sun. The stars therefore can reach speeds of several thousand kilometres per second, making it an unfavourable environment for the formation of binary star systems.
The researchers discovered D9 by taking a different approach to observing certain dust sources in the S star cluster. Normally, several individual observations over the course of a year are superimposed and added together to amplify the signal of the objects. “Nobody has looked closely at individual observations of the dust sources each night,” said Florian Peißker from the University of Cologne’s Institute of Astrophysics. “That was the crux of our study: investigating and analysing every single night. The data from the recordings is noisier, but still good enough. This is how we identified the binary star.”
The discovery of D9 now opens up the possibility for researchers to investigate the processes of star formation in more detail, as the system is very likely to merge in the coming decades to millennia and thus form a new, slightly heavier star. This would solve another mystery. Because the stars in the S star cluster close to the supermassive black hole are younger than any star cluster theory has predicted. The presence of the binary star system could therefore provide new clues as to how the stars form around the central black hole. The researchers assume that some of the young stars formed from binary star systems that had previously migrated from the area of the ‘inner parsec’ to the supermassive black hole.
Co-author Dr Michael Zajaček from Masaryk University in Brno, Czech Republic, said: “Until now, it was a mystery how such young stars could form so close to Sgr A*, which in principle should prevent any gravitational collapse that is necessary for star formation. The discovery of this binary star system will significantly expand our knowledge regarding star formation.” Dr Emma Bordier, co-author and postdoc in the Collaborative Research Centre 1601 ‘Habitats of Massive Stars across Cosmic Time’ at the University of Cologne, added: “Different generations of Very Large Telescope instruments were used for these observations. The new findings clearly demonstrate how the combination of archival data and recent observations can complement each other to enable innovative studies and lead to exciting discoveries.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-17
Penn Engineers have modified lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) — the revolutionary technology behind the COVID-19 mRNA vaccines — to not only cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) but also to target specific types of cells, including neurons. This breakthrough marks a significant step toward potential next-generation treatments for neurological diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
In a new paper in Nano Letters, the researchers demonstrate how peptides — short strings of amino ...
2024-12-17
“Passive thermotherapy positively modulates multiple physiological parameters and represents a nonpharmacological approach for potential disease modifying treatment.”
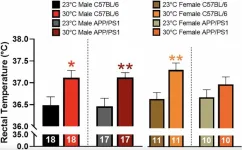
BUFFALO, NY- December 17, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21 on November 29, 2024, entitled, “Thermotherapy has sexually dimorphic responses in APP/PS1 mice.”
Researchers Samuel A. McFadden, Mackenzie R. Peck, Lindsey N. Sime, MaKayla F. Cox, Erol D. Ikiz, Caleigh A. Findley, ...
2024-12-17
An international team of researchers has detected a binary star orbiting close to Sagittarius A*, the supermassive black hole at the centre of our galaxy. It is the first time a stellar pair has been found in the vicinity of a supermassive black hole. The discovery, based on data collected by the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (ESO’s VLT), helps us understand how stars survive in environments with extreme gravity, and could pave the way for the detection of planets close to Sagittarius A*.
“Black holes are not as destructive as we thought,” says Florian Peißker, a researcher at the University of Cologne, Germany, and lead author of the ...
2024-12-17
WASHINGTON, Dec. 17, 2024 – Solar power is currently the fastest growing energy sector worldwide. Solar photovoltaic power plants convert sunlight into electricity and their vast potential for producing clean, renewable energy make solar power a cornerstone of the NetZero Emissions by 2050 initiative, which seeks to cut carbon dioxide emissions to zero by the year 2050.
Wind has both positive and negative effects on solar power grids. It helps maintain solar panel performance by eliminating the buildup of dirt and dust, and ...
2024-12-17
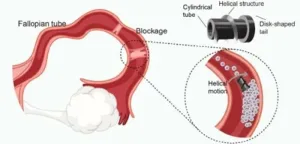
WASHINGTON, Dec. 17, 2024 — Infertility affects an estimated 186 million people worldwide, with fallopian tube obstruction contributing to 11%-67% of female infertility cases. In AIP Advances, from AIP Publishing, researchers at the SIAT Magnetic Soft Microrobots Lab have developed an innovative solution using a magnetically driven robotic microscrew to treat fallopian tube blockages.
“This new technology offers a potentially less invasive alternative to the traditional surgical methods currently used to clear tubal obstructions, which often involve ...
2024-12-17
LOS ANGELES — Scientists at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the U.S. with its National Medical Center named top 5 in the nation for cancer by U.S. News & World Report, have collared a tricky culprit that helps cancer cells evade CAR T cell therapy.
CAR T cell therapy harnesses the immune system to seek out and kill tumor cells. This treatment is used in certain types of leukemia and lymphoma — blood cancers. Some wily cancer cells, however, have learned how to hide from the immune system to avoid destruction. The study published today in the journal Cell could lead to more personalized therapies that ...
2024-12-17
The decades-old anesthetic ketamine could be a game changer for treating severe depression, but there are still many questions about how the drug works, including exactly how it affects the brain’s cells and circuits.
To help answer these questions, researchers are turning to an unlikely animal: tiny, days-old zebrafish.
The millimeters-long, translucent zebrafish may not get depressed exactly like humans do, but the fish do exhibit a “giving up” behavior: they stop swimming after they realize they aren’t getting anywhere – a passive behavior that scientists use to study ...
2024-12-17
About The Study: In this cohort study of Dutch children, early-life moderate to vigorous physical activity was not associated with executive function in middle childhood. Children participating in team sports at ages 10 to 11 consistently exhibited superior executive function compared with participants in individual sports.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lu Yang, MSc, email l.yang@umcg.nl.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.49879)
Editor’s Note: Please see ...
2024-12-17
When doctors and nurses pass patient information from one shift to another — an exchange known as a “handoff” — the specific words they use behind closed doors matter more than they might realize. A new study published in JAMA Network Open shows that when clinicians hear a patient described with negatively biased language, they develop less empathy towards the patient and, in some cases, become less accurate in recalling the patient’s critical health details. Such shifts in perception may be subtle and unintentional in many cases, but as these hidden biases stack up, they can influence the care patients ultimately receive.
“A lot is going on here ...
2024-12-17
Study shows how language, education and age affect someone’s ability to engage with digital health tools.
Digital health tools, such as patient portals, treatment apps and online appointment schedulers, are increasingly common. But not everyone is equally at home using them.
To find out how language, education and age may affect a person’s comfort in using digital tools, UC San Francisco researchers surveyed caregivers of hospitalized children at UCSF Benioff Children’s Hospitals.
The researchers found that being a Spanish speaker, having less education, and being older all made people feel less comfortable with digital health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Astrophysics: Mystery of the ‘missing’ binary stars solved