(Press-News.org) In a new study involving whole-genome data, researchers present “CASTER,” a tool that uses arrangements in DNA sequences known as site patterns to infer “species trees,” which are diagrams that depict the evolutionary relationships among species. The tool, which performs with exceptional accuracy and scalability and overcomes the limitations of traditional phylogenetic methods, offers transformative potential for evolutionary research. The growing availability of genomic data has revitalized efforts to construct precise species trees and model gene tree variations. However, the methodology for utilizing genome-wide data lags behind data availability. While traditional methods struggle with incomplete lineage sorting (ILS), and two-step approaches face computational hurdles, emerging site-based methods address ILS but are hampered by scalability and accuracy issues. In response, Chao Zhang and colleagues developed CASTER (Coalescence-aware Alignment-based Species Tree Estimator), a novel approach that directly infers species trees from whole-genome alignments. Through extensive simulations and analyses of previously studied genomic datasets, including for birds and mammals, Zhang et al. demonstrate that CASTER is typically faster and more accurate than other state-of-the-art methods in analyzing hundreds of recombining genomes with precise phylogenic inference. However, despite its promise, the authors note CASTER’s limitations, including the absence of branch lengths and reliance on specific evolutionary model assumptions. Future developments aim to address these theoretical and practical challenges, expanding the tool’s applicability to broader data types and more complex biological scenarios.
For reporters interested in research integrity issues, author Siavash Mir Arabbaygi notes, “Our field has made considerable strides in ensuring (almost) all tools used in practice are open source (including the method introduced in this paper and all other methods introduced by our lab). Top journals in the field also do a great job of nudging authors to provide data in public repositories such as Dryad, Zenodo, and FigShare. Authors provide data at various levels of detail, partially due to the effort needed to export large datasets and partially because of several limitations that public repositories have on the size of the provided data. Unlike some other fields, phylogenetics research has been very open and generous in terms of data sharing.”
END
Presenting CASTER – a novel method for evolutionary research
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-01-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Reforestation boosts biodiversity, while other land-based climate mitigation strategies fall short
2025-01-23
Reforestation is a win-win for climate and wildlife, but large-scale afforestation and bioenergy cropping may do more harm than good, according to a new study of land-based climate mitigation strategies (LBMS) for over 14,000 species. The findings emphasize the need to ensure well-intentioned climate action does not exacerbate biodiversity loss. While reducing greenhouse gas emissions is critical, increasing atmospheric carbon removal is equally essential to effectively combat climate change. LBMS considered among the most scalable ...
Seasonal vertical migrations limit role of krill in deep-ocean carbon storage
2025-01-23
The vertical migration of Antarctic krill may play a smaller role in oceanic carbon storage than previously believed, according to a year-long study in the Southern Ocean. The findings challenge conventional assumptions about the animal’s role in deep ocean carbon sequestration and underscore the need for more nuanced biogeochemical models incorporating ecological complexity. “Antarctic krill play an important role in the biological carbon pump, but without observational data, we risk using inaccurate and misleading assumptions about behaviors that influence carbon export and ...
Child mortality has risen since pandemic, new study shows
2025-01-23
While child deaths in England fell temporarily during the COVID-19 pandemic, they have now risen to new heights, a new study from researchers at the University of Bristol and based on unique National Child Mortality Database (NCMD) data has found.
The study, published in PLOS Medicine today [23 January], has shown that children were less likely to die during the pandemic lockdown (April 2020–March 2021) than at any time before or since, with 377 fewer deaths than expected from the previous year.
The number of deaths in the following year (2021-2022) was similar to before the pandemic, but in 2022−2023, there were 258 more deaths than expected from the pre-pandemic ...
Super enzyme that regulates testosterone levels in males discovered in ‘crazy’ bird species
2025-01-23
A single gene that regulates testosterone levels in a “crazy” species of shore bird controls the development of three wildly different types of males, an international study involving researchers at Simon Fraser University has found.
Ruffs have long fascinated scientists for their three types of males, known as morphs, that differ radically from each other in appearance and mating behaviours.
A new study published on the cover of the journal Science this month has discovered that these morphs are produced by a super enzyme (HSD17B2) ...
Study tracks physical and cognitive impairments associated with long COVID
2025-01-23
Two-thirds of people with post-COVID-19 syndrome have persistent, objective symptoms – including reduced physical exercise capacity and reduced cognitive test performances – for a year or more, with no major changes in symptom clusters during the second year of their illness, according to a new study published January 23rd in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Winfried Kern of Freiburg University, Germany, and colleagues.
Self-reported health problems following SARS-CoV-2 infection ...
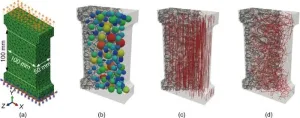
Novel model advances microfiber-reinforced concrete research
2025-01-23
Researchers from Hohai University, Northwestern University, and Politecnico di Milano have introduced a pioneering mesoscale mechanical discrete model, LDPM-MicroF, to simulate the fracture behavior of micro fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC), as reported in Engineering.
Microfibers, with diameters less than 100 µm, are crucial in preventing early shrinkage cracking and reducing pore pressure during fires. However, formulating an accurate mechanical constitutive law for micro-FRC has been challenging due to difficulties in understanding ...
Scientists develop new AI method to forecast cyclone rapid intensification
2025-01-23
Rapid Intensification (RI) of a tropical cyclone (TC), defined as a maximum sustained wind increase of at least 13 m/s within 24 hours, remains one of the most challenging weather phenomena to forecast because of its unpredictable and destructive nature. Although only 5% of TCs experience RI, its sudden and severe development poses significant risks to affected regions.
Traditional forecasting methods, such as numerical weather prediction and statistical approaches, often fail to consider the complex environmental and structural factors driving RI. While artificial intelligence ...
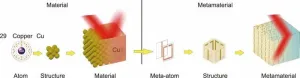
Interpreting metamaterials from an artistic view
2025-01-23
Two leading experts in the field of metamaterials from Tsinghua University co-authored a review article on this emerging scientific field in Engineering recently. Unlike traditional review articles, the authors interpret metamaterials from an artistic perspective. By drawing parallels with art, they reflect on significant achievements made over the past two decades and offer insights into the future development of the field. Their work introduces readers to the novel concept of metamaterials as “the art in materials science.”
Metamaterials refer to artificially engineered materials composed of structural units designed to exhibit extraordinary ...
Smoking cannabis in the home increases odds of detectable levels in children
2025-01-23
Researchers at University of California San Diego analyzed cannabis smoking practices in San Diego County to assess whether in-home smoking was associated with cannabis detection in children. The study, published in the Jan. 23, 2025, online edition of the Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open, found that in-home cannabis smoking increased the odds of child exposure to cannabis smoke.
Smoking is the most common method of cannabis use and is known to generate emissions that are harmful to those exposed. Cannabis is often smoked indoors, putting non-smokers such as children at risk for exposure.
“While the long-term health consequences of cannabis smoke are not ...
Ohio State astronomy professor awarded Henry Draper Medal
2025-01-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Adam Leroy, a professor of astronomy at The Ohio State University, has been named the recipient of the 2025 Henry Draper Medal.
The oldest medal awarded by the National Academy of Sciences, the Henry Draper Medal celebrates those who have made “a recent, original investigation in astronomical physics, of sufficient importance and benefit to science to merit such recognition.” It is awarded every four years.
Leroy’s work was selected for pathbreaking efforts that have characterized, “in unprecedented detail, the physical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Presenting CASTER – a novel method for evolutionary researchSummary author: Walter Beckwith