(Press-News.org) New evidence proves humans are continuing to evolve and that significant natural and sexual selection is still taking place in our species in the modern world.
Despite advancements in medicine and technology, as well as an increased prevalence of monogamy, research reveals humans are continuing to evolve just like other species.
Scientists in an international collaboration, which includes the University of Sheffield, analysed church records of about 6,000 Finnish people born between 1760-1849 to determine whether the demographic, cultural and technological changes of the agricultural revolution affected natural and sexual selection in our species.
Project leader Dr Virpi Lummaa, of the University's Department of Animal and Plant Sciences, said: "We have shown advances have not challenged the fact that our species is still evolving, just like all the other species 'in the wild'. It is a common misunderstanding that evolution took place a long time ago, and that to understand ourselves we must look back to the hunter-gatherer days of humans."
Dr Lummaa added: "We have shown significant selection has been taking place in very recent populations, and likely still occurs, so humans continue to be affected by both natural and sexual selection. Although the specific pressures, the factors making some individuals able to survive better, or have better success at finding partners and produce more kids, have changed across time and differ in different populations."
As for most animal species, the authors found that men and women are not equal concerning Darwinian selection.
Principal investigator Dr Alexandre Courtiol, of the Wissenschftskolleg zu Berlin, added: "Characteristics increasing the mating success of men are likely to evolve faster than those increasing the mating success of women. This is because mating with more partners was shown to increase reproductive success more in men than in women. Surprisingly, however, selection affected wealthy and poor people in the society to the same extent."
The experts needed detailed information on large numbers of study subjects to be able to study selection over the entire life cycle of individuals: survival to adulthood, mate access, mating success, and fertility per mate.
Genealogy is very popular in Finland and the country has some of the best available data for such research thanks to detailed church records of births, deaths, marriages and wealth status which were kept for tax purposes. Movement in the country was also very limited until the 20th century.
"Studying evolution requires large sample sizes with individual-based data covering the entire lifespan of each born person," said Dr Lummaa. "We need unbiased datasets that report the life events for everyone born. Because natural and sexual selection acts differently on different classes of individuals and across the life cycle, we needed to study selection with respect to these characteristics in order to understand how our species evolves."
###The project was funded by the European Research Council and the Kone Foundation (Finland) and was carried out with Wissenschftskolleg zu Berlin and the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research in Germany, University of Turku in Finland, University of Helsinki in Finland, and the Population Research Institute in Finland.
Notes to editors:
With nearly 25,000 students from 125 countries, the University of Sheffield is one of the UK's leading and largest universities. A member of the Russell Group, it has a reputation for world-class teaching and research excellence across a wide range of disciplines. The University of Sheffield has been named University of the Year in the Times Higher Education Awards for its exceptional performance in research, teaching, access and business performance. In addition, the University has won four Queen's Anniversary Prizes (1998, 2000, 2002, and 2007).
These prestigious awards recognise outstanding contributions by universities and colleges to the United Kingdom's intellectual, economic, cultural and social life. Sheffield also boasts five Nobel Prize winners among former staff and students and many of its alumni have gone on to hold positions of great responsibility and influence around the world. The University's research partners and clients include Boeing, Rolls Royce, Unilever, Boots, AstraZeneca, GSK, ICI, Slazenger, and many more household names, as well as UK and overseas government agencies and charitable foundations.
The University has well-established partnerships with a number of universities and major corporations, both in the UK and abroad. Its partnership with Leeds and York Universities in the White Rose Consortium has a combined research power greater than that of either Oxford or Cambridge.
For more information on the Department of Animal and Plant Sciences visit: http://www.shef.ac.uk/aps
For further information please contact: Paul Mannion, Media Relations Officer, on 0114 2229851 or email P.F.Mannion@sheffield.ac.uk
To read other news releases about the University of Sheffield, visit: http://www.shef.ac.uk/mediacentre
NR3055/ends
Darwinian selection continues to influence human evolution
2012-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-strength silk scaffolds improve bone repair
2012-05-01
MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (April 30, 2012, 3 PM EDT) -- Biomedical engineers at Tufts University's School of Engineering have demonstrated the first all-polymeric bone scaffold material that is fully biodegradable and capable of providing significant mechanical support during repair. The new technology uses micron-sized silk fibers to reinforce a silk matrix, much as steel rebar reinforces concrete. It could improve the way bones and other tissues are repaired following accident or disease.
The discovery is reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences ...
Prenatal exposure to insecticide chlorpyrifos linked to alterations in brain structure and cognition
2012-05-01
Even low to moderate levels of exposure to the insecticide chlorpyrifos during pregnancy may lead to long-term, potentially irreversible changes in the brain structure of the child, according to a new brain imaging study by researchers from the Columbia Center for Children's Environmental Health at the Mailman School of Public Health, Duke University Medical Center, Emory University, and the New York State Psychiatric Institute. The changes in brain structure are consistent with cognitive deficits found in children exposed to this chemical.
Results of the study appear ...
Venus to appear in once-in-a-lifetime event
2012-05-01
On 5 and 6 June this year, millions of people around the world will be able to see Venus pass across the face of the Sun in what will be a once-in-a-lifetime experience.
It will take Venus about six hours to complete its transit, appearing as a small black dot on the Sun's surface, in an event that will not happen again until 2117.
In this month's Physics World, Jay M Pasachoff, an astronomer at Williams College, Massachusetts, explores the science behind Venus's transit and gives an account of its fascinating history.
Transits of Venus occur only on the very rare ...
Redefining time
2012-05-01
WASHINGTON, April 30--Atomic clocks based on the oscillations of a cesium atom keep amazingly steady time and also define the precise length of a second. But cesium clocks are no longer the most accurate. That title has been transferred to an optical clock housed at the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in Boulder, Colo. that can keep time to within 1 second in 3.7 billion years. Before this newfound precision can redefine the second, or lead to new applications like ultra-precise navigation, the system used to communicate time around the globe ...
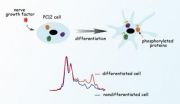
Molecular spectroscopy tracks living mammalian cells in real time as they differentiate
2012-05-01
Knowing how a living cell works means knowing how the chemistry inside the cell changes as the functions of the cell change. Protein phosphorylation, for example, controls everything from cell proliferation to differentiation to metabolism to signaling, and even programmed cell death (apoptosis), in cells from bacteria to humans. It's a chemical process that has long been intensively studied, not least in hopes of treating or eliminating a wide range of diseases. But until now the close-up view – watching phosphorylation at work on the molecular level as individual cells ...
Study shows halting an enzyme can slow multiple sclerosis in mice
2012-05-01
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Researchers studying multiple sclerosis(MS) have long been looking for the specific molecules in the body that cause lesions in myelin, the fatty, insulating cells that sheathe the nerves. Nearly a decade ago, a group at Mayo Clinic found a new enzyme, called Kallikrein 6, that is present in abundance in MS lesions and blood samples and is associated with inflammation and demyelination in other neurodegenerative diseases. In a study published this month in Brain Pathology, the same group found that an antibody that neutralizes Kallikrein 6 is capable ...
Global warming refuge discovered near at-risk Pacific island nation of Kiribati
2012-05-01
Scientists predict ocean temperatures will rise in the equatorial Pacific by the end of the century, wreaking havoc on coral reef ecosystems.
But a new study shows that climate change could cause ocean currents to operate in a way that mitigates warming near a handful of islands right on the equator.
Those islands include some of the 33 coral atolls that form the nation of Kiribati. This low-lying country is at risk from sea-level rise caused by global warming.
Surprisingly, these Pacific islands within two degrees north and south of the equator may become isolated ...
India designs its own image as global power
2012-05-01
Brand India is the name of the organisation that since the late 1990's has been tasked with convincing international corporations and heads of state that they should invest in new, modern India. In return for their investment, they get, among other things, access to cheap, well-educated labour.
"The branding campaigns produce seductive images of 'new' India: In the beginning the ads placed traditional Indian motifs together with images of mobile phones, computers, and motor ways to show the investors how India has developed," says Ravinder Kaur, who is director of Centre ...
The antibiotic, amoxicillin-clavulanate, before a meal may improve small bowel motility
2012-05-01
The common antibiotic, amoxicillin-clavulanate, may improve small bowel function in children experiencing motility disturbances, according to a study appearing in the June print edition of the Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition from Nationwide Children's Hospital.
Amoxicillan-clavulanate, also known as Augmentin, is most commonly prescribed to treat or prevent infections caused by bacteria. However, it has also been reported to increase small bowel motility in healthy individuals and has been used to treat bacterial overgrowth in patients with chronic ...
Video games can teach how to shoot guns more accurately and aim for the head
2012-05-01
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Just 20 minutes of playing a violent shooting video game made players more accurate when firing a realistic gun at a mannequin – and more likely to aim for and hit the head, a new study found.
Players who used a pistol-shaped controller in a shooting video game with human targets had 99 percent more completed head shots to the mannequin than did participants who played other video games, as well as 33 percent more shots that hit other parts of the body.
In addition, the study found that participants who reported habitual playing of violent shooting ...