(Press-News.org) STANFORD, Calif. — Researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have found a novel way to engineer key cells of the immune system so they remain resistant to infection with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
A new study describes the use of a kind of molecular scissors to cut and paste a series of HIV-resistant genes into T cells, specialized immune cells targeted by the AIDS virus. The genome editing was made in a gene that the virus uses to gain entry into the cell. By inactivating a receptor gene and inserting additional anti-HIV genes, the virus was blocked from entering the cells, thus preventing it from destroying the immune system, said Matthew Porteus, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at Stanford and a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Lucile Packard Children's Hospital.
"We inactivated one of the receptors that HIV uses to gain entry and added new genes to protect against HIV, so we have multiple layers of protection — what we call stacking," said Porteus, the study's principal investigator. "We can use this strategy to make cells that are resistant to both major types of HIV."
He said the new approach, a form of tailored gene therapy, could ultimately replace drug treatment, in which patients have to take multiple medications daily to keep the virus in check and prevent the potentially fatal infections wrought by AIDS. The work was done in the laboratory, and clinical trials would still be needed to determine whether the approach would work as a therapy.
"Providing an infected person with resistant T cells would not cure their viral infection," said Sara Sawyer, PhD, assistant professor of molecular genetics and microbiology at the University of Texas-Austin and a co-author of the study. "However, it would provide them with a protected set of T cells that would ward off the immune collapse that typically gives rise to AIDS."
The study will be published in the Jan. 22 issue of Molecular Therapy.
One of the big challenges in treating AIDS is that the virus is notorious for mutating, so patients must be treated with a cocktail of drugs — known as highly active antiretroviral therapy or HAART — which hit it at various stages of the replication process. The researchers were able to get around that problem with a new, multi-pronged genetic attack that blocks HIV on several fronts. Essentially, they hope to mimic HAART through genetic manipulation.
The technique hinges on the fact that the virus typically enters T cells by latching onto one of two surface proteins known as CCR5 and CXCR4. Some of the latest drugs now used in treatment work by interfering with these receptors' activity. A small number of people carry a mutation in CCR5 that makes them naturally resistant to HIV. One AIDS patient with leukemia, now famously known as the Berlin patient, was cured of HIV when he received a bone marrow transplant from a donor who had the resistant CCR5 gene.
Scientists at Sangamo BioSciences in Richmond, Calif., have developed a technique using a protein that recognizes and binds to the CCR5 receptor gene, genetically modifying it to mimic the naturally resistant version. The technique uses a zinc finger nuclease, a protein that can break up pieces of DNA, to effectively inactivate the receptor gene. The company is now testing its CCR5-resistant genes in phase-1 and -2 trials with AIDS patients at the University of Pennsylvania.
The Stanford scientists used a similar approach but with an added twist. They used the same nuclease to zero in on an undamaged section of the CCR5 receptor's DNA. They created a break in the sequence and, in a feat of genetic editing, pasted in three genes known to confer resistance to HIV, Porteus said. This technique of placing several useful genes at a particular site is known as "stacking."
Incorporating the three resistant genes helped shield the cells from HIV entry via both the CCR5 and CXCR4 receptors. The disabling of the CCR5 gene by the nuclease, as well as the addition of the anti-HIV genes, created multiple layers of protection.
Blocking HIV infection through both the CCR5 and CXCR4 receptors is important, Porteus said, as it hasn't been achieved before by genome editing. To test the T cells' protective abilities, the scientists created versions in which they inserted one, two and all three of the genes and then exposed the T cells to HIV.
Though the T cells with the single- and double-gene modifications were somewhat protected against an onslaught of HIV, the triplets were by far the most resistant to infection. These triplet cells had more than 1,200-fold protection against HIV carrying the CCR5 receptor and more than 1,700-fold protection against those with the CXCR4 receptor, the researchers reported. The T cells that hadn't been altered succumbed to infection with 25 days.
Porteus said he views the work as an important step forward in developing a gene therapy for HIV.
"I'm very excited about what's happened already," he said. "This is a significant improvement in that first-generation application."
He said a potential drawback of the strategy is that while the nuclease is designed to create a break in one spot, it could possibly cause a break elsewhere, leading to cancer or other cell aberration. He said it's also possible the cells may not tolerate the genetic change.
"It's possible the cells won't like the proteins they're asked to express, so they won't grow," he said.
But he said he believes both problems are technically surmountable. He said the researchers' next step is to test the strategy in T cells taken from AIDS patients, and then move on to animal testing. He said he hopes to begin clinical trials within three to five years.
Though the method is labor-intensive, requiring a tailored approach for each patient, it would save patients from a lifelong dependence on antiretroviral drugs, which have adverse side effects, Porteus noted.
He said he also hopes to adapt these techniques for use against other diseases, such as sickle cell anemia, one of his areas of interest. Porteus works with patients in the Pediatric Bone Marrow Transplant service at Packard Children's.
In addition to Sawyer, he collaborated with Richard Voit, a former Stanford graduate student who is now an MD/PhD candidate at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and Moira McMahon, PhD, a former postdoctoral scholar at Stanford who is now at the University of California-San Diego.
### The study was supported by a grant from the American Foundation for AIDS Research and by a Laurie Krauss Lacob Faculty Scholar Award from the Lucile Packard Foundation for Children's Health.
Information about Stanford's Department of Pediatrics, which also supported the work, is available at http://pediatrics.stanford.edu.
The Stanford University School of Medicine consistently ranks among the nation's top medical schools, integrating research, medical education, patient care and community service. For more news about the school, please visit http://mednews.stanford.edu. The medical school is part of Stanford Medicine, which includes Stanford Hospital & Clinics and Lucile Packard Children's Hospital. For information about all three, please visit http://stanfordmedicine.org/about/news.html.
Immune cells engineered in lab to resist HIV infection, Stanford study shows
2013-01-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sex of early birds suggests dinosaur reproductive style
2013-01-22
In a paper published in Nature Communications on January 22, 2013, a team of paleontologists including Dr. Luis Chiappe, Director of the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County's (NHM) Dinosaur Institute, has discovered a way to determine the sex of an avian dinosaur species.
Confuciusornis sanctus, a 125-million-year-old Mesozoic bird, had remarkable differences in plumage — some had long, almost body length ornamental tail feathers, others had none — features that have been interpreted as the earliest example of avian courtship. However, the idea that male Confuciusornis ...
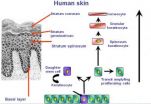
The skin aging regulator
2013-01-22
These mechanisms, described in vivo in mice, engage molecule CD98hc, which is involved in epidermis renewal and could be an indicator of the skin's capacity for regeneration.
The results were published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine review.
The epidermis, the surface layer of the skin, is mainly composed of keratinocytes cells, which, in humans, are renewed continuously over a 21-day cycle. These cells are located on a membrane made up of components from the extracellular matrix that provides the junction with the dermis, the deep layer of the skin (see diagram). ...
Harmful effects of bisphenol A proved experimentally
2013-01-22
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a chemical compound that is included in the composition of plastics and resins. It is used, for example, in the manufacture of food containers such as bottles and babies' feeding bottles. It is also found in the protective films used inside food and drink cans and on till receipts where it used as a discloser. Significant levels of BPA have also been found in human blood, urine, amniotic fluid and placentas. Recent studies have shown that this industrial component has harmful effects on reproductive ability, development and the metabolism of laboratory ...
Analysis of fracking wastewater yields some surprises
2013-01-22
DURHAM, N.C. -- Hydraulically fractured natural gas wells are producing less wastewater per unit of gas recovered than conventional wells would. But the scale of fracking operations in the Marcellus shale region is so vast that the wastewater it produces threatens to overwhelm the region's wastewater disposal capacity, according to new analysis by researchers at Duke and Kent State universities.
Hydraulically fractured natural gas wells in the Marcellus shale region of Pennsylvania produce only about 35 percent as much wastewater per unit of gas recovered as conventional ...
EARTH: The dangers of solar storms
2013-01-22
Alexandria, VA – Throughout history, humanity has steadily increased its dependence upon technology. Although technology has vastly improved the quality of life for billions of people, it has also opened us up to new risks and vulnerabilities. Terrorism and natural disasters might be at the forefront of the minds of policymakers and the U.S. population, but a significant threat lurks over our heads: the sun. A massive solar storm, the size last seen a century and a half ago, could easily leave hundreds of millions of people in the dark for days, weeks or even months.
The ...
Unprecedented glacier melting in the Andes blamed on climate change
2013-01-22
Glaciers in the tropical Andes have been retreating at increasing rate since the 1970s, scientists write in the most comprehensive review to date of Andean glacier observations. The researchers blame the melting on rising temperatures as the region has warmed about 0.7°C over the past 50 years (1950-1994). This unprecedented retreat could affect water supply to Andean populations in the near future. These conclusions are published today in The Cryosphere, an Open Access journal of the European Geosciences Union (EGU).
The international team of scientists – uniting researchers ...
How can evolutionary biology explain why we get cancer?
2013-01-22
Over 500 billion cells in our bodies will be replaced daily, yet natural selection has enabled us to develop defenses against the cellular mutations which could cause cancer. It is this relationship between evolution and the body's fight against cancer which is explored in a new special issue of the Open Access journal Evolutionary Applications.
"Cancer is far from a single well-defined disease which we can identify and eradicate," said Dr Athena Aktipis, Director, Human and Social Evolution, Center for Evolution and Cancer at the University of California, San Francisco. ...
Children with egg allergies can safely receive flu vaccine, U-M study says
2013-01-22
Ann Arbor, Mich. — Egg allergic children, including those with a history of anaphylaxis to egg, can safely receive a single dose of the seasonal influenza vaccine, according to a new study from the University of Michigan.
Historically, the CDC recommended that the seasonal influenza vaccine not be administered to egg allergic children. Recent research conducted at the University of Michigan, and elsewhere, helped modify this recommendation in 2011 so that caution was warranted for only those with severe egg allergy.
The new study, published in the Annals of Allergy, ...
Hypertension during pregnancy increases risk of end-stage renal disease
2013-01-22
Women with hypertensive disorders in pregnancy are at higher risk of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease compared with women without the disorders, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"We found that women with hypertensive disorders during pregnancy were at higher risk of end-stage renal disease than women without complicated pregnancies," writes Dr. I-Kuan Wang, Division of Nephrology, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, with coauthors.
Hypertensive disorders such as gestational hypertension and preeclampsia ...
Antibacterial agent used in common soaps found in increasing amounts in freshwater lakes
2013-01-22
When people wash their hands with antibacterial soap, most don't think about where the chemicals contained in that soap end up. University of Minnesota engineering researchers do.
A new University of Minnesota study determined that the common antibacterial agent, called triclosan, used in soaps and many other products is found in increasing amounts in several Minnesota freshwater lakes. The findings are directly linked to increased triclosan use over the past few decades.
In addition, the researchers found an increasing amount of other chemical compounds, called chlorinated ...