(Press-News.org) These findings are the result of a new study carried out at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health. In the study, women who took folic acid supplements from four weeks before conception to eight weeks into pregnancy had a 40 per cent lower risk of giving birth to children with childhood autism (classic autism).
"It appears that the crucial time interval is from four weeks before conception to eight weeks into pregnancy," states Pål Surén, MD and doctoral fellow at the Norwegian Institute of Public Health.
The study is based on the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa) and the Norway Autism Birth Cohort Study (ABC). It covered a total of 85 176 children born in the period 2002.
Inexpensive, simple prevention
Folic acid is a B vitamin that is essential for the construction and repair of DNA molecules, which control all body cells. Folate is the naturally occurring form of folic acid found in food and in the body.
Most pregnant women need folic acid supplements to reach the daily recommended levels. The Norwegian Directorate of Health recommends that women who are planning to become pregnant start to take folic acid supplements one month before conception and during the first three months of pregnancy.
The results of the study of the correlation between intake of folic acid supplements and childhood autism indicate that the lower risk is only associated with this specific supplement and not with the consumption of food or other supplements.
"Thus, the findings show that a measure already used here in Norway, one which is simple, inexpensive and without any known side effects among pregnant women, can prevent autism. Previous studies we have carried out have shown that folic acid may have a similar effect on other developmental disorders as well," Dr Surén says.
Important in other areas as well
The Directorate of Health's recommendations regarding pre-natal folic acid supplements are based on research that shows that the vitamin protects the foetus against spina bifida and other neural tube defects.
The researchers have also found a correlation between folic acid supplements and the reduced risk of severe language delay by the age of three. Such language problems are common in connection with autism but may also occur with many other conditions.
"It will be a tremendous breakthrough if it turns out that folic acid also prevents other developmental disorders," Dr Surén believes.
Some more vulnerable than others?
Dr Surén and his colleagues will conduct new analyses when the children involved in the study are older, among other things to examine whether there is any correlation between folic acid and a reduced risk of other developmental disorders such as ADHD and cerebral palsy. They will also carry out genetics studies.
"We know that there is a genetic component to the body's ability to use folate, so it is possible that some mothers are more prone to folic acid deficiency than others," Dr Surén adds.
### The study was recently published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
Folic acid lowers risk of autism
2013-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Peer support shows promise in epilepsy fight
2013-03-11
Peer support groups show promise for combating the debilitating stigma that surrounds epilepsy in much of the developing world, according to a new study led by a Michigan State University medical student.
The researchers report in the journal Epilepsy and Behavior that young people with the disease felt significantly less stigmatized after meeting regularly to discuss their illness.
While drugs are widely available to reduce epileptic seizures, the stigma and discrimination that arise from those seizures is a thornier problem, said Melissa Elafros, who is pursuing medical ...
Symptoms and care of irregular heartbeats differ by gender
2013-03-11
DURHAM, NC – Women with atrial fibrilation have more symptoms and lower quality of life than men with the same heart condition, according to an analysis of patients in a large national registry compiled by the Duke Clinical Research Institute.
The finding adds to a growing body of research that highlights gender disparities in how cardiovascular disease is managed, and serves as a caution to doctors to be alert to treatment decisions that might perpetuate the differences.
"We need to pay close attention to women with atrial fibrillation, and it's important for physicians ...
Denied the chance to cheat or steal, people turn to violent video games
2013-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study suggests that people get frustrated when they are offered the opportunity to cheat or steal and that chance is then taken away from them.
Other studies have shown that blocking people from achieving their positive goals increases frustration, which is not surprising. But this is the first to show that even denying people the chance to commit forbidden behaviors can increase frustration.
That's not all. The researchers also found that people who are frustrated in their attempts to cheat or steal are more likely than others to be attracted ...
Pittsburgh's leaky faucet: How aging sewers are impacting urban watersheds
2013-03-11
PITTSBURGH—Aging sewer systems are spilling a considerable amount of nitrogen into urban watersheds, diminishing both the quality of water and ecosystems' habitats. However, many studies documenting the impacts of nitrogen on urban environs have not properly estimated the contribution of leaky sewer systems—until now.
Aging sewer systems are spilling a considerable amount of nitrogen into urban watersheds, diminishing both the quality of water and the ecosystems' habitats.
Using water samples from the Pittsburgh-based Nine Mile Run watershed, a Pitt research team reveals ...
New program available to reduce stress among teenagers
2013-03-11
This press release is available in French.
Families with a child completing elementary school this year are now preparing their registration for high school, a transition that is often stressful for children. A new program has demonstrated that it is possible to significantly reduce stress in some of these children thanks to a new educational tool designed under the leadership of Sonia Lupien, Director of the Centre for Studies on Human Stress (CSHS) and professor at the University of Montreal.
A study published in February in Neuroscience confirms the benefits of ...
Discovery may explain how prion diseases spread between different types of animals
2013-03-11
Medical researchers at the University of Alberta have made a discovery that may explain how prion diseases, like chronic wasting disease and mad cow disease, adapt in order to spread between various types of animals.
The research team, led by neurologist Valerie Sim, discovered that a miniscule change in the prions' makeup appears to give the disease the ability to adapt – to mimic and recreate new strains with which it comes into contact. The team has been studying this area for two years.
"Prion diseases don't always successfully go from one animal to another, but when ...
Untangling life's origins
2013-03-11
URBANA – Researchers in the Evolutionary Bioinformatics Laboratory at the University of Illinois in collaboration with German scientists have been using bioinformatics techniques to probe the world of proteins for answers to questions about the origins of life.
Proteins are formed from chains of amino acids and fold into three-dimensional structures that determine their function. According to crop sciences professor Gustavo Caetano-Anollés, very little is known about the evolutionary drivers for this folding.
In collaboration with scientists at the Heidelberg Institute ...
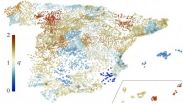
The dynamic of Spain's population follows the maximum entropy principle
2013-03-11
A team of Spanish and Argentinean researchers have verified that the distribution of the inhabitants in each Spanish province evolves in accordance with the maximum entropy principle in the field of physics. Therefore, this evolution is predictable. The results have allowed authors to put forward a 'socio-thermodynamic' theory that applies the laws of thermodynamics to collective human behaviour.
Spanish and Argentinean scientists have researched the way in which we as people group together on a large scale as a way of seeing whether there is any law or pattern that explains ...
Ground-level ozone falling faster than model predicted
2013-03-11
There is good news and better news about ground-level ozone in American cities. While dangerous ozone levels have fallen in places that clamp down on emissions from vehicles and industry, a new study from Rice University suggests that a model widely used to predict the impact of remediation efforts has been too conservative.
Particularly in Northeastern cities, ozone levels dropped even beyond what was anticipated by cutting emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from 2002 to 2006. The study published online by the journal Atmospheric Environment suggests the Community Multiscale ...
Can energy drinks improve the physical and mental performance of cyclists?
2013-03-11
New Rochelle, NY, March 11, 2013–Consumption of energy drinks containing caffeine may have beneficial effects on exercise but probably not for mental function. The effects of pre-exercise caffeine consumption by trained cyclists on racing times and cognitive performance were measured and are reported in Journal of Caffeine Research, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Caffeine Research website at http://www.liebertpub.com/jcr.
Race performance improved for all study participants after consuming ...