Review of pathogenesis, research and treatment of amyloidosis published in New England Journal of Medicine
2024-06-26
(Boston) — AL (immunoglobulin light chain) amyloidosis is a rare disease that often results in progressive organ dysfunction, organ failure and eventual death.
Clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow secrete free light chains into circulation. These light chains are part of immunoglobulins, also called antibodies. But in this disease, light chains misfold and aggregate into amyloid fibrils that deposit in organs and tissues.
In a review article of AL amyloidosis “Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis,” Vaishali Sanchorawala, MD, director of the Amyloidosis Center at the Chobanian & ...
New research tools reveal the dynamics behind breaking a sweat
2024-06-26
Excessive heat across the United States is making this summer a season of sweat. Perspiration and its evaporation are crucial to keeping us cool when things get hot. But our understanding of how sweat evaporates is limited to the profuse phases of the process, when our bodies are coated in a sticky film or even pools of perspiration. Relatively is little is known about the dynamics behind initial phases of sweating, when tiny droplets are emitted by individual sweat glands and then quickly evaporate.
“There are mechanical engineering researchers around the world, myself included, who are devoted to understanding the different parameters of droplet behavior on ...
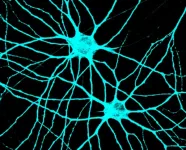
Neuroscience research leverages stem cells to understand how neurons connect and communicate in the brain
2024-06-26
Newly published research from Colorado State University answers fundamental questions about cellular connectivity in the brain that could be useful in the development of treatments for neurological diseases like autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia.
The work, highlighted in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focuses on how neurons in the brain transmit information between each other through highly specialized subcellular structures called synapses. These delicate structures are key to controlling many processes across the nervous system via electrochemical ...
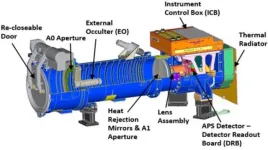
NRL CCOR launches on the GOES-U NOAA satellite to monitor space weather
2024-06-26
WASHINGTON – The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory’s (NRL) Compact Coronagraph (CCOR) was launched June 25, on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-U (GOES-U) from NASA – Kennedy Space Center to detect and characterize coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
The NOAA sponsored NRL to design, integrate, and test CCOR, a small space telescope that will create an artificial eclipse of the sun and ...
Study shows how liver damage from stress and aging might be reversible
2024-06-26
DURHAM, N.C. – While the liver is one of the body’s most resilient organs, it is still vulnerable to the ravages of stress and aging, leading to disease, severe scarring and failure. A Duke Health research team now might have found a way to turn back time and restore the liver.
In experiments using mice and liver tissue from humans, the researchers identified how the aging process prompts certain liver cells to die off. They were then able to reverse the process in the animals with an investigational drug.
The finding, which ...
Bone stem cells with IFITM5 mutation get caught in a loop leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V
2024-06-26
A study conducted by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions reveals the molecular events leading to osteogenesis imperfecta type V, a form of brittle bone disease caused by a mutation in the gene IFITM5.
The mutation blocks the normal development of bone stem cells into mature cells, which would form healthy bones. Instead, the mutation leads to the formation of bones that are extremely brittle. Children with this disorder have recurrent fractures, bone deformities, chronic pain and other complications. ...
Tai Chi reduces risk of inflammatory disease, treats insomnia among breast cancer survivors
2024-06-26
New research led by UCLA Health confirms that both Tai Chi and cognitive behavioral therapy can reduce insomnia in breast cancer survivors but also may provide additional health benefits by reducing inflammation and bolstering anti-viral defenses.
Chronic insomnia is one of the most prominent symptoms experienced among cancer survivors and poses significant health concerns, including the risk of inflammatory disease that could increase the risk of cancer recurrence.
About 30% of breast cancer survivors are reported to have insomnia, which is twice the rate of the general population. While previous research has shown cognitive behavioral therapy and mind-body ...
Technology presented for measuring carbon in media, advertising and generative AI
2024-06-26
Measuring energy consumption derived from digital activity from a scientific point of view is the challenge faced by Hiili, S.L., a company recently formed and driven by two researchers from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), Ángel and Rubén Cuevas Rumín, from the Telematics Engineering Department. Specifically, they develop technological solutions that combine Internet measurement techniques and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to make an accurate estimate of the energy consumption of a company's ...
Do people who exercise more have a lower risk of ALS?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Moderate levels of physical activity and fitness may be linked to a reduced risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) later in life, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study only found an association between physical activity and risk of ALS in male participants, not female participants.
ALS is a rare, progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord. People with ALS lose the ability to initiate ...
Could preventative drug be effective in people with migraine and rebound headache?
2024-06-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 26, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – A drug used to prevent migraine may also be effective in people with migraine who experience rebound headaches, according to a new study published in the June 26, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
People with chronic migraine who overused pain medication had fewer monthly migraine and headache days and fewer days using pain medication when taking the migraine prevention drug atogepant.
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication ...
Pathologists awarded grant from American Society of Hematology
2024-06-26
Dr. Zhen Mei, a clinical pathologist, and Dr. Vivian Chang, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist, both at UCLA Health, have been awarded $30,000 from the American Society of Hematology to revise blood cell ranges for people with Duffy-null Associated Neutrophil Count, which is also known as Duffy-negative.
Those who are Duffy-negative, estimated to be two out of three people identifying as Black in the U.S., lack Duffy antigens on the surface of their red blood cells as a mechanism to resist malaria. This helps provide protection but ...
Revolutionizing ovarian cancer treatment with adaptive PARP inhibitor therapy
2024-06-26
TAMPA, Fla. — Ovarian cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage, presents significant treatment challenges because patients tend to develop resistance to conventional therapies quickly. Despite aggressive treatment, recurrence rates remain high, and managing this disease effectively requires innovative approaches. Poly-adenosine ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have emerged as a treatment option, targeting specific DNA repair mechanisms in cancer cells. However, their use is often limited ...
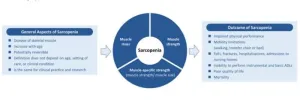
Global consensus for sarcopenia
2024-06-26
“[...] the development of a global conceptual definition of sarcopenia signifies a new dawn for this muscle disease.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 26, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 11, entitled, “Global consensus for sarcopenia.”
In this new editorial, researchers Ben Kirk, Peggy M. Cawthon, and Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft from the University of Melbourne and Western Health discuss the global societal issue of skeletal muscle loss and weakness, termed Sarcopenia. Low muscle ...
Ocean’s loss of oxygen caused massive Jurassic extinction. Could it happen again?
2024-06-26
DURHAM, NC – Researchers have discovered a clue in Italian limestone that helps explain a mass extinction of marine life millions of years ago, and may provide warnings about how oxygen depletion and climate change could impact today’s oceans.
“This event, and events like it, are the best analogs we have in Earth's past for what is to come in the next decades and centuries,” said Michael A. Kipp, an earth and climate science assistant professor at Duke University. Kipp co-authored a study published June 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences that measures oxygen loss ...
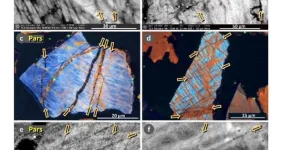
Shocked quartz reveals evidence of historical cosmic airburst
2024-06-26
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Researchers continue to expand the case for the Younger Dryas Impact hypothesis. The idea proposes that a fragmented comet smashed into the Earth’s atmosphere 12,800 years ago, causing a widespread climatic shift that, among other things, led to the abrupt reversal of the Earth’s warming trend and into an anomalous near-glacial period called the Younger Dryas.
Now, UC Santa Barbara emeritus professor James Kennett and colleagues report the presence of proxies associated with the cosmic airburst ...
Chemotherapy disrupts gut microbiome in patients with breast cancer
2024-06-26
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Chemotherapy is known to cause behavioral side effects, including cognitive decline. Notably, the gut microbiome communicates with the brain to affect behavior, including cognition.
“For the first time ever, our Intelligut Study found that the gut microbiome has been implicated in cognitive side effects of chemotherapy in humans,” said senior author Leah Pyter, associate professor of psychiatry and neuroscience with The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine. ...
Microrobot-packed pill shows promise for treating inflammatory bowel disease in mice
2024-06-26
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed a pill that releases microscopic robots, or microrobots, into the colon to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The experimental treatment, given orally, has shown success in mice. It significantly reduced IBD symptoms and promoted the healing of damaged colon tissue without causing toxic side effects.
The study was published June 26 in Science Robotics.
IBD, an autoimmune disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of the gut, ...
Sharing false political information on social media may be associated with positive schizotypy
2024-06-26
Sharing false political information on social media by users may be associated with aspects of personality such as positive schizotypy, a set of traits including paranoia, suspicion and disrupted thinking patterns. It may also be linked to a motivation to increase awareness according to a study published June 26, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Tom Buchanan, University of Westminster, UK, and colleagues.
The spread of false political information on social media can tarnish trust in authentic news and even contribute to social unrest. Knowingly or not, a small portion of social media users actively share false material.
Buchanan and ...
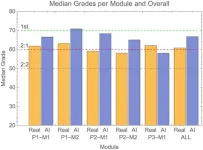
AI-generated exam submissions evade detection at reputable UK university
2024-06-26
In a test of the examinations system of the University of Reading in the UK, artificial intelligence (AI)-generated submissions went almost entirely undetected, and these fake answers tended to receive higher grades than those achieved by real students. Peter Scarfe of the University of Reading and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 26.
In recent years, AI tools such as ChatGPT have become more advanced and widespread, leading to concerns about students using them to cheat by submitting AI-generated work as their own. Such concerns are heightened ...
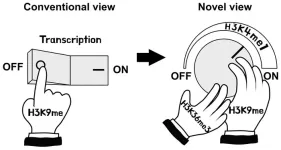
The on-and-off affair in DNA
2024-06-26
Researchers led by Kannosuke Yabe, Asuka Kamio, and Soichi Inagaki of the University of Tokyo have discovered that in thale cresses histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methylation, conventionally thought to be a mark of turning off gene transcription, can also turn on gene expression via the interactions of two other proteins and histone marks. The molecular mechanisms demonstrate that rather than functioning as a simple “off switch,” H3K9 methylation is more like a “dimmer switch” that fine-tunes DNA transcription. The discovery suggests there might be similar mechanisms in other ...
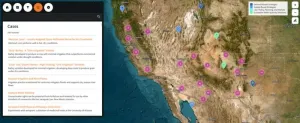
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the US Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought
2024-06-26
New interactive atlas of water scarcity solutions in the U.S. Southwest shares a library of case studies to help adapt to drought.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000246
Article Title: The water adaptation techniques atlas: A new geospatial library of solutions to water scarcity in the U.S. Southwest
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. END ...
AI generated exam answers go undetected in real-world blind test
2024-06-26
Experienced exam markers may struggle to spot answers generated by Artificial Intelligence (AI), researchers have found.
The study was conducted at the University of Reading, UK, where university leaders are working to identify potential risks and opportunities of AI for research, teaching, learning, and assessment, with updated advice already issued to staff and students as a result of their findings.
The researchers are calling for the global education sector to follow the example of Reading, and others who are also forming new ...
How do our memories last a lifetime? New study offers a biological explanation
2024-06-26
Whether it’s a first-time visit to a zoo or when we learned to ride a bicycle, we have memories from our childhoods kept well into adult years. But what explains how these memories last nearly an entire lifetime?
A new study in the journal Science Advances, conducted by a team of international researchers, has uncovered a biological explanation for long-term memories. It centers on the discovery of the role of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to other molecules, thereby solidifying memory formation.
“Previous efforts to understand ...
Mechanical computer relies on kirigami cubes, not electronics
2024-06-26
North Carolina State University researchers have developed a kirigami-inspired mechanical computer that uses a complex structure of rigid, interconnected polymer cubes to store, retrieve and erase data without relying on electronic components. The system also includes a reversible feature that allows users to control when data editing is permitted and when data should be locked in place.
Mechanical computers are computers that operate using mechanical components rather than electronic ones. Historically, these mechanical components have been things like levers or gears. However, mechanical computers can also be made using structures that are multistable, meaning ...
Acting for a common goal with humanoid robots
2024-06-26
Genova (Italy), 26 June 2024 – Researchers at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT-Italian Institute of Technology) have demonstrated that under specific conditions, humans can treat robots as co-authors of the results of their actions. The condition that enables this phenomenon is that a robot behaves in a human-like, social manner. Engaging in gaze contact and participating in a common emotional experience, such as watching a movie, are the key. The study was published in Science Robotics and paves the way for understanding and designing the optimal circumstances for humans and robots to collaborate in the same environment.
The ...
[1] ... [1089]
[1090]
[1091]
[1092]
[1093]
[1094]
[1095]
[1096]
1097
[1098]
[1099]
[1100]
[1101]
[1102]
[1103]
[1104]
[1105]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.