'Smart windows' have potential to keep heat out and save energy
2014-12-10
Windows allow brilliant natural light to stream into homes and buildings. Along with light comes heat that, in warm weather, we often counter with energy-consuming air conditioning. Now scientists are developing a new kind of "smart window" that can block out heat when the outside temperatures rise. The advance, reported in ACS' journal Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, could one day help consumers better conserve energy on hot days and reduce electric bills.
Xuhong Guo, Kaimin Chen, Yanfeng Gao and colleagues explain that researchers are pursuing smart windows ...
Theory details how 'hot' monomers affect thin-film formation
2014-12-10
HOUSTON - (Dec. 10, 2014) - Like a baseball player sliding into third, a hot monomer skids in a straight line along a cold surface until it's safely among its fellow molecules.
This is not what usually happens when scientists assemble monomers to make thin films for next-generation electronics, but the details remained a puzzle until a team led by Rice University got involved. Monomers are organic molecules that, in this application, form clusters and eventually complete layers.
Researchers at Rice and the University of Maryland led by Rice theoretical physicist ...
New insight into cancer defense mechanism
2014-12-10
A Danish Research Team identified a molecular mechanism that ensures that when cells divide, the genomic material passes correctly to the resulting daughter cells:
"The process, known as chromosome segregation, is vitally important because incorrect passage of the genomic material makes cells prone to develop into cancer cells," says Jakob Nilsson, associate professor at the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Protein Research.
The new discovery depends on a protein called BubR1 which if mutated can cause cancer.
The results have just been published in the scientific ...
How long can Ebola live?
2014-12-10
The Ebola virus travels from person to person through direct contact with infected body fluids. But how long can the virus survive on glass surfaces or countertops? How long can it live in wastewater when liquid wastes from a patient end up in the sewage system? In an article published Dec. 9 in the journal Environmental Science & Technology Letters, Kyle Bibby of the University of Pittsburgh reviews the latest research to find answers to these questions.
He and his co-investigators didn't find many answers.
"The World Health Organization has been saying you can put ...
New study measures methane emissions from natural gas production and offers insights into two large sources
2014-12-10
A team of researchers from the Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin and environmental testing firm URS reports that a small subset of natural gas wells are responsible for the majority of methane emissions from two major sources -- liquid unloadings and pneumatic controller equipment -- at natural gas production sites.
With natural gas production in the United States expected to continue to increase during the next few decades, there is a need for a better understanding of methane emissions during natural gas production. The study team ...
Study examines effects of family-friendly workplace policies
2014-12-10
A happy worker is a productive worker. That adage may be true, according to a new study from The University of Texas at Dallas.
Two UT Dallas public affairs researchers found that family-friendly policies are beneficial for increasing productivity of employees in public organizations, and the authors said the finding likely lends itself to job satisfaction and commitment.
The study, published in the Public Personnel Management, investigated the effects of family-friendly human resources policies in public organizations. Using the Korea Workplace Panel Survey data from ...
Students design workstations that accommodate groups and individual
2014-12-10
New school and office workspace designs created by a group of Penn State engineering students are intended to allow users to share space and materials while maintaining their own work areas -- a dual purpose the researchers say has been neglected.
The research began in 2010 as a class project, according to Joseph M. Mahoney, former Penn State graduate student, now assistant professor of mechanical engineering, Penn State, Berks. "There's a lot of interest from an ergonomics perspective and workplace efficiency perspective of designing workstations for single users," Mahoney ...
Ancient creature discovered in the depths of the Arctic Ocean
2014-12-10
In the depths of the Arctic Ocean, buried deep in the sediment, an ancient creature waited for over a million years to be discovered. Paul Valentich-Scott, from the Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History (California), and three scientists from the United States Geological Survey (USGS, Menlo Park, California), Charles L. Powell, Brian D. Edwards, and Thomas D. Lorenson were up to the challenge. Each with different expertise, they were able to collect, analyze, and identify a new genus and new species of bivalve mollusk.
The path to discovery is seldom simple or easy. ...
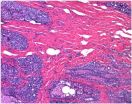
New breast cancer classification based on epigenetics
2014-12-10
Breast cancer is the most common in women. One in nine will suffer breast cancer over their lifetime. Progress in prevention and early detection, and the use of chemotherapy after surgery (adjuvant chemotherapy), have achieved significantly increase survival in this disease in the last ten years, but much remains to be done.
The identification of patients with high-risk breast cancer is key to knowing whether a patient will require only the removal of the tumor by surgery or whether if she will need additional chemotherapy to make sure the removal of breast cancer cells. ...
Analogues of a natural product are drug candidates against malaria
2014-12-10
Malaria is one of the most serious health problems worldwide, registering 200 million clinical cases and more than 600,000 attributable deaths per year, according to information from the World Health Organization in 2013. Given the emerging resistance to the standard treatment most widely used throughout the world, which is based on artemisinin and its analogs, there is a need for new antimalarial compounds.
In this regard, scientists headed by Lluís Ribas de Pouplana, ICREA researcher at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona), report on a new ...
As in a cloud
2014-12-10
This news release is available in German. FRANKFURT. Frankfurt physicists have once again contributed to resolving a disputed matter of theoretical physics. Science has long since known that, contrary to the old school of thought, helium forms molecules of two, three or even more atoms. Exactly what helium consisting of three atoms looks like, however, has been disputed by theoretical physicists for about 20 years. Besides the intuitive assumption that the three identical components form an equilateral triangle, there was also the hypothesis that the three atoms are ...
Lifestyle the key to gap in cardiac patient outcomes
2014-12-10
Patients suffering from the world's most common heart rhythm disorder can have their long-term outcomes significantly improved with an aggressive management of their underlying cardiac risk factors, according to University of Adelaide researchers.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is increasingly responsible for dementia, stroke and death, and has a significant impact on healthcare costs. With electrical "short circuits" believed to be responsible for the abnormal beating of the heart in AF patients, one currently used treatment is to burn the tissue surrounding the problem area, ...
Phenomenal fossil and detailed analysis reveal details about enigmatic fossil mammals
2014-12-10
Mammals that lived during the time of the dinosaurs are often portrayed as innocuous, small-bodied creatures, scurrying under the feet of the huge reptiles. In reality, this wasn't the case, and a new fossil from Madagascar further underscores this point, revealing fascinating perspectives on the growing diversity of Mesozoic mammals. Vintana sertich had previously been described in a preliminary note in November of this year, but a new memoir in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology delves far deeper into the morphology and paleoecology of this amazing fossil animal. ...
Supplement could reduce heart disease risk in people of low birth weight
2014-12-10
A simple supplement could be a safe and cost-effective way of reducing heart disease in individuals born with a low birth weight, suggests research from the University of Cambridge. The study, carried out in rats, also raises the possibility of developing a blood test to indicate how much damage there is in the aortas of these individuals.
Researchers at the Institute of Metabolic Science fed low birth weight rats a supplement of the molecule co-enzyme Q (CoQ) and found that in those rats that grew quickly after birth, the supplement prevented cells in the aorta from ...
Disney Researchers use multiple photos to estimate lighting conditions of outdoor scenes
2014-12-10
Techniques now used to reconstruct 3D models based on multiple photos of a building, object or scene can also be leveraged to automatically estimate illumination conditions depicted in a collection of photographs, scientists at Disney Research and Université Laval report.
Everyone knows that objects can look markedly different depending on lighting conditions, the physical characteristics of the objects and the angle at which they are viewed. That makes it difficult for photo editors to insert 3D objects into imagery and make them appear as if they are reflecting ...
Carbon soot particles, dust blamed for discoloring India's Taj Mahal
2014-12-10
The Taj Mahal's iconic marble dome and soaring minarets require regular cleaning to maintain their dazzling appearance, and scientists now know why. Researchers from the United States and India are pointing the finger at airborne carbon particles and dust for giving the gleaming white landmark a brownish cast.
Knowing the culprits in the discoloration is just the first step in cleaning up the Taj Mahal. Scientists now must determine where the particles are coming from to develop strategies for controlling them.
"Our team was able to show that the pollutants discoloring ...
Health care lessons learned in the aftermath of September 11, 2001
2014-12-10
New York, NY, December 9, 2014 - Fourteen years after the attack on the World Trade Center (WTC), a case study in the current issue of Annals of Global Health identifies several elements that have had a critical impact on the evolution of the WTC response and, directly or indirectly, on the health of the WTC-exposed population. The case study also recounts and assesses post-disaster monitoring efforts, recent scientific findings from the World Trade Center Health Program (WTCHP), and explores the implications of these experiences for ongoing and future environmental disaster ...
Uncovering complex network structures in nature
2014-12-10
The global spread of Ebola is due to the complex interactions between individuals, societies, and transportation and trade networks. Understanding and building appropriate statistical and mathematical models of these interactions is vital to responding to the challenges of living in a networked world. There are, of course, many other examples of complex networks -- from national power grids and airline networks to social networks, neuronal networks and protein-protein interactions.
In a new study published in the Beijing-headquartered journal National Science Review, ...
Shifting boundaries and changing surfaces
2014-12-10
This news release is available in Japanese.
New research published in the Proceedings of The Royal Society A by members of the Mathematical Soft Matter Unit at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University examines the energies at work in a closed flexible loop spanned by a soap film. While the underlying experiments are simple enough to be replicated in a kitchen sink, the research generates potentially important questions and changes how we think about different disciplines from material science to vertebrate morphogenesis. Aisa Biria and Professor ...
Limiting internet congestion a key factor in net neutrality debate
2014-12-10
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY'S HAAS SCHOOL OF BUSINESS -Too many vehicles on the highway inevitably slow down traffic. On the Internet information highway, consumers value high-speed Internet service, but there is little reason to think broadband traffic congestion will improve if the Federal Communications Commission abandons net neutrality, according to economic research.
In their paper, "The Economics of Network Neutrality," Ben Hermalin, Haas Economics Analysis and Policy Group, and Nicholas Economides, Berkeley-Haas visiting professor from NYU'S Stern School ...
Breakthrough simplifies design of gels for food, cosmetics and biomedicine
2014-12-10
Scientists at the University of Strathclyde and City University of New York have created methods that dramatically simplify the discovery of biological gels for food, cosmetics and biomedicine, as published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
Strathclyde's Dr Tell Tuttle and Professor Rein Ulijn, the director of nanoscience at City University New York's new advanced research centre who also holds a position at Strathclyde, believe their team's breakthrough dramatically simplifies discovery of functional gels that can be used in a wide range of applications.
Until now, ...
Daclatasvir for hepatitis C: Added benefit not proven
2014-12-10
The drug daclatasvir (trade name Daklinza) has been available since August 2014 for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis C (CHC) infection. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether this new drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy.
The drug manufacturer presented data for patients without cirrhosis of the liver who are infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1, and for patients with HCV genotype 4. However, these data are unsuitable in various aspects to ...
Revolutionary new procedure for epilepsy diagnosis unlocked by research
2014-12-10
Pioneering new research by the University of Exeter could revolutionise global diagnostic procedures for one of the most common forms of epilepsy.
Scientists from Exeter have investigated using mathematical modelling to assess susceptibility to idiopathic generalised epilepsy (IGE) by analysing electrical activity of the brain while the patient is in a resting state.
Current diagnosis practices typically observe electrical activities associated with seizures in a clinical environment.
The ground-breaking research has revealed differences in the way that distant regions ...
Anyone who is good at German learns English better
2014-12-10
"A tree must be bent while it is young," as one saying about learning a foreign language goes. In other words, the earlier you start learning a foreign language systematically, the better the language level will be in the long run. The second widely held view is that you need to be solid in your first language (L1) in order to develop good literacy skills in the foreign language. Linguist Simone Pfenninger from the University of Zurich has been examining these two myths in her five-year study involving Swiss high-school children in order to identify the optimal starting ...
Nuclear medicine treatment shows promise for cancer therapy
2014-12-10
Reston, Va. (December 9, 2014) - Cancer therapy can be much more effective using a new way to customize nuclear medicine treatment, researchers say in the December 2014 issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. The process could also be useful for other diseases that could benefit from targeted radiation.
Targeted therapy with radiopharmaceuticals--radioactive compounds used in nuclear medicine for diagnosis or treatment--has great potential for the treatment of cancer, especially for cancer cells that have migrated from primary tumors to lymph nodes and secondary organs ...
[1] ... [3133]
[3134]
[3135]
[3136]
[3137]
[3138]
[3139]
[3140]
3141
[3142]
[3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
[3149]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.