Effect of medical resident duty hour reforms on patient outcomes
2014-12-09
An examination of the effect of resident duty hour reforms in 2011 finds no significant change in mortality or readmission rates for hospitalized patients, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
In 2011, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) implemented new duty hour reforms for all ACGME-accredited residency programs. The revisions maintain the weekly limit of 80 hours set forth by the 2003 duty hour reforms but reduced the work hour limit from 30 consecutive hours to 16 hours for first­year ...
Study examines effect of resident duty hour reforms on general surgery patients
2014-12-09
An examination of the effect of resident duty hour reforms in 2011 finds no significant change in outcomes for general surgery patients, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
Ravi Rajaram, M.D., of the American College of Surgeons, Chicago, and colleagues conducted a study to determine if the 2011 Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) duty hour reform was associated with a change in general surgery patient outcomes or in resident examination performance.
The study examined general surgery patient ...
Region of medical residency training may affect future spending patterns of physician
2014-12-09
Among primary care physicians, the spending patterns in the regions in which their residency program was located were associated with expenditures for subsequent care they provided as practicing physicians, with those trained in lower-spending regions continuing to practice in a less costly manner, even when they moved to higher-spending regions, and vice versa, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
Regional and system-level variations in Medicare spending and overall intensity of medical services delivered to patients ...
Languages of medical residency applicants compared to patients with limited English
2014-12-09
An analysis of the non-English-language skills of U.S. medical residency applicants finds that although they are linguistically diverse, most of their languages do not match the languages spoken by the U.S. population with limited English proficiency, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
More than 25 million U.S. residents have limited English proficiency, an 80 percent increase from 1990 to 2010. Limited English proficiency (LEP) may impede participation in the English­language-dominant health care system. Little ...
Number of medical schools with student-run free clinics has more than doubled
2014-12-09
There has been a doubling during the last decade in the number of U.S. medical schools that have student-run free clinics, with more than half of medical students involved with these clinics, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
Sunny Smith, M.D., of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues conducted a study to assess whether there has been growth of student-run free clinics (SRFCs) in medical schools and describe the characteristics of these clinics. The first national study of SRFCs conducted in 2005 ...
Emergency department resource use by supervised residents vs. attending physicians alone
2014-12-09
In a sample of U.S. emergency departments, compared to attending physicians alone, supervised visits (involving both resident and attending physicians) were associated with a greater likelihood of hospital admission and use of advanced imaging and with longer emergency department stays, according to a study in the December 10 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on medical education.
A common assumption is that care at academic medical centers costs more than care at nonteaching hospitals in part because of a higher frequency of testing and other resource use in teaching settings. ...
No increase in patient deaths or readmissions following restrictions to residents' hours
2014-12-09
PHILADELPHIA - In the first year after the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME) reduced the number of continuous hours that residents can work, there was no change in the rate of death or readmission among hospitalized Medicare patients, according to a new study published in JAMA. The study was led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
"There has been a lot of speculation about the effect of the 2011 ACGME duty hour reforms on patient outcomes, so we looked ...
Mayo Clinic: Genotyping errors plague CYP2D6 testing for tamoxifen therapy
2014-12-09
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Clinical recommendations discouraging the use of CYP2D6 gene testing to guide tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer patients are based on studies with flawed methodology and should be reconsidered, according to the results of a Mayo Clinic study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
For years, controversy has surrounded the CYP2D6 gene test for breast cancer. Women with certain inherited genetic deficiencies in the CYP2D6 gene metabolize tamoxifen less efficiently, and thus have lower levels of tamoxifen's active cancer-fighting metabolite ...
Yeast are first cells known to cure themselves of prions
2014-12-09
Yeast cells can sometimes reverse the protein misfolding and clumping associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, according to new research from the University of Arizona.
The new finding contradicts the idea that once prion proteins have changed into the shape that aggregates, the change is irreversible.
"It's believed that when these aggregates arise that cells cannot get rid of them," said Tricia Serio, UA professor and head of the department of molecular and cellular biology. "We've shown that's not the case. Cells can clear themselves of these aggregates."
Prions ...
It doesn't add up: People who say they are good at math, but aren't
2014-12-09
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Thinking you're good at math and actually being good at it are not the same thing, new research has found.
About one in five people who say they are bad at math in fact score in the top half of those taking an objective math test. But one-third of people who say they are good at math actually score in the bottom half.
"Some people mis-categorize themselves. They really don't know how good they are when faced with a traditional math test," said Ellen Peters, co-author of the study and professor of psychology at The Ohio State University.
The results ...
Immunizing schoolkids fights flu in others, too
2014-12-09
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Mathematical models predicted it, and now a University of Florida study confirms it: Immunizing school-aged children from flu can protect other segments of the population, as well.
When half of 5- to 17-year-old children in Alachua County were vaccinated through a school-based program, the entire age group's flu rates decreased by 79 percent. Strikingly, the rate of influenza-like illness among 0-4 year olds went down 89 percent, despite the fact that this group was not included in the school-based vaccinations. Among all non-school-aged residents, ...
Women with dense breasts will have to look beyond ultrasound for breast cancer screening
2014-12-09
Supplemental ultrasound screening for all U.S. women with dense breasts would substantially increase healthcare costs with little improvement in overall health, according to senior author Anna Tosteson, ScD, at Dartmouth Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center and The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice.
In a study released Monday in the Annals of Internal Medicine, Tosteson and colleagues, including lead author Brian Sprague, MD, provide evidence on the benefits and harms of adding ultrasound to breast cancer screening for women who have had a ...
Now researchers can see how unfolded proteins move in the cell
2014-12-09
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- When a large protein unfolds in transit through a cell, it slows down and can get stuck in traffic. Using a specialized microscope -- a sort of cellular traffic camera -- University of Illinois chemists now can watch the way the unfolded protein diffuses.
Studying the relationship between protein folding and transport could provide great insight into protein-misfolding diseases such as Alzheimer's and Huntington's. Chemistry professor Martin Gruebele and graduate students Minghao Guo and Hannah Gelman published their findings in the journal PLOS ONE.
"We're ...
Multiple, short learning sessions strengthen memory formation in fragile X syndrome
2014-12-09
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 9, 2014 -- A learning technique that maximizes the brain's ability to make and store memories may help overcome cognitive issues seen in fragile X syndrome, a leading form of intellectual disability, according to UC Irvine neurobiologists.
Christine Gall, Gary Lynch and colleagues found that fragile X model mice trained in three short, repetitious episodes spaced one hour apart performed as well on memory tests as normal mice. These same fragile X rodents performed poorly on memory tests when trained in a single, prolonged session - which is a standard ...
Study links ADHD, conduct disorder with alcohol and tobacco use in young teens
2014-12-09
A new study links ADHD and conduct disorder in young adolescents with increased alcohol and tobacco use. The Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center study is among the first to assess such an association in this age group.
Conduct disorder is a behavioral and emotional disorder marked by aggressive, destructive or deceitful behavior.
The study is published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence.
"Early onset of substance abuse is a significant public health concern," says William Brinkman, MD, a pediatrician at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center ...
Study assesses hospice use in and out of nursing homes and by patients in transition
2014-12-09
INDIANAPOLIS -- As hospice for nursing home patients grows dramatically, a new study from the Regenstrief Institute and the Indiana University Center for Aging Research compares the characteristics of hospice patients in nursing homes with hospice patients living in the community. The study also provides details on how hospice patients move in and out of these two settings.
Longer lengths of hospice care, rising costs and concerns over possible duplication of services have led to increased scrutiny by policymakers of hospice patients living in nursing homes. Nursing ...
E-cigarettes less addictive than cigarettes
2014-12-09
E-cigarettes appear to be less addictive than cigarettes for former smokers and this could help improve understanding of how various nicotine delivery devices lead to dependence, according to researchers.
"We found that e-cigarettes appear to be less addictive than tobacco cigarettes in a large sample of long-term users," said Jonathan Foulds, professor of public health sciences and psychiatry, Penn State College of Medicine.
The popularity of e-cigarettes, which typically deliver nicotine, propylene glycol, glycerin and flavorings through inhaled vapor, has increased ...
Simeprevir-based therapy offers cost-effective alternative in treatment of hepatitis C
2014-12-09
PHILADELPHIA -Researchers at Penn Medicine, in collaboration with a multi-center international team, have shown that a protease inhibitor, simeprevir, a once a day pill, along with interferon and ribavirin has proven as effective in treating chronic Hepatitis C virus infection (HCV) as telaprevir with interferon and ribavirin, the standard of care in developing countries. Further, simeprevir proved to be simpler for patients and had fewer adverse events. The complete study is now available online and is scheduled to publish in January 2015 in The Lancet Infectious Diseases. ...
Light-based technology tracks oxygen levels underwater for swim performance, muscle repair
2014-12-09
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA, and COLCHESTER, UK -- Swimmers looking to monitor and improve technique and patients striving to heal injured muscles now have a new light-based tool to help reach their goals. A research article by scientists at the University of Essex in Colchester and Artinis Medical Systems published today (5 December) in the Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO) describes the first measurements of muscle oxygenation underwater and the development of the enabling technology.
The article, "Underwater near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy measurements of muscle ...
Increased BMI in the normal range has a negative effect on cardiometabolic risk markers
2014-12-09
Increases in excess fat adversely affect multiple cardiometabolic risk markers even in lean young adults according to a new study published this week in PLOS Medicine. The study by Peter Würtz from the University of Oulu, Finland, and colleagues suggests that, even within the range of body-mass index (BMI) considered to be healthy, there is no threshold below which a BMI increase does not adversely affect the metabolic profile of an individual.
Adiposity, or having excess body fat, is a growing global threat to public health. Compared to people with a lean body ...
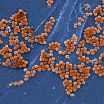
Genome sequencing traces MRSA spread in high transmission setting
2014-12-09
December 9, 2014 -- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a common cause of hospital-acquired infections, with the largest burden of infections occurring in under-resourced hospitals. While genome sequencing has previously been applied in well-resourced clinical settings to track the spread of MRSA, transmission dynamics in settings with more limited infection control is unknown. In a study published online today in Genome Research, researchers used genome sequencing to understand the spread of MRSA in a resource-limited hospital with high transmission rates.
Patients ...
Possible genetic link found in treatment-related cognitive issues in children with leukemia
2014-12-09
SAN FRANCISCO (DECEMBER 9, 2014) -Common variations in four genes related to brain inflammation or cells' response to damage from oxidation may contribute to the problems with memory, learning and other cognitive functions seen in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), according to a study led by researchers from Boston Children's Hospital, The Children's Hospital at Montefiore, and Dana-Farber/Boston Children's Cancer and Blood Disorders Center.
The data, presented at the 56th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (abstract #856), suggest ...
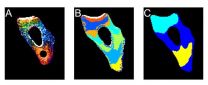
Altered movement of white blood cells may predict sepsis in patients with major burns
2014-12-09
A team of Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) investigators has identified what may be a biomarker predicting the development of the dangerous systemic infection sepsis in patients with serious burns. In their report in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, the researchers describe finding that the motion through a microfluidic device of the white blood cells called neutrophils is significantly altered two to three days before sepsis develops, a finding that may provide a critically needed method for early diagnosis.
"Neutrophils are the major white blood cell protecting ...
Birdsong study reveals how brain uses timing during motor activity
2014-12-09
Timing is key for brain cells controlling a complex motor activity like the singing of a bird, finds a new study published by PLOS Biology.
"You can learn much more about what a bird is singing by looking at the timing of neurons firing in its brain than by looking at the rate that they fire," says Sam Sober, a biologist at Emory University whose lab led the study. "Just a millisecond difference in the timing of a neuron's activity makes a difference in the sound that comes out of the bird's beak."
The findings are the first to suggest that fine-scale timing of neurons ...
Using genome sequencing to track MRSA in under-resourced hospitals
2014-12-09
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have used genome sequencing to monitor how the spread of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) occurs in under-resourced hospitals. By pinpointing how and when MRSA was transmitted over a three-month period at a hospital in northeast Thailand, the researchers are hoping their results will support evidence-based policies around infection control.
MRSA is a common cause of hospital-acquired infections, with the largest burden of infections occurring in under-resourced hospitals in the developing world. Whereas genome ...
[1] ... [3135]
[3136]
[3137]
[3138]
[3139]
[3140]
[3141]
[3142]
3143
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
[3149]
[3150]
[3151]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.