A pill for obesity?
2014-12-08
Harvard Stem Cell Institute researchers at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital have taken what they are describing as "the first step toward a pill that can replace the treadmill" for the control of obesity - though it of course would not provide all the additional benefits of exercise.
Chad Cowan, an HSCI Principal Faculty Member and his HSCI team report that they have created a system using human stem cells to screen for compounds that have the potential to turn white, or 'bad', fat cells into brown, or 'good' fat cells, and have already identified two compounds ...
University of Tennessee research offers explanation for Titan dune puzzle
2014-12-08
Titan, Saturn's largest moon, is a peculiar place. Unlike any other moon, it has a dense atmosphere. It has rivers and lakes made up of components of natural gas, such as ethane and methane. It also has windswept dunes that are hundreds of yards high, more than a mile wide and hundreds of miles long--despite data suggesting the body to have only light breezes.
Research led by Devon Burr, an associate professor in the Earth and Planetary Sciences Department at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, shows that winds on Titan must blow faster than previously thought to ...
UEA research could revolutionize genomic sequencing of drug-resistant bacteria
2014-12-08
New nanopore DNA sequencing technology on a device the size of a USB stick could be used to diagnose infection - according to new research from the University of East Anglia and Public Health England.
Researchers tested the new technology with a complex problem - determining the cause of antibiotic resistance in a new multi-drug resistant strain of the bacterium that causes Typhoid.
The results, published today in the journal Nature Biotechnology, reveal that the small, accessible and cost effective technology could revolutionise genomic sequencing.
Current technology ...
Genetic errors linked to aging underlie leukemia that develops after cancer treatment
2014-12-08
For a small percentage of cancer patients, treatment aimed at curing the disease leads to a form of leukemia with a poor prognosis. Conventional thinking goes that chemotherapy and radiation therapy induce a barrage of damaging genetic mutations that kill cancer cells yet inadvertently spur the development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a blood cancer.
But a new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis challenges the view that cancer treatment in itself is a direct cause of what is known as therapy-related AML.
Rather, the research suggests, ...
Disorder in gene-control system is a defining characteristic of cancer, study finds
2014-12-08
BOSTON and CAMBRIDGE -- The genetic tumult within cancerous tumors is more than matched by the disorder in one of the mechanisms for switching cells' genes on and off, scientists at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard report in a new study. Their findings, published online today in the journal Cancer Cell, indicate that the disarray in the on-off mechanism - known as methylation - is one of the defining characteristics of cancer and helps tumors adapt to changing circumstances.
The researchers also showed that derangement in ...
New agent causes small cell lung tumors to shrink in pre-clinical testing
2014-12-08
BOSTON -- Small cell lung cancer - a disease for which no new drugs have been approved for many years - has shown itself vulnerable to an agent that disables part of tumor cells' basic survival machinery, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology reported.
In a study published today in the journal Cancer Cell, the investigators found that the agent THZ1 caused human-like small cell lung tumors in mice to shrink significantly, with no apparent side effects. The compound is now being developed into a drug for testing ...
Organic mulch lets insect pollinators do their job
2014-12-08
COLUMBUS, OH - As interest in organic agricultural and horticultural practices continues to grow, so does the need to identify alternative weed control practices. Mulching, a common practice used to control weeds and reduce the need for tillage, can also reduce insect pollinators' exposure to harmful pesticides; however, finding the right mulch materials that allow pollinators to flourish can be challenging. Caitlin E. Splawski, from The Ohio State University Department of Horticulture and Crop Science, researched the effects of several types of organic mulch on squash ...
Baking soda is the best: Chemistry Life Hacks, Vol. 4 (video)
2014-12-08
WASHINGTON, Dec. 8, 2014 -- There's probably a box of it in your fridge or cupboard, and it has a million uses: baking soda. Reactions is back with volume four of its popular Chemistry Life Hacks series, with tips on how to de-skunk your dog, clean your kitchen and supercharge your washing machine. Check out the latest in the series that's one-part MacGyver, one-part Mendeleev here: http://youtu.be/85diRmuk-ow.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
The American Chemical Society ...
Half of US kids exposed to traumatic social or family experiences during childhood
2014-12-08
Nearly half of all children in the United States are exposed to at least one social or family experience that can lead to traumatic stress and impact their healthy development - be it having their parents divorce, a parent die or living with someone who abuses alcohol or drugs - increasing the risk of negative long-term health consequences or of falling behind in school, suggests new research led by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The study reports on new data showing the magnitude of these adverse experiences in the child population in the U.S., ...
Voters more inclined than consumers to pay for food safety
2014-12-08
Voters are more willing to pay for a decreased risk of food-related illness than consumers, but female consumers are more willing to pay than male consumers, according to an international team of researchers.
"The question is, what would consumers prefer?" said Amit Sharma, associate professor of hospitality management and finance, Penn State. "Would they prefer a market-driven, or a policy-driven approach? Either of those two approaches could lead to some price increase. Improving quality costs money, and food safety is no different."
Sharma and colleagues wanted to ...
Animal research sheds light on harmful mood disorders in new mothers
2014-12-08
In the days shortly after giving birth, most mothers experience a period of increased calmness and decreased stress responses, but around 20% of mothers experience anxiety. Some women may become depressed, and around one in a thousand can develop psychosis. The latest evidence indicates that these distressing responses to motherhood are still poorly understood, but that animal research could provide valuable clues to their causes.
Writing in the British Journal of Pharmacology, Dr David Slattery and Dr Clara Perani highlight that anxiety, depression and psychosis during ...
Wind farms to do not affect property values, study finds
2014-12-08
Wind turbine developments have no effect on property values of nearby homes and farms, according to new research from the University of Guelph.
Published in a recent issue of the Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics, the study is believed the first peer-reviewed study on this issue in Canada.
It was conducted by Richard Vyn, a professor in the Department of Food, Agricultural and Resource Economics, and Ryan McCullough, a former U of G graduate student and now a policy analyst for Health Canada.
They analyzed more than 7,000 home and farm sales in Melancthon ...
Bougainvillea's response to deficit irrigation tested
2014-12-08
PORTICI, ITALY - As water becomes scarcer in arid and semiarid regions across the globe, the floriculture industry is looking for ways to reduce water usage and produce ornamental plants more efficiently. Chiara Cirillo and members of an Italian research team coordinated by Professor Stefania De Pascale, say that understanding flowering plants' response to water management is critical for optimizing the production of high-quality potted ornamentals. "Water-saving irrigation management strategies are among the options available to horticultural growers to reduce water consumption ...
New model helps boost fishery profits and sustainability
2014-12-08
DURHAM, N.C. -- By identifying the most efficient fishing practices and behaviors, a new model developed by economists at Duke University and the University of Connecticut could help fishermen land larger paychecks while reducing the risk of fishery depletion.
"We're not talking about a trivial improvement. In some cases, we found that identifying the most efficient practices led to a 20 percent annual increase in total revenues if the fishery is managed differently," said Martin D. Smith, professor of environmental economics at Duke's Nicholas School of the Environment.
"Under ...
Solid-state proteins maximize the intensity of fluorescent-protein-based lasers
2014-12-08
The same research team that developed the first laser based on a living cell has shown that use of fluorescent proteins in a solid form rather than in solution greatly increases the intensity of light produced, an accomplishment that takes advantage of natural protein structures surrounding the light-emitting portions of the protein molecules. The findings from investigators Seok Hyun Yun, PhD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Malte Gather, PhD, of the University of St. Andrews in the U.K. appear in the online journal Nature ...
Chesapeake Bay region streams are warming
2014-12-08
CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. -- The majority of streams in the Chesapeake Bay region are warming, and that increase appears to be driven largely by rising air temperatures. These findings are based on new U.S. Geological Survey research published in the journal Climatic Change.
Researchers found an overall warming trend in air temperature of 0.023 C (0.041 F) per year, and in water temperature of 0.028 C (0.050 F) per year over 51 years. This means that air temperature has risen 1.1 C (1.98 F), and water temperature has risen 1.4 C (2.52 F) between 1960 and 2010 in the Chesapeake ...
Office jerks beware - your good ideas may not always be welcomed by colleagues
2014-12-08
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...
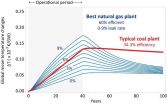
Is natural gas a 'bridge' to a hotter future?
2014-12-08
Washington, D.C.-- Natural gas power plants produce substantial amounts of gases that lead to global warming. Replacing old coal-fired power plants with new natural gas plants could cause climate damage to increase over the next decades, unless their methane leakage rates are very low and the new power plants are very efficient.
These are the principal findings of new research from Carnegie's Ken Caldeira and Xiaochun Zhang, and Nathan Myhrvold of Intellectual Ventures that compares the temperature increases caused by different kinds of coal and natural gas power plants. ...
High level engagement in comment sections can curb internet trolling
2014-12-08
Washington, DC (December 8, 2014) - Scrolling through the comments section on a news site is like seeing a verbal war before your eyes. Internet trolls flourish in an anonymous world, so much so that sites like Reuters and Popular Science have done away with the comment sections altogether. But there has to be a better way to let the audience engage in a civil manner. A recent study published in the Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication by researchers at the University of Texas, Purdue University, and University of Wyoming, found that having a journalist engage with ...
Genes that cause pancreatic cancer identified by new tool
2014-12-08
A technique that can identify causes of cancer invisible to genetic sequencing has uncovered large sets of previously unknown pancreatic cancer genes. It is hoped that this study will boost research into a disease that is still poorly understood and for which five-year survival rates have stood at around 5 per cent for the past four decades.
The technique works by introducing sections of DNA called piggyBac transposons into the mouse genome. Transposons jump around within the genome, reinserting themselves at random and causing a different mutation in each cell of the ...
Commentary calls for new 'science of climate diversity'
2014-12-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - There is cloud hanging over climate science, but one Cornell University expert on communication and environmental issues says he knows how to help clear the air.
In the December issue of Nature Climate Change, Jonathon Schuldt, assistant professor of communication, argues that only by creating a "science of climate diversity" can climate science and the larger climate change movement overcome a crippling lack of ethnic and racial diversity.
"There is an invisible, but very real barrier to climate engagement," Schuldt said. "We need to engage with all ...
Targeting microRNA may benefit some ovarian and breast cancer patients
2014-12-08
A genetic misfire called the 3q26.2 amplicon can cause real havoc. In fact, it is among the most frequent chromosomal aberrations seen in many cancers, including ovarian and breast cancers.
Researchers behind a study at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center believe they may have found a molecule-based approach to halting 3q26.2's destructive nature. By manipulating a non-coding microRNA (miRNA) known as miR569 that is part of the amplicon, scientists were able to increase cell death in vitro and in vivo. MicroRNAs are short, non-coding RNA molecules that are ...
EARTH Magazine: Hundreds of methane seeps discovered along the US East Coast
2014-12-08
Alexandria, Va. -- Methane is often found naturally leaking from the seafloor, particularly in petroleum basins like the Gulf of Mexico or along tectonically active continental margins like the U.S. West Coast, but such plumes were not expected along passive margins, like the East Coast of North America. Now, however, the discovery of hundreds of methane seeps on the seafloor along the U.S. East Coast suggests that such reservoirs may be more common along passive margins than previously thought. The release of such methane globally may have a significant influence on climate, ...
IU's DiMarchi lab sees another success on path to cure adult-onset diabetes, obesity
2014-12-08
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- A new treatment for adult-onset diabetes and obesity developed by researchers at Indiana University and the German Research Center for Environmental Health has essentially cured lab animals of obesity, diabetes and associated lipid abnormalities through improved glucose sensitivity, reduced appetite and enhanced calorie burning.
In preclinical trials, the new peptide -- a molecular integration of three gastrointestinal hormones -- lowered blood sugar levels and reduced body fat beyond all existing drugs, according to the work co-led by IU Distinguished ...
CNIO team has visualized the DNA double-strand break process for the first time
2014-12-08
Scientists from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), led by Guillermo Montoya, have developed a method for producing biological crystals that has allowed scientists to observe --for the first time-- DNA double chain breaks. They have also developed a computer simulation that makes this process, which lasts in the order of millionths of a second, visible to the human eye. The study is published today by the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
"We knew that enzymes, or proteins, endonucleases, are responsible for these double strand breaks, but ...
[1] ... [3141]
[3142]
[3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
3149
[3150]
[3151]
[3152]
[3153]
[3154]
[3155]
[3156]
[3157]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.