Vaccine holds hope of preventing antibiotic resistant skin infections
2014-12-08
LOS ANGELES - (Dec. 8, 2014) - In the U.S. and around the globe, skin and soft tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) continue to endanger the health and lives of patients and otherwise healthy individuals.
Treatment is difficult because MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics, and the infections can recur, placing family members and other close contacts at risk of infection.
A study reported online today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA holds new hope for preventing or reducing the severity of infections ...
Shedding new light on the formation of emotional fear memories
2014-12-08
Everyday events are easy to forget, but unpleasant ones can remain engraved in the brain. A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences identifies a neural mechanism through which unpleasant experiences are translated into signals that trigger fear memories by changing neural connections in a part of the brain called the amygdala. The findings show that a long-standing theory on how the brain forms memories, called Hebbian plasticity, is partially correct, but not as simple as was originally proposed.
The effort led by Joshua Johansen from ...
New therapy holds promise for restoring vision
2014-12-08
A new genetic therapy not only helped blind mice regain enough light sensitivity to distinguish flashing from non-flashing lights, but also restored light response to the retinas of dogs, setting the stage for future clinical trials of the therapy in humans.
The therapy employs a virus to insert a gene for a common ion channel into normally blind cells of the retina that survive after the light-responsive rod and cone photoreceptor cells die as a result of diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa. Photoswitches - chemicals that change shape when hit with light -are then ...
Heat-shock protein enables tumor evolution and drug resistance in breast cancer
2014-12-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass. (December 8, 2014) - Long known for its ability to help organisms successfully adapt to environmentally stressful conditions, the highly conserved molecular chaperone heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90) also enables estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancers to develop resistance to hormonal therapy.
This HSP90-mediated evolutionary mechanism of drug resistance, reported by Whitehead Institute scientists in this week's online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), provides a strong therapeutic rationale for combining HSP90 ...
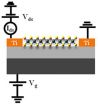
High photosensitivity 2-D-few-layered molybdenum diselenide phototransistors
2014-12-08
Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials are now attracting a lot of interest due to their unique optoelectronic properties at atomic thicknesses. Among them, graphene has been mostly investigated, but the zero-gap nature of graphene limits its practical applications. Therefore, 2D layered materials with intrinsic band gaps such as MoS2, MoSe2, and MoTe2 are of interest as promising candidates for ultrathin and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
Here, Pil Ju Ko and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan have fabricated back-gated field-effect phototransistors ...
Hummingbird's hover surprisingly easy to hack
2014-12-08
Hummingbirds' remarkable ability to hover in place is highly contingent on the tiny bird having a completely stationary visual field, according to University of British Columbia research published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
UBC zoologists Benjamin Goller and Douglas Altshuler projected moving spiral and striped patterns in front of free-flying hummingbirds attempting to feed from a stationary feeder.
Even minimal background pattern motion caused the hummingbirds to lose positional stability and drift. Giving the birds time to get used ...
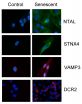
Study offers future hope for tackling signs of aging
2014-12-08
A new advance in biomedical research at the University of Leicester could have potential in the future to assist with tackling diseases and conditions associated with ageing - as well as in treating cancer.
The research, which has shown promise in clinical samples, has been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death and Disease.
The group of scientists coordinated by Dr Salvador Macip from the Mechanisms of Cancer and Ageing Lab and the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Leicester carried out the study to find new ways of identifying old ...
Office jerks beware -- your good ideas may not always be welcomed by colleagues
2014-12-08
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...
Detecting gases wirelessly and cheaply
2014-12-08
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT chemists have devised a new way to wirelessly detect hazardous gases and environmental pollutants, using a simple sensor that can be read by a smartphone.
These inexpensive sensors could be widely deployed, making it easier to monitor public spaces or detect food spoilage in warehouses. Using this system, the researchers have demonstrated that they can detect gaseous ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, and cyclohexanone, among other gases.
"The beauty of these sensors is that they are really cheap. You put them up, they sit there, and then you come around ...
Many memories, many rooms
2014-12-08
Researchers have long wondered if there is an upper limit to our capacity to store memories and how we manage to remember so many events without mixing up events that are very similar.
To explore this issue, researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience and Centre for Neural Computation and colleagues from the Czech Republic and Italy tested the ability of rats to remember a number of distinct but similar locations. Their findings are published in the 8 December edition of the Proceedings of the National ...
UT Arlington team proposes new model for snake venom evolution
2014-12-08
Technology that can map out the genes at work in a snake or lizard's mouth has, in many cases, changed the way scientists define an animal as venomous. If oral glands show expression of some of the 20 gene families associated with "venom toxins," that species gets the venomous label.
But, a new study from The University of Texas at Arlington challenges that practice, while also developing a new model for how snake venoms came to be. The work, which is being published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, is based on a painstaking analysis comparing groups of ...
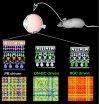
Injectable 3-D vaccines could fight cancer and infectious diseases
2014-12-08
(BOSTON and CAMBRIDGE, Massachusetts) - One of the reasons cancer is so deadly is that it can evade attack from the body's immune system, which allows tumors to flourish and spread. Scientists can try to induce the immune system, known as immunotherapy, to go into attack mode to fight cancer and to build long lasting immune resistance to cancer cells. Now, researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and Harvard's School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) show a non-surgical injection of programmable biomaterial that spontaneously assembles ...
Does smoking hamper treatment for alcohol abuse?
2014-12-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A new study has shown that smoking can inhibit the success of treatment for alcohol abuse, putting people who are addicted to both tobacco and alcohol in a double bind.
According to findings by the University at Buffalo Research Institute on Addictions (RIA), clients who smoke have shorter stays in alcohol treatment programs than non-smokers and may have poorer treatment outcomes than non-smokers.
Kimberly Walitzer, PhD, deputy director and senior research scientist at RIA, led the study, which analyzed more than 21,000 adult treatment seekers from ...
Testing for drug-resistant bacteria before prostate biopsy can reduce infections
2014-12-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Some infections after prostate biopsy due to drug-resistant Escherichia coli can be thwarted by simple rectal swab cultures prior to the procedure. The cultures test for antibiotic-resistant E. coli, and the findings are used to direct the selection of antimicrobial prophylaxis used for the procedure, according to Rhode Island Hospital researchers. The study was recently published in Urology.
For patients undergoing transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided biopsies, Ciprofloxacin may not be the best prophylactic option to use for patients colonized with ...
NASA catches 3 days of Typhoon Hagupit's motion over Philippines
2014-12-08
NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites flew over Typhoon Hagupit from Dec. 6 through Dec. 8 and the MODIS instrument that flies aboard both satellites provided images of the storm as it moved through the country.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite caught a picture of Hagupit on Dec. 6 before it made landfall. On Dec. 7, the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite took an image of the storm as it was making landfall in the eastern Philippines.
On Dec. 8 at 04:50 UTC (Dec. 7 at 11:50 p.m. EST) when NASA's ...
MCW researchers find link between sleep deprivation and cell damage
2014-12-08
Scientists at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) have discovered a link between sleep loss and cell injury. Results of a new study find sleep deprivation causes the damage to cells, especially in the liver, lung, and small intestine. Recovery sleep following deprivation heals the damage.
The findings are published in the December issue of Sleep, a joint publication of the Sleep Research Society and the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The lead author is Carol Everson, Ph.D., professor of neurology, cell biology, neurobiology and anatomy at MCW. Co-authors are Christopher ...
Public servants are individually motivated to help environment
2014-12-08
Athens, Ga. - New University of Georgia research shows that while on the job, public servants contribute not just to mandated sustainability but also to discretionary eco-friendly initiatives of their own.
"Some people are born with a higher intrinsic need to serve the public," said study co-author Robert K. Christensen, an associate professor in the School of Public and International Affairs. "They have a desire to help others and serve society. Government and nonprofit managers, for example, typically have higher levels of public service motivation than business managers."
The ...
Toughest breast cancer may have met its match
2014-12-08
Triple-negative breast cancer is as bad as it sounds. The cells that form these tumors lack three proteins that would make the cancer respond to powerful, customized treatments. Instead, doctors are left with treating these patients with traditional chemotherapy drugs that only show long-term effectiveness in 20 percent of women with triple-negative breast cancer. Now, researchers at The Johns Hopkins University have discovered a way that breast cancer cells are able to resist the effects of chemotherapy -- and they have found a way to reverse that process.
A report of ...
UH Case Medical Center experts present data at ASH Annual Meeting
2014-12-08
CLEVELAND: Researchers from Seidman Cancer Center at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine presented new research findings this weekend at the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) in San Francisco.
In a poster presentation (Abstract #4053), Jane Little, MD, and colleagues presented promising findings related to a novel biochip aimed at improving outcomes for patients with sickle cell disease. Although it is well-known that red cell interactions are important in sickle cell disease, ...
NOAA: Researchers offer new insights into predicting future droughts in California
2014-12-08
According to a new NOAA-sponsored study, natural oceanic and atmospheric patterns are the primary drivers behind California's ongoing drought. A high pressure ridge off the West Coast (typical of historic droughts) prevailed for three winters, blocking important wet season storms, with ocean surface temperature patterns making such a ridge much more likely. Typically, the winter season in California provides the state with a majority of its annual snow and rainfall that replenish water supplies for communities and ecosystems.
Further studies on these oceanic conditions ...
World record for compact particle accelerator
2014-12-08
Using one of the most powerful lasers in the world, researchers have accelerated subatomic particles to the highest energies ever recorded from a compact accelerator.
The team, from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Lab (Berkeley Lab), used a specialized petawatt laser and a charged-particle gas called plasma to get the particles up to speed. The setup is known as a laser-plasma accelerator, an emerging class of particle accelerators that physicists believe can shrink traditional, miles-long accelerators to machines that can fit on a table.
The ...
Punishing kids for lying just doesn't work
2014-12-08
If you want your child to tell the truth, it's best not to threaten to punish them if they lie. That's what researchers discovered through a simple experiment involving 372 children between the ages of 4 and 8.
How the Experiment was Done
The researchers, led by Prof. Victoria Talwar of McGill's Dept. of Educational and Counselling Psychology, left each child alone in a room for 1 minute with a toy behind them on a table, having told the child not to peek during their absence.
While they were out of the room, a hidden video camera filmed what went on.
When the ...
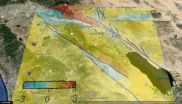
Re-thinking Southern California earthquake scenarios in Coachella Valley, San Andreas Fault
2014-12-08
AMHERST, Mass. - New three-dimensional (3D) numerical modeling that captures far more geometric complexity of an active fault segment in southern California than any other, suggests that the overall earthquake hazard for towns on the west side of the Coachella Valley such as Palm Springs and Palm Desert may be slightly lower than previously believed.
New simulations of deformation on three alternative fault configurations for the Coachella Valley segment of the San Andreas Fault conducted by geoscientists Michele Cooke and Laura Fattaruso of the University of Massachusetts ...
Researchers identify hormone that reduces calorie burning, contributes to obesity
2014-12-08
Hamilton, ON (Dec. 8, 2014) - Researchers from McMaster University have identified an important hormone that is elevated in obese people and contributes to obesity and diabetes by inhibiting brown fat activity.
Brown adipose tissue, widely known as brown fat, is located around the collarbone and acts as the body's furnace to burn calories. It also keeps the body warm. Obese people have less of it, and its activity is decreased with age. Until now, researchers haven't understood why.
There are two types of serotonin. Most people are familiar with the first type in the ...
Rule of 3: Hormone triplet offers hope for obesity and diabetes
2014-12-08
Recently, the researchers had constructed several single molecules with dual hormone action. Now, for the first time, the researchers succeeded in designing a substance that combines three metabolically active hormone components (GLP-1, GIP and glucagon) and offers unmatched potency to fight metabolic diseases in pre-clinical trials.
The team headed by physician scientist Matthias Tschöp (Helmholtz Diabetes Center at HMGU and Metabolic Diseases Chair at TUM) and peptide chemist Richard DiMarchi (Indiana University) has been cooperating for almost a decade to invent ...
[1] ... [3140]
[3141]
[3142]
[3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
3148
[3149]
[3150]
[3151]
[3152]
[3153]
[3154]
[3155]
[3156]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.