HPV vaccine, riskier sexual activity not linked researchers say
2014-12-08
Sexual behaviour of teenage girls does not appear to be impacted by the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine, according to Queen's researchers Drs. Leah Smith and Linda Lévesque.
There are concerns the vaccine, which guards against four types of the HPV shown to cause cervical cancer and anogenital warts, may give girls a false sense of security about contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and lead them to engage in riskier sexual activity.
"These findings suggest fears of increased risky sexual behaviour following HPV vaccination are unwarranted and should ...
A yardstick to measure the malignancy of prostate cancer
2014-12-08
When cancer is diagnosed, the grade of its malignancy is a central concern for both patients and their physicians. This value is used to determine how intensively and how radically the cancer must be treated. Particularly in the case of prostate cancer, the disease can take widely varying courses in different patients. Therefore, cancer researchers have been looking for measurable, reliable biomarkers that give clues about the aggressiveness of a tumor in order to choose an appropriate therapy.
In many types of cancer, alterations in a tumor's genetic material indicate ...
New research suggests Caribbean gorgonian corals are resistant to ocean acidification
2014-12-08
MIAMI - A new study on tropical shallow-water soft corals, known as gorgonians, found that the species were able to calcify and grow under elevated carbon dioxide concentrations. These results suggest that Caribbean gorgonian corals may be more resilient to the ocean acidification levels projected by the end of the 21st century than previously thought.
An international team of scientists, including from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, tested the effects of elevated CO2 concentrations on the growth and calcification rates ...
Experimental gene therapy successful in certain lymphomas and leukemia
2014-12-08
Study results of CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) therapy using the Sleeping Beauty non-viral transduction system to modify T cells has demonstrated further promise in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies.
Patients who had acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) or chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) were part of clinical trials at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, which used the Sleeping Beauty gene transfer system initially discovered at the University of Minnesota.
Results from the study were presented ...
Enzyme identified which could lead to targeted treatment for PMS
2014-12-08
Low doses of fluoxetine - better known as the anti-depressant Prozac - could hold the key to preventing PMS symptoms, an international team of researchers has found.
Up to 80 per cent of women are thought to suffer from premenstrual syndrome (PMS), which can be a debilitating condition with symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, fatigue, sleep deprivation and increased sensitivity to pain.
PMS appears to be triggered by the fall in secretion of the ovarian sex steroid hormone progesterone that occurs towards the end of the menstrual cycle and leads to a decline in ...
Evidence of life on Mars?
2014-12-08
In 2012 the Mars Science Laboratory landed in the fascinating Gale crater. The Gale crater is of such great interest because of the 5.5 km high mountain of layered materials in the middle. This material tells an intricate story of the history of Mars, perhaps spanning much of the existence of this mysterious planet.
Once positioned, the Curiosity rover began field studies on its drive toward Aeolis Mons (also unofficially known as Mount Sharp), the central peak within the crater. Curiosity has travelled more than 9.4 km so far and during its trip up the mountain, Curiosity ...
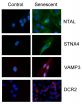
Study offers future hope for tackling signs of ageing
2014-12-08
A new advance in biomedical research at the University of Leicester could have potential in the future to assist with tackling diseases and conditions associated with ageing - as well as in treating cancer.
The research, which has shown promise in clinical samples, has been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death and Disease.
The group of scientists coordinated by Dr Salvador Macip from the Mechanisms of Cancer and Ageing Lab and the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Leicester carried out the study to find new ways of identifying old ...
Biomimetic dew harvesters
2014-12-08
Insects are full of marvels - and this is certainly the case with a beetle from the Tenebrionind family, found in the extreme conditions of the Namib desert. Now, a team of scientists has demonstrated that such insects can collect dew on their backs - and not just fog as previously thought. This is made possible by the wax nanostructure on the surface of the beetle's elytra. These findings by José Guadarrama-Cetina, then working at ESPCI ParisTech, France - on leave from the University of Navarra, in Spain - and colleagues were recently published in EPJ E. They bring ...
Machine harvesting may increase apple supply for hard cider market
2014-12-08
MOUNT VERNON, WA - Cider - or "hard cider" as it is typically known in the United States - is experiencing a real revival. The fermented apple juice with 0.5% to 7% alcohol-by-volume is the fastest growing alcohol market segment in the US, boasting a 54% increase in production annually from 2007 to 2012. Naturally, increasing consumer demand for cider translates to a need for more apples to make quality cider products.
Carol A. Miles and Jaqueline King from Washington State University's Department of Horticulture published a study in HortTechnology that can provide apple ...
Study finds Affordable Care Act leaves many children without important benefits
2014-12-08
An article published in the Health Affairs December issue is the first ever comprehensive analysis to investigate the Affordable Care Act's (ACA) Essential Health Benefit (EHB) as it relates to children. The study found that the EHB has resulted in a state-by-state patchwork of coverage for children and adolescents that has significant exclusions, particularly for children with developmental disabilities and other special health care needs.
Previous studies have compared the EHB standard more broadly to the Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP), but this analysis ...
High tunnels found effective for finishing cold-tolerant annuals
2014-12-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, IN/ITHACA, NY - Energy costs account for one of the largest expenses in commercial greenhouse production of annual bedding plants. Naturally, bedding plant producers are searching for more energy-efficient production methods that can reduce fuel usage and increase profits. Christopher Currey, Roberto Lopez, and Neil Mattson published a study in HortTechnology that gives growers in northern latitudes valuable information on finishing practices for annual bedding plants. The researchers compared traditional heated greenhouses with unheated high tunnels for ...
Advances in lymphoma and multiple myeloma treatment seek to improve outcomes for patients
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - New treatment combinations and targeted therapies for lymphoma and multiple myeloma are improving outcomes for vulnerable patient populations with hard-to-treat disease, according to studies presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Despite advances in lymphoma treatments, improving the prognosis for patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant disease remains a challenge. The early success of several precision therapies associated with fewer side effects than conventional approaches ...
Studies compare blood clot treatments, illuminate recurrence risk in high-risk groups
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 7, 2014) - Studies presented at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition compare new and standard-of-care treatments for blood clots and further illuminate clot risks in vulnerable populations, such as cancer patients.
Although significant advances have been made in the treatment and prevention of blood clots through new and improved therapies for clotting disorders, challenges remain in balancing the benefits and risks of these therapies. Specifically, while these treatments can reduce patients' risk of suffering ...
Researchers at Mainz University explore new approach for treating Alzheimer's disease
2014-12-08
It is estimated that about 35 million people worldwide currently suffer from dementia and it is expected that the number will increase to 135 million by the year 2050. The disease is already one of the most common health problems in the elderly, which is why experts predict that the numbers of people affected will increase over time. Researchers at the Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have recently gained new insights into how it may in future be possible to treat patients with the currently ...
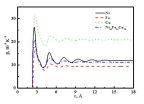
How many atoms does it take to predict the thermal expansion of liquid metals?
2014-12-08
The ability to predict macroscopic physical and chemical properties from information derived at the micro-scale or atomic scale for various kinds of materials has yet to be perfected in the field of materials physics and chemistry. Although macro-scopic properties are determined by the micro or atomic structure of materials, it is still difficult to obtain such properties as hardness, intensity, surface tension, density, thermal expansion, thermal diffusion, viscosity and specific heat from a cell with just several atoms because of multi-scale effects.
For solids, particularly ...
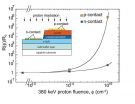
Finding the Achilles' heel of GaN-based LEDs in harsh radiation environments
2014-12-08
Gallium nitride (GaN) based devices are attractive for harsh environment electronics because of their high chemical and the mechanical stability of GaN itself that has a higher atomic displacement energy than other semiconductor materials.
However, degradation mechanisms of GaN device under radiation environments is not clear mainly because devices consist of many different types of semiconductors, such as p-type and n-type layers in light emitting diode (LED), and each layer has different hardness to radiation.
Now, researchers at the Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary ...
Macrophages chase neutrophils away from wounds to resolve inflammation
2014-12-08
Macrophages are best known for their Pac Man-like ability to gobble up cellular debris and pathogens in order to thwart infection. A new study in The Journal of Cell Biology describes how these immune cells also help resolve inflammation by inducing white blood cells called neutrophils to leave wounded tissue.
Neutrophils are "first responders" that are attracted to wounds by signaling molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate a protein kinase. When neutrophils finish their work, inflammation is partly resolved through apoptosis, or cell suicide, and ...
Drawing lessons from Philadelphia's large-scale ob unit closures
2014-12-08
What does it mean for expectant mothers and hospitals when there are large-scale closures of maternity units? A new study led by researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia provides an inside view from hospital staff members in Philadelphia, where 13 out of 19 obstetric units closed in a 15-year period.
The researchers found that sharp surges in patient volume in the remaining units strained the healthcare system, eroded workforce morale, and fragmented care for mothers and babies until hospitals adjusted to added demands.
"While the degree of obstetric ...
Two papers in Health Affairs expose gaps in health coverage for children, recommend solutions
2014-12-08
WASHINGTON, DC (December 8, 2014)-- Despite the promise of health reform, millions of U.S. children still lack quality health coverage or have trouble getting the services they need to stay healthy or to develop properly, according to two articles published in the December issue of Health Affairs. To address these gaps in coverage, broad reforms aimed at improving the quality of coverage for all children are needed, according to the authors.
In the first article, Sara Rosenbaum, JD, the Harold and Jane Hirsh Professor of Health Law and Policy at Milken Institute School ...
Seasonal flu vaccines boost immunity to many types of flu viruses
2014-12-08
WASHINGTON, DC - December 9, 2014 - Seasonal flu vaccines may protect individuals not only against the strains of flu they contain but also against many additional types, according to a study published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The work, directed by researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., found that some study participants who reported receiving flu vaccines had a strong immune response not only against the seasonal H3N2 flu strain from 2010, when blood samples were ...
San Francisco public housing type a strong predictor of kids' use of emergency rooms
2014-12-08
San Francisco children living in non-redeveloped public housing are 39 percent more likely to repeatedly visit emergency rooms, according to new research from UC San Francisco and UC Berkeley.
"The average emergency department (ED) visit costs two to five times more than an office visit, and many children visit EDs for potentially preventable reasons," said Nancy Adler, PhD, senior author of the research, and vice chair of the department of psychiatry and director of the Center for Health and Community at UCSF. "There is a clear need to better understand the range of ...
New research shows fewer deaths related to RSV than previously thought
2014-12-08
(SALT LAKE CITY)- It's a virus that has long been characterized as dangerous and even deadly, but new research shows infant deaths from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are actually quite uncommon in the 21st century.
Researchers at the University of Utah have shown there are approximately 42 deaths annually associated with RSV in the United States, and of those deaths, the majority are in infants and young children that have complex preexisting chronic conditions.
"The news is very good for parents and their babies," says Carrie Byington, M.D., professor of pediatrics ...
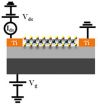
High photosensitivity 2D-few-layered molybdenum diselenide phototransistors
2014-12-08
Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials are now attracting a lot of interest due to their unique optoelectronic properties at atomic thicknesses. Among them, graphene has been mostly investigated, but the zero-gap nature of graphene limits its practical applications. Therefore, 2D layered materials with intrinsic band gaps such as MoS2, MoSe2, and MoTe2 are of interest as promising candidates for ultrathin and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
Here, Pil Ju Ko and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan have fabricated back-gated field-effect phototransistors ...
Vitamin C may help people who suffer from respiratory symptoms after exercise
2014-12-08
Physical activity increases oxidative stress, and therefore, as an antioxidant vitamin C might have particularly evident effects on people who are participating in vigorous exercise. In several studies, vitamin C administration attenuated the increases in oxidative stress markers caused by exercise. Furthermore, vitamin C is involved in the metabolism of histamine, prostaglandins, and cysteinyl leukotrienes, all of which appear to be mediators in the pathogenesis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
A meta-analysis of three studies found that vitamin C halved post-exercise ...
Confounding factors contribute to unexpected results of trial of renal denervation
2014-12-08
A new analysis of an important trial of the blood pressure-lowering procedure, renal denervation, shows that the main results may have been affected by a number of confounding factors that partially explain the unexpected blood pressure responses in patients.
The analysis, published in the European Heart Journal [1], identified factors in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial, such as variations in the way the procedure was performed and changes in patients' medications and drug adherence, which may have had a significant impact on the results.
Results of the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 ...
[1] ... [3142]
[3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
[3149]
3150
[3151]
[3152]
[3153]
[3154]
[3155]
[3156]
[3157]
[3158]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.