Guidelines for treatment of Ebola patients are urgently needed
2014-12-10
London, United Kingdom, December 9, 2014 - As the Ebola Virus Diseases (EVD) epidemic continues to rage in West Africa, infectious diseases experts call attention to the striking lack of treatment guidelines. With over 16,000 total cases and more than 500 new infections reported per week, and probable underreporting of both cases and fatalities, the medical community still does not have specific approved treatment in place for Ebola, according to an editorial published in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Not only are treatment guidelines lacking, but ...
With experience, people can tell bears apart
2014-12-10
Studying the social interaction of bears through the use of camera traps and visual observations requires that humans be able to tell individuals apart. A study done using volunteers to study the vulnerable Andean bear indicates that people can learn to identify individual bears, given a little practice. The research, done by San Diego Zoo conservationists with international collaborators using photos spanning many years, also indicates that young bears usually retain many of their unique markings as they grow older.
"Knowing, scientifically, that people who have been ...
German researchers propose better substances for treating the dengue virus
2014-12-10
Researchers from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and the Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg are proposing potential new active substances for treating the dengue virus. Just like Ebola, dengue fever is also caused by a virus for which there is currently no cure and no vaccine and can be fatal.
In the quest for medication to treat the dengue virus, the scientific community is focusing on a particular enzyme of the pathogen, the protease known as NS2B/NS3. The reason for this is that inhibitors of similar proteases have been revealed to be very effective ...
Immune function marker does not predict benefit of trastuzumab in HER-2+ breast cancer
2014-12-10
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. -- A marker of immune function that predicts for better outcomes in patients treated with chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer is also linked to improved prognosis in patients treated with chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. But that marker -- the quantity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (S-TILs) in a biopsy -- appears irrelevant when trastuzumab is used.
And since trastuzumab, and not chemotherapy alone, is the standard of care for the HER2-positive sub-class of breast cancer, there is no need to test for these lymphocytes in ...
Early trial of new drug shows promise for patients with triple-negative breast cancer
2014-12-10
In patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer--a disease with no approved targeted therapies--infusion of pembrolizumab produced durable responses in almost one out of five patients enrolled in a phase-Ib clinical trial, according to data presented Dec. 10, at the 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
The multi-center, non-randomized trial was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and antitumor activity of bi-weekly infusions of pembrolizumab (MK-3475, marketed as Keytruda®). The researchers enrolled 27 patients, aged 29 to 72 years, who had ...
Link between power lines and ill-health called into question
2014-12-10
Several past studies have suggested that the magnetic fields created by phones, high-voltage power lines and other electrical equipment are harmful for humans.
Research first carried out in the 1970's and again subsequently, found an association between people living near overhead power lines and an increased risk of childhood leukaemia. Although some later studies have failed to find such a link, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has categorised low frequency magnetic fields as "possibly carcinogenic."
But a mechanism for this association has never been ...
Brain inflammation a hallmark of autism, large-scale analysis shows
2014-12-10
While many different combinations of genetic traits can cause autism, brains affected by autism share a pattern of ramped-up immune responses, an analysis of data from autopsied human brains reveals. The study, a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins and the University of Alabama at Birmingham, included data from 72 autism and control brains. It will be published online Dec. 10 in the journal Nature Communications.
"There are many different ways of getting autism, but we found that they all have the same downstream effect," says Dan Arking, Ph.D. , an associate professor ...
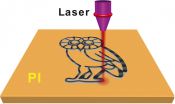
Defects are perfect in laser-induced graphene
2014-12-10
HOUSTON - (Dec. 10, 2014) - Researchers at Rice University have created flexible, patterned sheets of multilayer graphene from a cheap polymer by burning it with a computer-controlled laser. The process works in air at room temperature and eliminates the need for hot furnaces and controlled environments, and it makes graphene that may be suitable for electronics or energy storage.
Under a microscope, what the researchers call laser-induced graphene (LIG) doesn't look like a perfect chicken wire-like grid of atoms. Instead, it's a jumble of interconnected graphene flakes ...
Brain reward circuits respond differently to 2 kinds of sugar
2014-12-10
Phoenix, AZ (December 10th, 2014) - The brain responds differently to two kinds of sugar, according to a report today at the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology annual meeting in Phoenix Arizona. The study suggests that fructose heightens the response of brain reward circuits to food cues, promoting feeding behavior.
Currently, roughly two out of three U.S. adults are overweight and one out of three is obese. Changes in lifestyle and dietary intake during the past quarter century are thought to be the main culprits, with the increase in fructose consumption of ...
Alcohol-control law may curb partner abuse
2014-12-10
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Communities with fewer places to buy or drink alcohol also tend to have lower rates of intimate partner violence, new evidence suggests.
The research, published in the January issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, suggests that laws limiting what is called "alcohol outlet density" could offer one way to address violence within intimate relationships.
States and communities throughout the United States have enacted various laws to reduce excessive use of alcohol, including limiting outlet density, limiting hours and days of sale, and ...
Saving old information can boost memory for new information
2014-12-10
The simple act of saving something, such as a file on a computer, may improve our memory for the information we encounter next, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The research suggests that the act of saving helps to free up cognitive resources that can be used to remember new information.
Our findings show that people are significantly better at learning and remembering new information when they save previous information," says psychological scientist and study author Benjamin Storm of ...
Drug developed at Pitt proves effective against antibiotic-resistant 'superbugs'
2014-12-10
PITTSBURGH, Dec. 9, 2014 - A treatment pioneered at the University of Pittsburgh Center for Vaccine Research (CVR) is far more effective than traditional antibiotics at inhibiting the growth of drug-resistant bacteria, including so-called "superbugs" resistant to almost all existing antibiotics, which plague hospitals and nursing homes.
The findings, announced online in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy and funded by the National Institutes of Health, provide a needed boost to the field of antibiotic development, which has been limited in the last four ...
Can organic crops compete with industrial agriculture?
2014-12-10
Berkeley -- A systematic overview of more than 100 studies comparing organic and conventional farming finds that the crop yields of organic agriculture are higher than previously thought. The study, conducted by researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, also found that certain practices could further shrink the productivity gap between organic crops and conventional farming.
The study, to be published online Wednesday, Dec. 10, in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, tackles the lingering perception that organic farming, while offering an environmentally ...
Experts call for faster mobilization of 'overlooked' survivors to contain Ebola epidemic
2014-12-10
In an editorial published online today in the International Journal of Epidemiology, experts from the Departments of Psychiatry and Epidemiology at Columbia University, New York, are calling for survivors of the Ebola epidemic to be mobilised in a bid to hasten containment of the disease.
We already know that the current Ebola outbreak is unique in its magnitude and for its dispersion in dense, mobile populations. Physicians and nurses face high mortality, and foreign aid in the form of medical supplies and staff continues to be unequal to the scope of the problem. With ...
You are what you eat -- if you're a coral reef fish
2014-12-10
In a world first study researchers have found a coral-eating fish that disguises its smell to hide from predators.
"For many animals vision is less important than their sense of smell," says study lead author Dr Rohan Brooker from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University.
"Because predators often rely on odors to find their prey, even visually camouflaged animals may stick out like a sore thumb if they smell strongly of 'food'." Dr Brooker says.
The research, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, ...
Insulin dosage for type 2 diabetes linked with increased death risk
2014-12-10
In a report published today in the journal of Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, researchers from Cardiff University were also able to show a correlation between patients treated with a higher dosage of insulin and a raised risk of cancer development, heart attacks and stroke.
Researchers identified these trends by scrutinizing the medical history of 6,484 patients with type 2 diabetes extracted from the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD). Patients were on average aged 64 at the beginning of the study in 2000, and were followed for an average of 3 years from ...
Fathering offspring is more than just a race to the egg
2014-12-10
Fathering offspring is more than just a race to the egg
Longer sperm are better at fertilising eggs, study reveals
But females also influence a male's fertilising success
Research may produce clues to understanding human fertility
The chance of a male fathering offspring may not be a simple race to the egg, but is influenced by the length of the male's sperm, say scientists from the University of Sheffield.
Using a captive population of zebra finches, the researchers carried out sperm competition experiments between pairs of males, where one male consistently ...
Annual NHS spend on management consultancy has doubled since 2010
2014-12-10
Annual NHS spending on management consultancy has doubled from £313m to £640m between 2010 and 2014, despite a promise by Health Secretary Andrew Lansley to 'slash' spending after the 2010 election, reveals an article in The BMJ this week.
This is enough to run three medium sized hospitals or employ about 2000 extra nurses, says David Oliver, a former clinical director at the Department of Health, who obtained the figures through a Freedom of Information request.
"In times of war, arms dealers, rebuilders, and racketeers profit from the chaos," he writes. ...
Can doctors be trained in a 48-hour working week?
2014-12-10
Since August 2009 all UK trainee doctors have been restricted to a 48 hour week, but some say this has had negative effects on the quantity and quality of medical training. Is there any evidence to substantiate these fears? Doctors discuss the issue in The BMJ this week.
Andrew Hartle and Sarah Gibb of the Association of Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland find no evidence that implementation of the European Working Time Directive has led to a decline in the quality of training.
They point out that several reviews on the impact of restricting working time have ...
Delayed cancer diagnosis unlikely to be due to poor medical practice
2014-12-10
Poor professional performance is an unlikely cause of delays in referral for suspected cancer, argue researchers in The BMJ this week.
Instead, such delays largely reflect "limitations in scientific knowledge and in the organisation and delivery of healthcare." And they question government plans to rank general practices according to how promptly patients are referred to specialist services for suspected cancer.
Most patients who have cancer diagnosed after the onset of symptoms are referred after one or two GP consultations (80%), but a substantial minority (20%) ...
Most exaggeration in health news is already present in academic press releases
2014-12-10
Most exaggeration in health related science news is already present in academic press releases, finds a study published in The BMJ this week.
The researchers suggest that improving the accuracy of academic press releases "could represent a key opportunity for reducing misleading health related news."
Health related news has widespread potential to influence health related behaviour but often misreports the science. It is not known whether exaggerations - claims going beyond those made in the research paper - originate in the news stories themselves or in press releases ...
BMJ investigation sheds light on alleged NHS privatisation since government reforms
2014-12-10
The analysis of 3,494 contracts awarded by 182 Clinical Commissioning Groups (CCGs) in England between April 2013 and August 2014 - disclosed to the BMJ under the Freedom of Information (FOI) Act - showed that in total, non NHS providers have secured 45% of contracts awarded since April 2013.
A total of 1,149 contracts (33%) were awarded to private sector providers, 335 contracts (10%) were awarded to voluntary and social enterprise sector providers, while 100 contracts (2%) were awarded to other providers, such as joint ventures or local authorities.
A further 1,910 ...
Doctors trained in higher expenditure regions spend more, may add to rising health care costs
2014-12-09
WASHINGTON, DC (December 9, 2014)--A study published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) shows that physicians who do residency training in regions of the country with higher health care spending patterns continue to practice in a more costly manner - even when they move to a geographic area where health care spending is lower.
Immediately following residency, physicians whose residencies were in higher-spending regions spent 29 percent more on average than their peers who had trained in lower-spending areas of the country, according to the ...
Study shows cognitive training can improve brain performance of students in poverty
2014-12-09
The cognitive effects of poverty can be mitigated during middle school with a targeted intervention, according to researchers at the Center for BrainHealth at The University of Texas at Dallas.
In a paper published today in the open-access journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, researchers for the first time examine the efficacy of cognitive training in a large and diverse group of 7th and 8th grade public middle school students as compared to typically developing students who received no specific training.
"Previous research has shown that growing up in poverty ...
Restricting surgical residents' hours doesn't improve outcomes
2014-12-09
Rules don't reduce death, morbidity or adverse effects
Surgeon who best knows patient should continue with critical care
Restrictions may hurt patient safety
CHICAGO --- Controversial restrictions on hospital residents' duty hours imposed in 2011 did not improve surgery patients' outcomes, reports a large new Northwestern Medicine study of U.S. hospitals, one of the first national evaluations of the results of the restrictions.
The restrictions also did not result in any differences in surgical residents' performance on exams.
"Our study suggests that these ...
[1] ... [3134]
[3135]
[3136]
[3137]
[3138]
[3139]
[3140]
[3141]
3142
[3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
[3149]
[3150]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.