NTU leads global research to uncover one of mankind's most ancient lineages
2014-12-04
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University (NTU Singapore) and Penn State University in the United States have successfully discovered one of modern human's ancient lineages through the sequencing of genes.
World-renowned geneticist from NTU, Professor Stephan Christoph Schuster, who led an international research team from Singapore, United States and Brazil, said this is the first time that the history of mankind populations has been analysed and matched to Earth's climatic conditions over the last 200,000 years.
Their breakthrough findings are published today ...
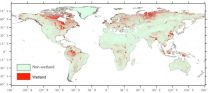
Chinese scientists create new global wetland suitability map
2014-12-04
Wetlands are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth. Yet with increasing urbanization and agricultural expansion, wetlands around the globe are in danger. Better mapping of wetlands worldwide will help in their protection.
But compiling globe-spanning maps of wetlands is impeded by the dramatic diversity and evolving dynamics of wetlands, and by myriad difficulties in doing field work.
To develop a better model, Gong Peng and other scientists at the State Key Laboratory of Remote Sensing Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing incorporated hydrologic, ...
Natural substance in red wine has an anti-inflammatory effect in cardiovascular diseases
2014-12-04
A natural substance present in red wine, resveratrol, inhibits the formation of inflammatory factors that trigger cardiovascular diseases. This has been established by a research team at the Department of Pharmacology of the University Medical Center of Johannes Gutenberg University of Mainz (JGU) working in collaboration with researchers of the Friedrich Schiller University in Jena and the University of Vienna. Their results have recently been published in the scientific journal Nucleic Acids Research.
Despite the fact that they eat more fatty foods, the French tend ...
Don't worry, be happy: Just go to bed earlier
2014-12-04
When you go to bed, and how long you sleep at a time, might actually make it difficult for you to stop worrying. So say Jacob Nota and Meredith Coles of Binghamton University in the US, who found that people who sleep for shorter periods of time and go to bed very late at night are often overwhelmed with more negative thoughts than those who keep more regular sleeping hours. The findings appear in Springer's journal Cognitive Therapy and Research.
People are said to have repetitive negative thinking when they have bothersome pessimistic thoughts that seem to repeat in ...
Electron pairs on demand
2014-12-04
This news release is available in German.
In quantum optics, generating entangled and spatially separated photon pairs (e.g. for quantum cryptography) is already a reality. So far, it has, however, not been possible to demonstrate an analogous generation and spatial separation of entangled electron pairs in solids. Physicists from Leibniz University Hannover and from the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB) have now taken a decisive step in this direction. They have demonstrated for the first time the on-demand emission of electron pairs from a semiconductor ...
More evidence for impact of lung cancer targeted therapy from practice-changing trial
2014-12-04
Some patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have changes in the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene, which can drive the development of their cancer. A drug recently developed by Pfizer, crizotinib, targets ALK and is currently given to patients with ALK positive lung cancer when their cancer has worsened after initial chemotherapy. Now doctors have investigated the use of crizotinib in patients with ALK positive lung cancer who have not yet received any chemotherapy treatment.
Dr Fiona Blackhall, a senior lecturer in The University of Manchester's Institute ...
When noise gets electrons moving
2014-12-04
New York | Heidelberg, 4 December 2014 Studying the motion of electrons in a disordered environment is no simple task. Often, understanding such effects requires a quantum simulator designed to expose them in a different physical setup. This was precisely the approach adopted by Denis Makarov and Leonid Kon'kov from the Victor I. Il'ichev Pacific Oceanological Institute in Vladivostok in a new study published in EPJ B. They relied on a simulator of electronic motion subjected to noise stemming from a flux of sound waves.
Their findings could lead to semi-conductor devices ...
Reliable RNA analysis now easier with NIST 'dashboard' tool
2014-12-04
A new, innovative "dashboard" from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) won't help you drive your car, but it will help enable reproducible research in biology.
In a recent paper in the journal Nature Communications,* an international multi-laboratory team demonstrates a new software tool, the "erccdashboard," to evaluate the performance of experimental methods used to study gene expression. The analysis tool is designed for use with RNA spike-in controls developed by the NIST-hosted External RNA Controls Consortium (ERCC**). These ERCC controls are ...
Thirty new spider species found in one of China's richest biodiversity hotspots
2014-12-04
Scientists from the Institute of Zoology with the Chinese Academy of Sciences have devoted years of their careers to study the astounding diversity hidden in the depths of the Xishuangbanna tropical rain forests. In a recent paper published in the open access journal ZooKeys Prof. Shuqiang Li and his team reveal 30 new spider species, which constitutes a minor share of what is yet to be found in this biodiversity hotspot.
Xishuangbanna is situated in the southern part of Yunnan with the Lancang (Mekong) River flowing through it. The region is well-known for its rich biodiversity ...
Are the benefits of breast milk stimulant worth the risk?
2014-12-04
Los Angeles, CA (Nov 4, 2014) Most women can make all the milk their baby needs, but some mothers turn to medications to help increase their supply. While some specialists encourage the off-label use of domperidone to stimulate breast milk production, some studies have suggested it may be related to negative side effects, including irregular heartbeat and sudden cardiac death. In a new article out today, researchers concluded that although domperidone can increase breast milk production, and there is no known risk to the babies who drink the milk, risks to women are still ...
Mini chromosomes that strengthen tumors
2014-12-04
Cancers are due to genetic aberrations in certain cells that gain the ability to divide indefinitely. This proliferation of sick cells generates tumors, which gradually invade healthy tissue. Therefore, current therapies essentially seek to destroy cancer cells to stop their proliferation. Through high-throughput genetic sequencing of glioblastoma cells, one of the most deadly brain tumors, a team of geneticists from the University of Geneva's (UNIGE) Faculty of Medicine discovered that some of these mutations are caused by supplemental extrachromosomal DNA fragments, called ...
Localized climate change contributed to ancient southwest depopulation
2014-12-04
PULLMAN, Wash.--Washington State University researchers have detailed the role of localized climate change in one of the great mysteries of North American archaeology: the depopulation of southwest Colorado by ancestral Pueblo people in the late 1200s.
In the process, they address one of the mysteries of modern-day climate change: How will humans react?
Writing in Nature Communications, WSU archaeologist Tim Kohler and post-doctoral researcher Kyle Bocinsky use tree-ring data, the growth requirements of traditional maize crops and a suite of computer programs to make ...
Technology breakthrough reveals cellular transcription process
2014-12-04
This news release is available in French. A new technology that reveals cellular gene transcription in greater detail has been developed by Dr. Daniel Kaufmann of the University of Montreal Hospital Research Centre (CRCHUM) and the research team he directed. "This new research tool offers us a more profound view of the immune responses that are involved in a range of diseases, such as HIV infection. At the level of gene transcription, this had been difficult, complex and costly to do with current technologies, such as microscopy," explained the University of Montreal ...
Dirt provides new insight into Roman burials
2014-12-04
The first scientific evidence of frankincense being used in Roman burial rites in Britain has been uncovered by a team of archaeological scientists led by the University of Bradford. The findings - published today in the Journal of Archaeological Science - prove that, even while the Roman Empire was in decline, these precious substances were being transported to its furthest northern outpost.
The discovery was made by carrying out molecular analysis of materials previously thought to be of little interest - debris inside burial containers and residues on skeletal remains ...
Preliminary study suggests Parkinson's drugs safe for the heart
2014-12-04
Vienna, Austria - 04 December 2014: Non-ergot derived dopamine agonists used to treat Parkinson's disease may be safe for the heart, according to preliminary research presented at EuroEcho-Imaging 2014 by Dr Hilal Erken Pamukcu, cardiologist at Ankara Diskapi Education and Research Hospital in Turkey.
EuroEcho-Imaging is the annual meeting of the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), and is held 3-6 December in Vienna, Austria.
Dr Erken Pamukcu said: "Parkinson's disease is a neurological ...
Medications for patients with first episode psychosis may not meet guidelines
2014-12-04
Many patients with first-episode psychosis receive medications that do not comply with recommended guidelines for first-episode treatment, researchers have found. Current guidelines emphasize low doses of antipsychotic drugs and strategies for minimizing the side effects that might contribute to patients stopping their medication. A study finds that almost 40 percent of people with first-episode psychosis in community mental health clinics across the country might benefit from medication treatment changes.
Psychosis is a mental disorder in which thoughts and emotions ...
Cancer from asbestos caused by more than one cell mutation
2014-12-04
It has been a long held belief that tumors arising from exposure to asbestos are caused by mutations in one cell, which then produces multiple clones. This hypothesis is challenged by new research published in the open access Journal of Translational Medicine, which suggests it is caused by mutations in multiple cells.
Malignant mesothelioma is a rare form of cancer that affects the mesothelium - the protective lining that covers the internal organs, such as the lungs, the heart and the abdominal cavity. It is estimated that malignant mesothelioma affects up to 3,200 ...
No link found between bladder cancer and use of pioglitazone or rosiglitazone, Avandia
2014-12-04
Some previous studies have linked the diabetes medication pioglitazone to bladder cancer. However a new study − including more than one million people in six populations worldwide − has found no link between either pioglitazone or rosiglitazone (also known as Avandia) and bladder cancer. The new study is published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes), and is by Dr Samira Bell, Professor Helen Colhoun and Mr Danny Levin, University of Dundee, UK, and colleagues from the International Diabetes and Cancer Research ...
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine: Current guidelines not clear on which children most at risk of severe flu complications
2014-12-04
Children born prematurely are at an increased risk of flu-related complications, despite not being identified as an "at risk" group in UK, USA, or WHO guidelines, and should be a priority group for the seasonal flu vaccination, new research published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine suggests.
"Until now, guidelines highlighting groups at greater risk of developing complications from influenza, such as pneumonia, have been based on consensus opinion rather than on systematic assessment of the evidence"*, explains Dr Kay Wang from the University of Oxford in the UK. ...
NIH researchers link chromosome region to duplication of gene on X chromosome appears to cause excessive growth
2014-12-04
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health have found a duplication of a short stretch of the X chromosome in some people with a rare disorder that causes excessive childhood growth. They believe that a single gene within the region likely has a large influence on how much children grow. The research comes from a lab at NIH's Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), which seeks to understand growth.
"Finding the gene responsible for childhood overgrowth would be very helpful, but the much wider question is what ...
Buckyballs enhance carbon capture
2014-12-04
HOUSTON - (Dec. 3, 2014) - Rice University scientists have discovered an environmentally friendly carbon-capture method that could be equally adept at drawing carbon dioxide emissions from industrial flue gases and natural gas wells.
The Rice lab of chemist Andrew Barron revealed in a proof-of-concept study that amine-rich compounds are highly effective at capturing the greenhouse gas when combined with carbon-60 molecules.
The research is the subject of an open-access paper today in Nature's online journal Scientific Reports.
"We had two goals," Barron said. "One ...
Longer surgery duration associated with increased risk for blood clots
2014-12-03
The longer surgery lasts the more prone patients appear to be to develop blood clots (venous thromboembolisms, VTE), according to a report published online by JAMA Surgery.
The association between longer surgical procedures and death, including VTE, is widely accepted but it has yet to be quantitatively addressed. More than 500,000 hospitalizations and 100,000 deaths are associated each year with VTEs. Examining the link between VTE and surgical time could allow for more informed medical and surgical decisions, according to the study background.
John Y.S. Kim, M.D., ...
Higher blood clot risk in longer surgeries
2014-12-03
CHICAGO --- The longer the duration of surgery, the higher the risk of a life-threatening blood clot, according to the first large-scale, quantitative national study of the risk across all surgical procedures.
The Northwestern Medicine study was published Dec. 3 in JAMA Surgery, the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The finding will help guide surgical decision-making by enabling surgeons and patients to better understand the potential risk of procedures. These findings may also spur surgeons to take more aggressive preventative measures such as giving ...
Ever tried a 'laser delicious' apple?
2014-12-03
WASHINGTON, Dec. 3, 2014--The ability to detect when to harvest "climacteric" fruits -- such as apples, bananas, pears and tomatoes -- at the precise moment to ensure "peak edibleness" in terms of both taste and texture may soon be within reach for farmers, thanks to the work of a team of researchers from Saint Joseph University in Lebanon and the Université de Bretagne Occidentale de Brest in France.
As the team reports in a paper published in The Optical Society's (OSA) journal Applied Optics, they recently demonstrated a laser biospeckle technique capable of detecting ...
Study discovers RX approach that reduces herpes virus infection
2014-12-03
New Orleans, LA - A multi-institutional study reports an effective treatment approach to inhibit and keep latent viruses like herpes simplex from reactivating and causing disease. The work, whose lead author is the late James Hill, PhD, LSU Health New Orleans Professor and Director of Pharmacology and Infectious Disease at the LSU Eye Center, is published in the December 3, 2014, issue of Science Translational Medicine.
The research team, led by Thomas M. Kristie, PhD, Chief of the Molecular Genetics Section in the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases' ...
[1] ... [3149]
[3150]
[3151]
[3152]
[3153]
[3154]
[3155]
[3156]
3157
[3158]
[3159]
[3160]
[3161]
[3162]
[3163]
[3164]
[3165]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.