King Richard III -- case closed after 529 years
2014-12-02
International research led by the University of Leicester published in Nature Communications reveals:
Analysis of all the available evidence confirms identity of King Richard III to the point of 99.999% (at its most conservative).
Analysis of the mitochondrial DNA shows a match between Richard III and modern female-line relatives, Michael Ibsen and Wendy Duldig.
The male line of descent is broken at one or more points in the line between Richard III and living male-line relatives descended from Henry Somerset, 5th Duke of Beaufort.
King Richard was almost certainly ...
Chemists fabricate novel rewritable paper
2014-12-02
RIVERSIDE, Calif. - First developed in China in about the year A.D. 150, paper has many uses, the most common being for writing and printing upon. Indeed, the development and spread of civilization owes much to paper's use as writing material.
According to some surveys, 90 percent of all information in businesses today is retained on paper, even though the bulk of this printed paper is discarded after just one-time use.
Such waste of paper (and ink cartridges)--not to mention the accompanying environmental problems such as deforestation and chemical pollution to air, ...
Health boost for fitness centers
2014-12-02
Health is high on the agenda in many countries with efforts to get more people exercising in order to reduce the problems associated with obesity, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Unfortunately, risk assessment is inadequate in terms of sports facilities and many fitness programs rely on the participants taking out insurance and signing legal waivers rather than their being taught safe practices and given a safe environment in which to exercise.
Writing in the International Journal of Business Continuity and Risk Management, Betul Sekendiz, School ...
Traces of Martian biological activity could be locked inside a meteorite
2014-12-02
This news release is available in French.
"So far, there is no other theory that we find more compelling," says Philippe Gillet, director of EPFL's Earth and Planetary Sciences Laboratory. He and his colleagues from China, Japan and Germany performed a detailed analysis of organic carbon traces from a Martian meteorite, and have concluded that they have a very probable biological origin. The scientists argue that carbon could have been deposited into the fissures of the rock when it was still on Mars by the infiltration of fluid that was rich in organic matter.
Ejected ...
Crime Victims' Institute investigates human trafficking
2014-12-02
HUNTSVILLE, TX 12/2/14 -- Human sex trafficking is a serious problem both domestically and internationally and enhanced education is necessary to address the risk factors for entry into the sex trade, the physical and mental health consequences of victimization, and institutional responses to victims, according to a new series published by the Crime Victims' Institute at Sam Houston State University.
"Human Sex Trafficking: An Overview" by Lindsay Ashworth and Cortney Franklin, Ph.D., reports that estimates on prevalence of sex trafficking victims are difficult to establish ...
Meteorology meets metrology: Climate research high up in the clouds
2014-12-02
This news release is available in German.
Barely has the research aircraft HALO entered the kilometre-high clouds towering above the Brazilian rainforest than the researchers find themselves in a complete haze, but they can rely on the measuring instruments that are working at full capacity. HAI - a new, highly accurate hygrometer of the German National Metrological Institute PTB - is aboard. The shooting star among hygrometers has been developed only recently by metrologists (metrology = the science of measurement) especially for use on board aircraft and in the ...
Combination of autism spectrum disorder and gender nonconformity presents unique challenges
2014-12-02
New Rochelle, NY, December 2, 2014--The challenges in providing psychotherapy to individuals with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) who also are struggling with their gender identity are explored in two case studies of high-functioning persons with diagnoses of ASD and gender dysphoria (GD). The authors describe the unique complexities presented by these two diagnoses and offer suggested techniques for helping these individuals explore their gender identities in an article in LGBT Health, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available ...
Fighting air pollution in China with social media
2014-12-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio - The serious air pollution problem in China has attracted the attention of online activists who want the government to take action, but their advocacy has had only limited success, a new study has revealed.
Instead, much of the online conversation has been co-opted by corporations wanting to sell masks, filters and other products and by government officials advancing its own environmental narrative, the study finds.
Researchers at The Ohio State University analyzed about 250,000 posts on the Chinese social media site Sina Weibo (similar to Twitter) that ...
See it, touch it, feel it
2014-12-02
Technology has changed rapidly over the last few years with touch feedback, known as haptics, being used in entertainment, rehabilitation and even surgical training. New research, using ultrasound, has developed an invisible 3D haptic shape that can be seen and felt.
The research paper, published in the current issue of ACM Transactions on Graphics and which will be presented at this week's SIGGRAPH Asia 2014 conference [3-6 December], demonstrates how a method has been created to produce 3D shapes that can be felt in mid-air.
The research, led by Dr Ben Long and ...
New research shows parents play vital role in molding future scientists
2014-12-02
Parents and family make all the difference in creating the next generation of scientists, engineers and mathematicians, according to new research by George Mason University.
"We were surprised to learn that the family is more important than we ever thought in terms of igniting the passion of future scientists," says Lance Liotta, a study author and co-director of George Mason's Center for Applied Proteomics and Molecular Medicine.
The study, featured in CBE-Life Sciences Education, is the first peer-reviewed article of its kind to focus on what initially attracts young ...
New techniques for estimating Atlantic bluefin tuna reproduction
2014-12-02
AMHERST, Mass. - Using a new approach for determining the age at sexual maturity for wild stocks of western Atlantic bluefin tuna, researchers led by Molly Lutcavage of the University of Massachusetts Amherst and Gilad Heinisch of Israel's Oceanographic and Limnological Research Center, suggest that these fish mature at a considerably younger age than cuurently assumed. These findings could lead to changes in how fisheries scientists estimate the population.
Lutcavage says, "Whether a bluefin tuna or cod, for realistic fish stock assessments it's important to know at ...
E-signatures less trusted than handwritten signatures
2014-12-02
December 2, 2014 - Now you don't even have live in Estonia to open a business there. A new program lets people purchase e-signatures that enable them to open bank accounts and run a domestic business without being physically present. But according to new research, people may not have the same trust in such businesses as they would others. A new paper finds that people are much more likely to discount the validity of an e-signature than a hand-signed document.
"Although e-signatures provide greater efficiency and convenience, they just seem a bit inauthentic," says Eileen ...
Researchers recreate stem cells from deceased patients to study present-day illnesses
2014-12-02
LOS ANGELES (Dec. 1, 2014) - Research scientists have developed a novel method to re-create brain and intestinal stem cells from patients who died decades ago, using DNA from stored blood samples to study the potential causes of debilitating illnesses such as inflammatory bowel disease.
The lab research, published in the journal STEM CELLS Translational Medicine, could yield new therapies for people who suffer from aggressive motor-neuron and gut-related conditions that proved fatal to the deceased patients who long-ago volunteered their blood samples.
"The potential ...
Prognostic role found for miR-21 expression in triple-negative breast cancer
2014-12-02
Philadelphia, PA, December 1, 2014 - "Triple-negative" breast cancer (TNBC) occurs in patients whose cells do not express receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and/or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (ER/PR/HER2). Because of the absence of these predictive biomarkers, treatment assignment can be difficult. Now, researchers report that high levels of the microRNA miR-21 in the tumor microenvironment, but not in the tumor epithelia (cancer cells), are associated with worse clinical outcomes for patients with TNBC, thus identifying a possible ...
Stressed-out cancers may provide drug target
2014-12-02
Research at the University of Adelaide has discovered cancer cells may be particularly susceptible to metabolic stress - opening the way for new targeted therapy that won't harm normal cells.
The researchers showed that chromosomal instability - which is a hallmark of rapidly dividing cancer cells - makes them stressed and vulnerable to mild metabolic disruption. Metabolism is the normal process by which the body turns food into energy.
"A common problem in treating cancers is that they don't respond to chemotherapy, or they respond for a while, but then come back," ...
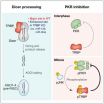
Protein kinase R and dsRNAs, new regulators of mammalian cell division
2014-12-02
The research team of the Center for RNA Research at IBS has succeeded in revealing that the dsRNAs and Protein Kinase R (PKR) regulate division of mammalian cells.
This finding will provide important clues to understanding the process of tumor formation and the mechanism for suppressing cancer since the abnormal cell division marks the early events of cancer development.
For the first time, the IBS research team has found that during mitosis, the cellular dsRNAs activate PKR, an enzyme previously known as a trigger of immune response during virus infection. Activated ...
Inflammatory discovery sheds new light on skin disease
2014-12-02
Inflammatory skin diseases such as psoriasis may result from abnormal activation of cell death pathways previously believed to suppress inflammation, a surprise finding that could help to develop new ways of treating these diseases.
Mr James Rickard, Associate Professor John Silke and colleagues from the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute made the discovery while investigating how cell death pathways are linked to inflammatory disease development. The study was published today in the journal eLife.
Infected cells, cancerous cells, or those that are simply unnecessary to ...
Vitamin D deficiency, depression linked in international study
2014-12-02
Vitamin D deficiency is not just harmful to physical health--it also might impact mental health, according to a team of researchers that has found a link between seasonal affective disorder, or SAD, and a lack of sunlight.
"Rather than being one of many factors, vitamin D could have a regulative role in the development of SAD," said Alan Stewart of the University of Georgia College of Education.
An international research partnership between UGA, the University of Pittsburgh and the Queensland University of Technology in Australia reported the finding in the November ...
Cover crops can sequester soil organic carbon
2014-12-02
URBANA, Ill. - A 12-year University of Illinois study shows that, although the use of cover crops does not improve crop yields, the practice does increase the amount of sequestered soil organic carbon using three different soil management systems.
U of I soil scientist Ken Olson evaluated plots that were subjected to no-till, chisel plow and moldboard plow treatments with and without hairy vetch and cereal rye cover crops.
"By 2012, we found that the soil tillage plots that had cover-crop treatments had more soil organic carbon stock than those without cover crops ...
Triple-negative breast cancer patients should undergo genetic screening: Mayo Clinic
2014-12-02
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Most patients with triple-negative breast cancer should undergo genetic testing for mutations in known breast cancer predisposition genes, including BRCA1 and BRCA2, a Mayo Clinic-led study has found. The findings come from the largest analysis to date of genetic mutations in this aggressive form of breast cancer. The results of the research appear in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
"Clinicians need to think hard about screening all their triple-negative patients for mutations because there is a lot of value in learning that information, both in ...
Identifying the cellular origin of fibrosis
2014-12-02
Researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) have identified what they believe to be the cells responsible for fibrosis, the buildup of scar tissue. Fibrotic diseases, such as chronic kidney disease and failure, lung disease, heart failure and cirrhosis of the liver, are estimated to be responsible for up to 45 percent of deaths in the developed world.
The findings are published online in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
"Previous research indicated that myofibroblasts are the cells responsible for fibrosis," said Benjamin Humphreys, MD, PhD, senior author of ...
Nutrition, safety key to consumer acceptance of nanotech, genetic modification in foods
2014-12-02
New research from North Carolina State University and the University of Minnesota shows that the majority of consumers will accept the presence of nanotechnology or genetic modification (GM) technology in foods - but only if the technology enhances the nutrition or improves the safety of the food.
"In general, people are willing to pay more to avoid GM or nanotech in foods, and people were more averse to GM tech than to nanotech," says Dr. Jennifer Kuzma, senior author of a paper on the research and co-director of the Genetic Engineering in Society Center at NC State. ...
Celiac disease does not increase clinical consultations for fertility problems
2014-12-02
Bethesda, MD (Dec. 2, 2014) -- Women with celiac disease present with fertility problems no more often than women in the general population, according to a new study in Gastroenterology1, the official journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Despite inconsistent findings from small studies, concern has been raised that celiac disease may cause infertility," said lead study author Nafeesa N. Dhalwani, PhD, from the University of Nottingham, United Kingdom. "Celiac patients should rest assured; our findings indicate that women with celiac disease do not ...
Researchers control adhesion of E. coli bacteria
2014-12-02
A research team from Kiel University (CAU) and Goethe University Frankfurt has jointly created a synthetic surface on which the adhesion of E. coli bacteria can be controlled. The layer, which is only approximately four nanometres thick, imitates the saccharide coating (glycocalyx) of cells onto which the bacteria adhere such as during an infection. This docking process can be switched on and off using light. This means that the scientists have now made an important step towards understanding the relationship between sugar (carbohydrates) and bacterial infections. Their ...
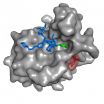
Tailor-made pharmaceuticals as basis for novel antidepressants
2014-12-02
This news release is available in German.
The FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51) is an established risk factor for stress-related psychiatric disorders such as major depression. Drug discovery for FKBP51 has been hampered by the inability to pharmacologically differentiate against the very similar functional counterplayer FKBP52. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry in Munich have now developed the first potent and highly selective inhibitor of FKBP51. The so-called SAFit-ligand inhibits FKBP51 enhancing growth of neuronal cell cultures and improving ...
[1] ... [3156]
[3157]
[3158]
[3159]
[3160]
[3161]
[3162]
[3163]
3164
[3165]
[3166]
[3167]
[3168]
[3169]
[3170]
[3171]
[3172]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.