X-ray laser acts as tool to track life's chemistry
2014-12-08
An international research team that includes researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has captured the highest-resolution protein snapshots ever taken with an X-ray laser, revealing how a key protein in a photosynthetic bacterium changes shape when hit by light.
Human biology is a massive collection of chemical reactions and all involve proteins, known as the molecules of life. Scientists have been moving steadily toward their ultimate goal of following these life-essential reactions step by step in real time, at the scale of atoms and electrons.
"These ...
Novel strategies direct immune system to attack recurrent, hard-to-treat blood cancers
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - Novel treatments that harness the body's own immune cells to attack cancer cells demonstrate safe and durable responses in patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant blood cancers, according to data presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Therapies designed to target the immune system and ignite the body's own disease-fighting mechanisms have become an increasingly promising field of study, particularly in blood cancers. While the immune system can easily recognize viruses ...
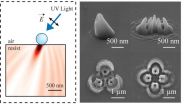
New technique allows low-cost creation of 3-D nanostructures
2014-12-08
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new lithography technique that uses nanoscale spheres to create three-dimensional (3-D) structures with biomedical, electronic and photonic applications. The new technique is significantly less expensive than conventional methods and does not rely on stacking two-dimensional (2-D) patterns to create 3-D structures.
"Our approach reduces the cost of nanolithography to the point where it could be done in your garage," says Dr. Chih-Hao Chang, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering ...
Cell division induces tissue ordering
2014-12-08
Nature's ingenious systems: A layer of cells called endothelial cells lines the interior of blood vessels. When blood flows through the vessels, such cells only divide to replace dead cells. However, if there is a blood clot preventing blood from flowing across the endothelial cells, they begin to divide more actively. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates that cell division is very ordered. The new cells move away from each other and create a dynamic movement with eddies in a large area. This presumably helps to widen the vessel around the blockage. The ...
Study finds early warning signals of abrupt climate change
2014-12-08
A new study by researchers at the University of Exeter has found early warning signals of a reorganisation of the Atlantic oceans' circulation which could have a profound impact on the global climate system.
The research, published today in the journal Nature Communications, used a simulation from a highly complex model to analyse the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), an important component of the Earth's climate system.
It showed that early warning signals are present up to 250 years before it collapses, suggesting that scientists could monitor ...
Scientists pinpoint a new line of defence used by cancer cells
2014-12-08
Cancer Research UK scientists have discovered a new line of defence used by cancer cells to evade cell death, according to research published in Nature Communications* today (Monday).
The team identified a critical pathway of molecular signals which throw a lifeline to cancer cells, enabling them to survive even though they contain vast DNA errors which would usually trigger cell death.
The PKCƐ signal pathway**, which is used by cancer cells but rarely by normal cells, could be important in targeting some cancer cells as they rely on this pathway to survive.
The ...
Unusual electronic state found in new class of unconventional superconductors
2014-12-08
UPTON, NY-A team of scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, Columbia Engineering, Columbia Physics and Kyoto University has discovered an unusual form of electronic order in a new family of unconventional superconductors. The finding, described in the journal Nature Communications, establishes an unexpected connection between this new group of titanium-oxypnictide superconductors and the more familiar cuprates and iron-pnictides, providing scientists with a whole new family of materials from which they can gain deeper insights ...
Most elderly women with early stage breast cancer receive a treatment that may not be as effective
2014-12-08
A new analysis has found that while clinical trial data support omitting radiation treatments in elderly women with early stage breast cancer, nearly two-thirds of these women continue to receive it. The findings are published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Results published in 2004 from a large, randomized clinical trial showed that adding radiation therapy to surgery plus tamoxifen does not reduce 5-year recurrence rates or prolong survival in elderly women with early stage tumors. Despite the findings, many doctors still ...
Older breast cancer patients still get radiation despite limited benefit
2014-12-08
DURHAM, N.C. - Women over the age of 70 who have certain early-stage breast cancers overwhelmingly receive radiation therapy despite published evidence that the treatment has limited benefit, researchers at Duke Medicine report.
The study suggests that doctors and patients may find it difficult to withhold treatment previously considered standard of care, even in the setting of high quality data demonstrating that the advantages are small.
"The onus is on physicians to critically analyze data to shape our treatment recommendations for patients, weighing the potential ...
Scientists reveal parchment's hidden stories
2014-12-08
Dublin, IRELAND Monday December 8th, 2014 - Millions of documents stored in archives could provide scientists with the key to tracing agricultural development across the centuries, according to new research completed at Trinity College Dublin and the University of York.
Amazingly, thanks to increasingly progressive genetic sequencing techniques, the all-important historical tales these documents tell are no longer confined to their texts; now, vital information also comes from the DNA of the parchment on which they are written.
Researchers used these state-of-the-art ...
Correcting metabolic abnormalities may help lessen urinary problems
2014-12-08
Metabolic syndrome is linked with an increased frequency and severity of lower urinary tract symptoms, but weight loss surgery may lessen these symptoms. The findings, which come from two studies published in BJU International, indicate that urinary problems may be added to the list of issues that can improve with efforts that address altered metabolism.
Lower urinary tract symptoms related to urinary frequency and urgency, bladder leakage, the need to urinate at night, and incomplete bladder emptying are associated with obesity in both men and women. To see if these ...
Dartmouth/Univ. of Exeter Study: Correcting myths about the flu vaccine
2014-12-08
HANOVER, N.H. - December 8, 2014 - With health systems in the U.S., U.K., and around the world trying to increase vaccination levels, it is critical to understand how to address vaccine hesitancy and counter myths about vaccine safety. A new article in the journal "Vaccine" concludes, however, that correcting myths about vaccines may not be the most effective approach to promoting immunization among vaccine skeptics. The study, which was co-authored by Brendan Nyhan, an assistant professor of government at Dartmouth College, and Jason Reifler, a senior lecturer of politics ...
Penn researchers announce latest results of investigational cellular therapy
2014-12-08
SAN FRANCISCO - The latest results of clinical trials of more than 125 patients testing an investigational personalized cellular therapy known as CTL019 will be presented by a University of Pennsylvania research team at the 56th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition. Highlights of the new trial results will include a response rate of more than 90 percent among pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, and results from the first lymphoma trials testing the approach, including a 100 percent response rate among follicular lymphoma patients and ...
Narrow subset of cells is responsible for metastasis in multiple myeloma, study finds
2014-12-08
Although it is among the most highly metastatic of all cancers, multiple myeloma is driven to spread by only a subset of the myeloma cells within a patient's body, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have found in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
The study suggests that attacking those subsets with targeted drugs may degrade the disease's ability to spread throughout the bone marrow of affected patients, the authors say.
The discovery was made by developing a mouse model of the disease that enabled researchers ...
Oral inhibitor shows clinical activity in poor-prognosis AML
2014-12-08
An oral targeted drug has shown encouraging activity and tolerable side effects in patients with treatment-resistant or relapsed acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) - a poor-prognosis group with few options - report investigators from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.
Of 32 patients treated with the oral inhibitor ABT-199, five had eradication of their leukemia and several more had stable disease, according to Anthony Letai, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber, senior author of the report.
The phase 2 multicenter trial was the first ...
Combination therapy shown as effective for higher-risk MDS/AML patients
2014-12-08
A phase two study that investigated the potential of the drugs azacitidine (AZA) and lenalidomide (LEN), demonstrated that the two therapies in combination may be an effective frontline treatment regimen for patients with higher-risk forms of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia.
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow does not make enough healthy blood cells, resulting in abnormal (blast) cells in the blood and/or bone marrow. Higher-risk patients experience an unusually large percentage of blasts in their blood. Patients ...
New study identifies first gene associated with familial glioma
2014-12-07
HOUSTON - (Dec. 7, 2014) - An international consortium of researchers led by Baylor College of Medicine has identified for the first time a gene associated with familial glioma (brain tumors that appear in two or more members of the same family) providing new support that certain people may be genetically predisposed to the disease.
"It is widely thought amongst the clinical community that there is no association between family history and development of glioma. Because we know very little about the contributing genetic factors, when cases occur in two or more family ...
Study shows improved survival in aggressive acute myeloid leukemia
2014-12-07
Patients who relapse in their battle with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) may benefit from a phase three study of therapies that combine an existing agent, cytarabine, with a newer compound, vosaroxin.
The study, led by Farhad Ravandi, M.D, professor of medicine, department of leukemia at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, demonstrated increased survival rates, particularly in AML patients over age 60.
Ravandi's study results were presented today at the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) annual conference in San Francisco and ...
Young adults with ALL benefit from therapies developed for children
2014-12-07
Results from a large, prospective clinical trial add to mounting evidence that adolescent and young adult patients--aged 16 to 39 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)--tend to fare better when treated with high-intensity pediatric protocols than previous patients who were treated with standard adult regimens.
The intergroup trial, presented at the 56th annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, enrolled 296 adolescent and young adult patients with ALL. All participants were treated by adult hematologists-oncologists on a pediatric protocol, including four ...
Stem cell transplant without radiation or chemotherapy pre-treatment shows promise
2014-12-07
SAN FRANCISCO (DECEMBER 7, 2014) - Researchers at Dana-Farber/Boston Children's Cancer and Blood Disorders Center report promising outcomes from a clinical trial with patients with a rare form of bone marrow failure who received a hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) after pre-treatment with immunosuppressive drugs only. This is the first trial reporting successful transplant in dyskeratosis congenita (DC) patients without the use of any radiation or conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy beforehand.
The trial's data were presented by study authors Leslie Lehmann, MD, ...
Novel combinations yield promising results for leukemia patients with poor prognoses
2014-12-07
(SAN FRANCISCO, DECEMBER 7, 2014) - Recognizing that leukemia cannot be conquered with a "one-size-fits-all" approach, researchers are pursuing novel targeted therapies and combinations of existing treatment regimens with new agents for patient populations with historically poor prognoses, according to data presented today during the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
In recent years, outcomes for patients with leukemia have steadily improved with the emergence of numerous therapies that target specific genetic drivers of disease, ...
Study shows new kind of targeted drug has promise for leukemia patients
2014-12-07
SAN FRANCISCO, CA, December 7, 2014--A new type of cancer therapy that targets an oncometabolite produced dramatic results in patients with advanced leukemia in an early-phase clinical trial. The study, led by Eytan M. Stein, MD, a medical oncologist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, was presented today at the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Approximately 15 percent of acute myeloid leukemia patients have a mutated form of the IDH2 gene. IDH2 normally makes a protein that plays a critical role in cell metabolism. However, when the gene ...
In world first -- UNSW researchers convert sunlight to electricity with over 40 percent efficiency
2014-12-07
UNSW Australia's solar researchers have converted over 40% of the sunlight hitting a solar system into electricity, the highest efficiency ever reported.
The record efficiency was achieved in outdoor tests in Sydney, before being independently confirmed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) at their outdoor test facility in the United States.
The work was funded by the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) and supported by the Australia-US Institute for Advanced Photovoltaics (AUSIAPV).
"This is the highest efficiency ever reported for sunlight conversion ...
Circulating RNA may provide prognostic tool for multiple myeloma
2014-12-07
The "molecular mail" sent by multiple myeloma cells provides clues to how well patients with the disease are likely to respond to treatment, according to a study being presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) by researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
The findings - to be presented in poster form on December 6, from 5:30 PM to 7:30 PM, in the West Building, Level 1 - may ultimately guide doctors in deciding which therapies are best for individual patients with myeloma, the study authors say.
The study focused on ...
Benefits persist in T cell therapy for children with relapsed leukemia
2014-12-06
An innovative cell therapy against a highly aggressive form of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) continues to show highly promising results in children treated in a pilot study. Ninety-two percent of the 39 children receiving bioengineered T cells had no evidence of cancer at one month after treatment, with this complete response persisting in some cases for more than two years. The personalized cell therapy reprograms a patient's immune system and offers the potential of long-term success.
"As we continue to follow children in this study, we see exciting results for ...
[1] ... [3143]
[3144]
[3145]
[3146]
[3147]
[3148]
[3149]
[3150]
3151
[3152]
[3153]
[3154]
[3155]
[3156]
[3157]
[3158]
[3159]
... [8824]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.