Penn study: Sepsis patients fare better in hospitals with higher case volumes
2014-09-03
PHILADELPHIA – Patients with sepsis, one of the most time-sensitive and hard-to-detect illnesses in medicine, are more likely to survive the life-threatening condition when treated at a hospital that sees a higher volume of sepsis cases. New research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania shows a clear relationship between hospitals that treat the most cases of severe sepsis and lower rates of inpatient deaths among those patients. The study, led by David F. Gaieski, MD, an associate professor of Emergency Medicine at Penn, is published online ...
Pesticide risk assessments seen as biased
2014-09-03
In the October issue of BioScience, a group of ecotoxicologists argue that the US Environmental Protection Agency's (USEPA) current practices for evaluating pesticide safety are inadequate and likely to result in decisions biased toward industry interests.
In their article, Michelle Boone of Miami University and her colleagues note that most pesticide toxicity tests used in risk assessments are conducted by pesticide manufacturers themselves, which the authors believe can result in untenable conflicts of interest. Moreover, rigid inclusion criteria often mean that potentially ...
Seizures and sudden death: When SUMO 'wrestles' potassium channels
2014-09-03
A gene crucial for brain and heart development may also be associated with sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP), the most common cause of early mortality in epilepsy patients.
Scientists at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have created a new animal model for SUDEP and have shown that mice who have a partial deficiency of the gene SENP2 (Sentrin/SUMO-specific protease 2) are more likely to develop spontaneous seizures and sudden death. The finding occurred when observing mice originally bred for studying a link between SENP2 deficiency and cancer.
"SENP2 ...
Researchers unlock new mechanism in pain management
2014-09-03
It's in the brain where we perceive the unpleasant sensations of pain, and researchers have long been examining how calcium channels in the brain and peripheral nervous system contribute to the development of chronic pain conditions.
Neuroscientist Gerald Zamponi, PhD, and his team at the University of Calgary's Hotchkiss Brain Institute have discovered a new mechanism that can reverse chronic pain. Using an animal model, their research has found that pain signals in nerve cells can be shut off by interfering with the communication of a specific enzyme with calcium ...
Changing temperature powers sensors in hard-to-reach places
2014-09-03
A centuries-old clock built for a king is the inspiration for a group of computer scientists and electrical engineers who hope to harvest power from the air.
The clock, powered by changes in temperature and atmospheric pressure, was invented in the early 17th century by a Dutch builder. Three centuries later, Swiss engineer Jean Leon Reutter built on that idea and created the Atmos mechanical clock that can run for years without needing to be wound manually.
Now, University of Washington researchers have taken inspiration from the clock's design and created a power ...
Tweets during 2013 Colorado floods gave engineers valuable data on infrastructure damage
2014-09-03
Tweets sent during last year's massive flooding on Colorado's Front Range were able to detail the scope of damage to the area's infrastructure, according to a study by the University of Colorado Boulder.
The findings can help geotechnical and structural engineers more effectively direct their reconnaissance efforts after future natural disasters—including earthquakes, tsunamis and tornadoes—as well as provide them data that might otherwise be lost due to rapid cleanup efforts.
"Because the flooding was widespread, it impacted many canyons and closed off access to communities ...
Galapagos invasion is global warning
2014-09-03
A new study led by a PhD researcher at The University of Western Australia has revealed that parts of the iconic Galapagos Islands have been overrun by invasive plants from other parts of the world.
"People may be shocked that a place considered so iconic for biodiversity is so overrun with weeds in some areas despite ongoing control effort by National Park rangers, but this is really a global story," lead author from the UWA School of Plant Biology Mandy Trueman said.
The results published in the open access journal Neobiota confirm that in the humid highland part ...
Peptoid nanosheets at the oil-water interface
2014-09-03
From the people who brought us peptoid nanosheets that form at the interface between air and water, now come peptoid nanosheets that form at the interface between oil and water. Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed peptoid nanosheets - two-dimensional biomimetic materials with customizable properties - that self-assemble at an oil-water interface. This new development opens the door to designing peptoid nanosheets of increasing structural complexity and chemical functionality for a broad ...
How well does bariatric surgery work?
2014-09-03
SEATTLE—The number of bariatric surgeries done each year in the United States has ballooned. Now, in an August 27 state-of-the-art review in The BMJ and a September 3 editorial in JAMA, David Arterburn, MD, MPH, weighs the evidence on the benefits and risks of the various types of this surgery.
"It's critical that we find effective—and cost-effective—ways to treat severe obesity," said Dr. Arterburn, an associate investigator at Group Health Research Institute, a Group Health physician, and an affiliate associate professor of medicine at the University of Washington School ...
Are human breast milk microbiomes 'neutral'?
2014-09-03
Human breast milk is considered the most ideal source of nutrition for infants and it should have played a critical role in the evolution and civilizations of human beings. Unlike our intuitive perception, human milk contains a large number of bacterial species, including some opportunistic pathogens of humans. This phenomenon comes as no surprise to scientists and physicians.
Indeed, the existence of milk microbiome is considered to be the result of co-evolutionary and co-adaptive interactions between the microbiome and human host. Furthermore, the dynamic balance in ...
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine: Household air pollution puts more than 1 in 3 people worldwide at risk of ill health and early death
2014-09-03
Household air pollution, caused by the use of plant-based or coal fuel for cooking, heating, and lighting, is putting nearly three billion people worldwide at risk of ill health and early death, according to a new Commission, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal.
A third of the world's population use plant-based solid fuels such as wood or charcoal, or coal, to cook, heat, and light their homes, primarily in Asia and Africa. These smoky, dirty fuels are often used in an open fire or simple stove, resulting in high levels of household air pollution in poorly ...
Researchers reveal carbon emissions of PlayStation 3 game distribution
2014-09-03
It's not always true that digital distribution of media will have lower carbon emissions than distribution by physical means, at least when file sizes are large.
That's the conclusion of a study published in Yale's Journal of Industrial Ecology that looked at the carbon footprint of games for consoles such as PlayStation®3. Researchers found that Blu-ray Discs delivered via retail stores caused lower greenhouse gas emissions than game files downloaded over broadband Internet. For their analysis, the investigators estimated total carbon equivalent emissions for an 8.8-gigabyte ...
'Prepped' by tumor cells, lymphatic cells encourage breast cancer cells to spread
2014-09-03
Breast cancer cells can lay the groundwork for their own spread throughout the body by coaxing cells within lymphatic vessels to send out tumor-welcoming signals, according to a new report by Johns Hopkins scientists.
Writing in the Sept. 2 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe animal and cell-culture experiments that show increased levels of so-called signaling molecules released by breast cancer cells. These molecules cause lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in the lungs and lymph nodes to produce proteins called CCL5 and VEGF. CCL5 attracts tumor ...
Exposure of pregnant women to certain phenols may disrupt the growth of boys
2014-09-03
A research consortium bringing together teams from Inserm, the Nancy and Poitiers University Hospitals, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, USA), and coordinated by the Inserm and University of Grenoble Environmental Epidemiology team (Unit 823), has just published an epidemiological study indicating that exposure to certain phenols during pregnancy, especially parabens and triclosan, may disrupt growth of boys during foetal growth and the first years of life. Bisphenol A was not associated with any definite modification in growth. These results ...
Survey: Number of Texans without health insurance drops under Affordable Care Act
2014-09-03
HOUSTON – (Sept. 3, 2014) – The percentage of Texans without health insurance dropped after the first enrollment period of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), according to a report released today by the Episcopal Health Foundation and Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy.
The report found that since the opening of the ACA's Health Insurance Marketplace, the percentage of uninsured adult Texans dropped by a little more than 2 percent. The report estimates 378,000 more Texans had health insurance in June 2014 than in September 2013.
The small gain in Texans ...
Tree frogs speed up their life cycle when becoming lunch
2014-09-03
Think again if you've always believed that events in the life cycle of animals happen consistently, almost rigidly, as part of the natural rhythm of nature. Studies by Sinlan Poo and David Bickford of the National University of Singapore, Singapore, show that Mother Nature is much more flexible than you might think. In a paper in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, the researchers describe how Hansen's tree frog (Chiromantis hansenae) speeds up its life cycle to hatch earlier once its eggs are preyed upon.
Hansen's tree frog is found in Thailand and ...
UTHealth researchers gain insights into severe form of dwarfism
2014-09-03
HOUSTON – (Sept. 3, 2014) – A better understanding of the pathology of a severe form of dwarfism as well as a possible window of treatment have been discovered by researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The preclinical research was published in a recent issue of the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH) is a disorder that affects the cells in the growth plate, resulting in dwarfism, limb deformities, joint pain and early onset osteoarthritis. Children with PSACH show no signs of it at birth. Slowing ...
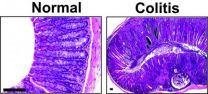
UCLA-led study identifies genetic factors involved in pediatric ulcerative colitis
2014-09-03
UCLA researchers were part of a team that has discovered the interplay of several genetic factors that may be involved in the development of early-onset ulcerative colitis, a severe type of inflammatory bowel disease.
The early research findings in mice suggest possible new targets for prevention and treatment strategies to address the inflammation generated by early-onset ulcerative colitis. The rare disease affects infants and young children and can lead to early development of colon cancer and an increased risk of liver damage.
Scientists from the David Geffen School ...
Are rising health care costs inevitable?
2014-09-03
New Rochelle, NY, September 3, 2014–If continuing increases in health care costs are inevitable, as some economists predict, is it possible for health care delivery reform to succeed in reducing the overall burden of health care expenditures on the U.S. economy? According to the results of a new study, the focus should shift from cost control to improving utilization rates and quality outcomes, as described in detail in an article in Population Health Management, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Population ...
Lowering coal-fired power plant emissions may have saved 1,700 lives in 1 year
2014-09-03
After scoring a Supreme Court victory this spring, the Environmental Protection Agency can move forward with its strategy to cut air pollution from coal-fired power plants in several states — and new research suggests the impact could be lifesaving. Scientists assessed the effects of one state's prescient restrictions on plant emissions in a report in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology. They estimated that the state's legislation prevented about 1,700 premature deaths in 2012.
Jacqueline MacDonald Gibson and Ya-Ru Li explain that the U.S. has been working ...
'Drink responsibly' messages in alcohol ads promote products, not public health
2014-09-03
Alcohol industry magazine ads reminding consumers to "drink responsibly" or "enjoy in moderation" fail to convey basic public health information, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A report on the research, published in the September issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence, analyzed all alcohol ads that appeared in U.S. magazines from 2008 to 2010 to determine whether messages about responsibility define responsible drinking or provide clear warnings about the risks associated with alcohol consumption.
According to the study, ...
Live from inside a battery
2014-09-03
Mobile phones, digital cameras, camcorders, notebooks: They all run on lithium-ion batteries. These are characterized by high energy densities while remaining small and light enough to be used in portable devices. "A lithium-ion battery can store three to four times the energy of a comparably sized nickel-cadmium battery," explains Dr. habil. Ralph Gilles, scientist at the Neutron Source Heinz Maier-Leibnitz (FRM II). Even temperature fluctuations and longer-term storage do not pose problems for lithium-ion batteries.
These advantages make lithium-ion batteries a key ...
Rising risk of failed seasons as climate change puts pressure on Africa's farmers
2014-09-03
ADDIS ABABA, Ethiopia (2 September 2014)—Small-scale family farmers across Africa— already struggling to adapt to rapidly rising temperatures and more erratic rains—risk being overwhelmed by the pace and severity of climate change, according to the 2014 African Agriculture Status Report (AASR).The analysis, prepared by the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA), with contributions from several African scholars, provides the most comprehensive review to date of how climate change will affect Africa's smallholder farmers and highlights the most promising paths to ...
Why HIV patients develop dementia
2014-09-03
Since the introduction of the combination anti-retroviral therapy (cART) in the mid-90s, the life expectancy of HIV patients has significantly improved. As a result, long-term complications are becoming more relevant: almost every second HIV patient is affected by neurocognitive disorders, which can lead to dementia. It has not as yet been fully understood how these disorders occur. Researchers from Bochum have now successfully demonstrated that infected cells activate specific immune cells in a patient's brain, which subsequently display harmful behaviour and lead to the ...
A fix to our cell-phone waste problem?
2014-09-03
When it comes to cell phones, the world is stunningly wasteful. Customers will buy more than 1.8 billion new ones by the end of this year only to abandon almost half of them to drawers, and they'll recycle a mere 3 percent of them. But creative and enterprising efforts are underway to reverse the seemingly unstoppable tide, says an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly news magazine of the American Chemical Society.
Alex Scott, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that there is much to be recovered and re-used from a cell phone. An average mobile contains ...
[1] ... [3368]
[3369]
[3370]
[3371]
[3372]
[3373]
[3374]
[3375]
3376
[3377]
[3378]
[3379]
[3380]
[3381]
[3382]
[3383]
[3384]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.