Women and health professionals spark new cycle of improving maternal and newborn health
2014-09-08
Demand for better care by women linked with the expansion of basic services, rather than political pressure, has helped to improve midwifery services in low to middle-income countries, according to international research involving the University of Southampton.
An examination of maternal and newborn health systems for the Lancet Series on Midwifery found that after initial investment in maternal and newborn health infrastructure, a virtuous cycle developed in these countries – with increased demand for care leading to the deployment of more midwives, better services, ...
Facial plastic surgery can safely address the major aspects of aging in 1 operation
2014-09-08
AUGUSTA, Ga. – A total facial rejuvenation that combines three procedures to address the multiple signs of an aging face and neck can be performed safely at one time, a new study shows.
Total facial rejuvenation, which combines an extensive facelift to tighten skin and muscle; specialized, midface implants to restore fullness; and laser resurfacing to reduce skin's irregular texture and discoloration, can be safely performed at one time, reports Dr. Achih H. Chen, facial plastic surgeon.
Chen, Director of Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the Medical ...
Enigmatic Viking fortress discovered in Denmark
2014-09-08
It is the first time for over 60 years that a new Viking fortress is found in Denmark, says curator Nanna Holm of The Danish Castle Centre. Søren Sindbæk, professor of medieval archeology at Aarhus University, explains: "The Vikings have a reputation as a berserker and pirates. It comes as a surprise to many that they were also capable of building magnificent fortresses. The discovery of the new Viking fortress is a unique opportunity to gain new knowledge about Viking war and conflicts, and we get a new chance to examine the Vikings' most famous monuments. " The previously ...
Bureaucracy consumes one-quarter of US hospitals' budgets, twice as much as other nations
2014-09-08
A study of hospital administrative costs in eight nations published today in the September issue of Health Affairs finds that hospital bureaucracy consumed 25.3 percent of hospital budgets in the U.S. in 2011, far more than in other nations.
Administrative costs were lowest (about 12 percent) in Scotland and Canada, whose single-payer systems fund hospitals through global, lump-sum budgets, much as a fire department is funded in the U.S.
The study is the first analysis of administrative costs across multiple nations with widely varying health systems. It was carried ...
Climate change to increase forest fire danger in Europe
2014-09-08
Climate change is expected to bring increased temperatures and longer droughts—conditions that will make forests more susceptible to fires.
By 2090, the area burned by forest fires in the European Union could increase by 200% because of climate change, according to a new study published in the journal Regional Environmental Change. However, preventive fires could keep that increase to below 50%, the study shows. Improved firefighting response could provide additional protection against forest fires.
The study was the first to examine adaptation to forest fire danger ...
Sun-powered desalination for villages in India
2014-09-08
CAMBRIDGE, Mass-- Around the world, there is more salty groundwater than fresh, drinkable groundwater. For example, 60 percent of India is underlain by salty water — and much of that area is not served by an electric grid that could run conventional reverse-osmosis desalination plants.
Now an analysis by MIT researchers shows that a different desalination technology called electrodialysis, powered by solar panels, could provide enough clean, palatable drinking water to supply the needs of a typical village. The study, by MIT graduate student Natasha Wright and Amos Winter, ...
New mechanism in gene regulation revealed
2014-09-08
The information encoded in our genes is translated into proteins, which ultimately mediate biological functions in an organism. Messenger RNA (mRNA) plays an important role, as it is the molecular template used for translation. Scientists from the Helmholtz Zentrum Muenchen and the Technische Universität Muenchen, in collaboration with international colleagues, have now unraveled a molecular mechanism of mRNA recognition, which is essential for understanding differential gene regulation in male and female organisms. The results are published in the renowned scientific journal ...
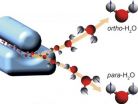
Researchers part water
2014-09-08
Using an "electric prism", scientists have found a new way of separating water molecules that differ only in their nuclear spin states and, under normal conditions, do not part ways. Since water is such a fundamental molecule in the universe, the recent study may impact a multitude of research areas ranging from biology to astrophysics. The research team from the Center for Free-Electron Laser Science (CFEL) – a collaboration of DESY, the Max Planck Society and Universität Hamburg – reported its results in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
At first ...
Simeprevir in hepatitis C: Added benefit for certain patients
2014-09-08
The drug simeprevir (trade name: Olysio) has been available since May 2014 for the treatment of adult patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. In an early benefit assessment pursuant to the Act on the Reform of the Market for Medicinal Products (AMNOG), the German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined whether this new drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy.
The drug manufacturer dossier provided indications and hints of an added benefit of simeprevir when the patients infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV) ...
Plant diversity in China vital for global food security
2014-09-08
With climate change threatening global food supplies, new research claims the rich flora of China could be crucial to underpin food security in the future.
A team from the University of Birmingham and partners in China have identified 871 wild plant species native to China that have the potential to adapt and maintain 28 globally important crops, including rice, wheat, soybean, sorghum, banana, apple, citrus fruits, grape, stone fruits and millet. 42% of these wild plant species, known as crop wild relatives (CWR) occur nowhere else in the world.
CWR are wild plant ...
Plant insights could help develop crops for changing climates
2014-09-08
Crops that thrive in changing climates could be developed more easily, thanks to fresh insights into plant growth.
A new computer model that shows how plants grow under varying conditions could help scientists develop varieties likely to grow well in future.
Scientists built the model to investigate how variations in light, day length, temperature and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere influence the biological pathways that control growth and flowering in plants.
They found differences in the way some plant varieties distribute nutrients under varying conditions, ...
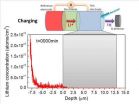
First-ever look inside a working lithium-ion battery
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
Using a neutron beam, chemists and engineers at The Ohio State University were able to track the flow of lithium atoms into and out of an electrode in real time...
Click here for more information.
COLUMBUS, Ohio—For the first time, researchers have been able to open a kind of window into the inner workings of a lithium-ion battery.
Using a neutron beam, chemists and engineers at The Ohio State University were able to track the flow of lithium atoms into and out ...
Targeted immune booster removes toxic proteins in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
2014-09-08
Alzheimer's disease experts at NYU Langone Medical Center and elsewhere are reporting success in specifically harnessing a mouse's immune system to attack and remove the buildup of toxic proteins in the brain that are markers of the deadly neurodegenerative disease.
Reporting on their experiments in the journal Acta Neuropathologica Communications online Sept. 3, the researchers say the work advances the development of more effective clinical treatments for Alzheimer's because their immune booster reduced both amyloid beta plaques and tau tangles. Previous immunomodulatory ...
Nearly half of older adults have care needs
2014-09-08
Nearly half of older adults – 18 million people—have difficulty or get help with daily activities, according to a new study.
Researchers from the University of Michigan and the Urban Institute analyzed data from a national sample of older adults drawn from Medicare enrollment files. In all, 8,245 people were included in the 2011 the National Health and Aging Trends Study. The analysis was published in the current (September 2014) issue of the Milbank Memorial Quarterly.
"Although 51 percent reported having no difficulty in the previous month, 29 percent reported receiving ...
The future of our crops is at risk in conflict zones, say Birmingham scientists
2014-09-08
Wild species related to our crops which are crucial as potential future food resources have been identified by University of Birmingham scientists, however, a significant proportion are found in conflict zones in the Middle East, where their conservation is increasingly comprised.
The scientists have identified 'hotspots' around the globe where crop wild relatives (CWR) – species closely related to our crops which are needed for future crop variety development – could be conserved in the wild in order to secure future global food resources.
The hotspot where CWR ...
New parasitoid wasp species found in China
2014-09-08
For the first time, wasps in the genus Spasskia (family: Braconidae) have been found in China, according to an article in the open-access Journal of Insect Science. In addition, a species in that genus which is totally new to science was also discovered.
The new species, Spasskia brevicarinata, is very small — male and female adults are less than one centimeter long. It is similar to a previously described species called Spasskia indica, but the ridges on some of its body segments are different. In fact, the species epithet brevicarinata reflects a short ridge on its ...
Unusual immune cell needed to prevent oral thrush, Pitt researchers find
2014-09-08
PITTSBURGH, Sept. 8 – An unusual kind of immune cell in the tongue appears to play a pivotal role in the prevention of thrush, according to the researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine who discovered them. The findings, published online today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, might shed light on why people infected with HIV or who have other immune system impairments are more susceptible to the oral yeast infection.
Oral thrush is caused by an overgrowth of a normally present fungus called Candida albicans, which leads to painful white lesions ...
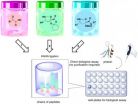
'Pick 'n' Mix' chemistry to grow cultures of bioactive molecules
2014-09-08
Chemists at ETH-Zürich and ITbM, Nagoya University have developed a new method to build large libraries of bioactive molecules – which can be used directly for biological assays – by simply mixing a small number of building blocks in water.
Zürich, Switzerland and Nagoya, Japan – Professor Jeffrey Bode of ETH-Zürich and the Institute of Transformative Bio-Molecules (ITbM) of Nagoya University, and his co-worker have established a new strategy called "synthetic fermentation" to rapidly synthesize a large number of bioactive molecules, which can be directly screened in ...
Trial shows improved overall survival for patients with liver cancer not amenable to surgery
2014-09-08
Singapore, 04 September 2014 – The mature results from a trial conducted by the Asia-Pacific Hepatocellular Carcinoma Trials Group led by the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS) and Singapore General Hospital (SGH) have shown that patients who suffer from inoperable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) may have a chance to live significantly longer by using a combined therapy.
The multi-centre phase II clinical trial was conducted at four Asia Pacific tertiary medical centres to evaluate the efficacy of combining two existing treatment modalities, Sorafenib and ...
New knowledge of cannabis paves the way for drug development
2014-09-08
Revolutionary nanotechnology method could help improve the development of new medicine and reduce costs. Researchers from the Nano-Science Center and the Department of Chemistry at the University of Copenhagen have developed a new screening method that makes it possible to study cell membrane proteins that bind drugs, such as cannabis and adrenaline, while reducing the consumption of precious samples by a billion times.
About 40% of all medicines used today work through the so-called "G protein-coupled receptors". These receptors react to changes in the cell environment, ...
Study examines discrimination among homeless adults in Toronto with mental illness
2014-09-08
TORONTO, Sept. 8, 2014—Vulnerable populations in ethnically diverse Toronto reported more discrimination by health care workers based on their housing status, mental health or substance abuse issues than race, a new study has found.
Forty-two per cent of people surveyed reported at least one form of perceived discrimination by health care workers, lead author Dr. Vicky Stergiopoulos wrote in a paper published today in the journal BMC Health Services Research.
The most prevalent form of perceived discrimination was due to mental illness or substance abuse (33 per cent) ...
Poor recording of physical health and medication could be causing dementia trials to fail
2014-09-08
Dementia trials could be failing because they all-too-often overlook the physical health of patients – according to new research from the University of East Anglia and Aston University.
More than 60 per cent of people with dementia are estimated to have three or more other conditions (co-morbidities).
The research shows how the combined effects of co-morbidities including diabetes, lung disease, arthritis and chronic heart failure are not being adequately described in dementia trials.
It investigates the extent of co-morbidities in people with dementia and the recording ...
Food craving is stronger, but controllable, for kids
2014-09-08
Children show stronger food craving than adolescents and adults, but they are also able to use a cognitive strategy that reduces craving, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"These findings are important because they suggest that we may have another tool in our toolbox to combat childhood obesity," says psychological scientist and lead researcher Jennifer A. Silvers, a post-doctoral fellow at Columbia University in the laboratory of Professor Kevin Ochsner.
Most interventions aimed at ...
Quick-cooled beers, perfect burgers and more: Chemistry Life Hacks, Vol. 3 (video)
2014-09-08
WASHINGTON, September 8, 2014 — It's the series that's one-part MacGyver, one-part Mendeleev. "Chemistry Life Hacks" is back with new tips that can change your life, or at least the temperature of your beer. Learn how to cool your brews quickly before the big game starts, get fruit flies out of your kitchen for good, and how to cook the perfect patty on the grill. Check out these tips and more at: http://youtu.be/QUE2O1276P8.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The ...
Layered graphene sandwich for next generation electronics
2014-09-08
Writing in Nature Nanotechnology, the researchers have demonstrated how combining the two-dimensional materials in a stack could create perfect crystals capable of being used in next generation transistors.
Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN), otherwise known as white graphene, is one of a family of two-dimension materials discovered in the wake of the isolation of graphene at the University in 2004. Manchester researchers have previously demonstrated how combining 2D materials, in stacks called heterostructures, could lead to materials capable of being designed to meet industrial ...
[1] ... [3360]
[3361]
[3362]
[3363]
[3364]
[3365]
[3366]
[3367]
3368
[3369]
[3370]
[3371]
[3372]
[3373]
[3374]
[3375]
[3376]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.