Sodium's influence on blood pressure statistically insignificant
2014-09-08
A new study published in American Journal of Hypertension finds evidence that increased Body Mass Index, age, and non-sodium dietary factors are much more closely related to increases in systolic blood pressure than sodium intake.
The study, "Relationship between nutrition and blood pressure: A cross-sectional analysis from the NutriNet-Santé study, a French web-based cohort study," measured the effects of sodium intake, Body Mass Index, physical activity, alcohol consumption, and non-sodium dietary factors on the blood pressure of 8,670 French adults and concluded ...
Agricultural revolution in Africa could increase global carbon emissions
2014-09-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Productivity-boosting agricultural innovations in Africa could lead to an increase in global deforestation rates and carbon emissions, a Purdue University study finds.
Historically, improvements in agricultural technology have conserved land and decreased carbon emissions at the global level: Gaining better yields in one area lessens the need to clear other areas for crops, sidestepping a land conversion process that can significantly raise the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere.
Agricultural advances in Africa, however, could ...
Watchful waiting isn't right for everyone
2014-09-08
(PHILADELPHIA) – There is an active controversy among oncologists about when to treat prostate cancer patients, with some suggesting that the word "cancer" be removed from the description of low grade disease, in order to prevent overtreatment. However a new study shows that these guidelines may not be appropriate for everyone, especially African American men.
"We know that African American men have more aggressive prostate cancer than Caucasian men," says Kosj Yamoah M.D., Ph.D., Chief Resident, Department of Radiation Oncology at Thomas Jefferson University. "Our study ...
Study traces ecological collapse over 6,000 years of Egyptian history
2014-09-08
Depictions of animals in ancient Egyptian artifacts have helped scientists assemble a detailed record of the large mammals that lived in the Nile Valley over the past 6,000 years. A new analysis of this record shows that species extinctions, probably caused by a drying climate and growing human population in the region, have made the ecosystem progressively less stable.
The study, published September 8 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), found that local extinctions of mammal species led to a steady decline in the stability of the animal communities ...
Broken signals lead to neurodegeneration
2014-09-08
Researchers from the RIKEN Brain Science Institute in Japan, in collaboration with Juntendo University and the Japan Science and Technology Agency, have discovered that a cell receptor widely involved in intracellular calcium signaling--the IP3R receptor--can be locked into a closed state by enzyme action, and that this locking may potentially play a role in the reduction of neuron signaling seen in neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington's and Alzheimer's disease.
In the research published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the scientists ...
In directing stem cells, study shows context matters
2014-09-08
MADISON, Wis. — Figuring out how blank slate stem cells decide which kind of cell they want to be when they grow up — a muscle cell, a bone cell, a neuron — has been no small task for science.
Human pluripotent stem cells, the undifferentiated cells that have the potential to become any of the 220 types of cells in the body, are influenced in the lab dish by the cocktail of chemical factors and proteins upon which they are grown and nurtured. Depending on the combination of factors used in a culture, the cells can be coaxed to become specific types of cells.
Now, in ...
Co-flowing liquids can stabilize chaotic 'whipping' in microfluidic jets
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
This video show jets emerging from the same glass needle in chaotic whipping (left) and a steady state helical whipping. By controlling the viscosity and speed of the liquid surrounding...
Click here for more information.
Industrial wet spinning processes produce fibers from polymers and other materials by using tiny needles to eject continuous jets of liquid precursors. The electrically charged liquids ejected from the needles normally exhibit a chaotic "whipping" structure ...
Brain injuries no match for sPIF treatment
2014-09-08
New Haven, Conn. — Researchers at Yale School of Medicine and their colleagues have uncovered a new pathway to help treat perinatal brain injuries. This research could also lead to treatments for traumatic brain injuries and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
The findings are published in the Sept. 8 issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The microRNA let-7 is known to cause the death of neurons in the central nervous system. The research team found that a synthetic molecule derived from the embryo called PreImplantation ...
Textbook theory behind volcanoes may be wrong
2014-09-08
In the typical textbook picture, volcanoes, such as those that are forming the Hawaiian islands, erupt when magma gushes out as narrow jets from deep inside Earth. But that picture is wrong, according to a new study from researchers at Caltech and the University of Miami in Florida.
New seismology data are now confirming that such narrow jets don't actually exist, says Don Anderson, the Eleanor and John R. McMillian Professor of Geophysics, Emeritus, at Caltech. In fact, he adds, basic physics doesn't support the presence of these jets, called mantle plumes, and the ...
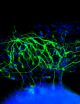
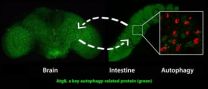
UCLA biologists delay the aging process by 'remote control'
2014-09-08
UCLA biologists have identified a gene that can slow the aging process throughout the entire body when activated remotely in key organ systems.
Working with fruit flies, the life scientists activated a gene called AMPK that is a key energy sensor in cells; it gets activated when cellular energy levels are low.
Increasing the amount of AMPK in fruit flies' intestines increased their lifespans by about 30 percent — to roughly eight weeks from the typical six — and the flies stayed healthier longer as well.
The research, published Sept. 4 in the open-source journal Cell ...
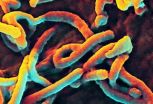
Rapid and durable protection against ebola virus with new vaccine regimens
2014-09-08
One shot of an experimental vaccine made from two Ebola virus gene segments incorporated into a chimpanzee cold virus vector (called chimp adenovirus type 3 or ChAd3) protected all four macaque monkeys exposed to high levels of Ebola virus 5 weeks after inoculation, report National Institutes of Health (NIH) scientists and their collaborators. The ability of the ChAd3 Ebola virus vaccine to elicit rapid protection in monkeys is notable as the world health community battles an ongoing Ebola virus disease outbreak in West Africa. While the protective effects of the single ...
Teens living with 2 college-educated parents less likely to use alcohol and marijuana
2014-09-08
ARLINGTON, Texas -- A high school senior who lives with two college-educated parents is significantly less likely to drink alcohol or smoke marijuana than a teenager who lives with one parent, a new University of Texas at Arlington study has found.
For example, teens living with their mother only are 54 percent more likely to use alcohol, and 58 percent more likely to smoke if they live only with their father.
Eusebius Small, an assistant professor in the UT Arlington School of Social Work, analyzed data on 14,268 teenagers to determine the impact of family structure ...
Ohio University paleontologists discover new species of titanosaurian dinosaur in Tanzania
2014-09-08
ATHENS, Ohio (Sept. 8, 2014)—Ohio University paleontologists have identified a new species of titanosaurian, a member of the large-bodied sauropods that thrived during the final period of the dinosaur age, in Tanzania. Although many fossils of titanosaurians have been discovered around the globe, especially in South America, few have been recovered from the continent of Africa.
The new species, named Rukwatitan bisepultus, was first spotted by scientists embedded in a cliff wall in the Rukwa Rift Basin of southwestern Tanzania. Using the help of professional excavators ...
In one of nature's innovations, a single cell smashes and rebuilds its own genome
2014-09-08
Life can be so intricate and novel that even a single cell can pack a few surprises, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
The pond-dwelling, single-celled organism Oxytricha trifallax has the remarkable ability to break its own DNA into nearly a quarter-million pieces and rapidly reassemble those pieces when it's time to mate, the researchers report in the journal Cell. The organism internally stores its genome as thousands of scrambled, encrypted gene pieces. Upon mating with another of its kind, the organism rummages through these jumbled genes ...
Gobbling up poison: A method for killing colon cancer
2014-09-08
(PHILADELPHIA) – These days, cancer researchers aim to design targeted and specific therapy – those that kill cancer but spare the surrounding tissue. Immunotoxins, which use cancer-targeted antibodies linked to deadly toxins such as ricin, are one such therapy. However, few have succeeded to date in part because cancer cells share many molecules with normal cells, and because it can be challenging to unlock the deadly chemical only after the antibody has homed to the diseased tissue.
Now researchers at Thomas Jefferson University have discovered the unique biological ...
Soft robot squirms over fire, ice, and withstands crushing force
2014-09-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – Engineers have created a shape-changing "soft" robot that can tread over a variety of adverse environmental conditions including snow, puddles of water, flames, and the crushing force of being run over by an automobile.
Videos: https://cornell.box.com/softrobot
The engineers from Cornell and Harvard Universities will detail the robot in an upcoming edition of the journal Soft Robotics. An early online version of the study can be found at: http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/soro.2014.0008
The pneumatically powered, fully untethered robot was ...
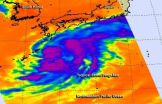
NASA sees large Tropical Storm Fengshen skirting eastern Japan's coastline
2014-09-08
Tropical Storm Fengshen is a large storm and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows that it's about as long as the big island of Japan.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Fengshen on September 7 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument known as AIRS gathered temperature data about the storm's cloud tops and surrounding sea surface temperatures. The infrared data showed strong thunderstorms surrounded the center of circulation and also appeared in large bands south and northeast of the storm's center. Another large and fragmented band on ...
Yale study shows how conversion of forests to cropland affected climate
2014-09-08
The conversion of forests into cropland worldwide has triggered an atmospheric change that, while seldom considered in climate models, has had a net cooling effect on global temperatures, according to a new Yale study.
Writing in the journal Nature Climate Change, Professor Nadine Unger of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies (F&ES) reports that large-scale forest losses during the last 150 years have reduced global emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs), which control the atmospheric distribution of many short-lived climate pollutants, ...
Brain damage caused by severe sleep apnea is reversible
2014-09-08
DARIEN, IL – A neuroimaging study is the first to show that white matter damage caused by severe obstructive sleep apnea can be reversed by continuous positive airway pressure therapy. The results underscore the importance of the "Stop the Snore" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project, a collaboration between the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Sleep Research Society and other partners.
Results show that participants with severe, untreated sleep apnea had a significant reduction in white matter fiber integrity ...
A bird-pollinated flower with a rather ingenious twist
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
When a bird forages on nectar, the flower twists as the spur complies with the shape of the
bird's bill. In consequence, pollen is placed in an unusual location on...
Click here for more information.
When researchers studying several bird-pollinated species of Impatiens flowers in the mountains of western Cameroon noticed one with an odd, upwardly curving nectar spur, they couldn't imagine how any sunbird could ever sip from it. After recording visitors to the flower continuously ...
Coral trout pick their collaborators carefully
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
Coral trout are choosey about moray collaborators.
Click here for more information.
Coral trout not only work with moray eels to improve their chances of a meal, but they can also be choosy when it comes to picking the best moray partner. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 8 show that such sophisticated collaborative abilities are not limited to apes and humans.
The fish's behavior is remarkable in other ways too, the researchers ...
Fish as good as chimpanzees at choosing the best partner for a task
2014-09-08
Coral trout are fast when chasing prey above the reefs of their habitat, but can't pursue their quarry if it buries itself into a hard-to-reach reef crevice.
When this happens, the trout will team up with a snake-like moray eel to flush out the unfortunate fish in a remarkable piece of interspecies collaboration: either the eel takes the prey in the reef, or scares it back into the open so the trout can pounce.
Coral trout - along with close relative the roving coral grouper - will use gestures and signals to flag the location of prey to an eel, including head shakes ...
Hog workers carry drug-resistant bacteria even after they leave the farm
2014-09-08
A new study suggests that nearly half of workers who care for animals in large industrial hog farming operations may be carrying home livestock-associated bacteria in their noses, and that this potentially harmful bacteria remains with them up to four days after exposure.
Researchers had believed that livestock-associated bacteria would clear from the noses of hog workers quickly – within 24 hours. But this small study of hog workers in North Carolina, reported online Sept. 8 in the journal Occupational and Environmental Medicine, suggests it can stick around longer. ...
Popular cancer drug target implicated in cardiovascular defects
2014-09-08
September 8, 2014 CHAPEL HILL – UNC School of Medicine researchers have discovered an unlikely relationship between CXCR7 – a protein implicated in tumor growth and metastasis – and adrenomedullin – a hormone involved in cardiovascular health. Deleting CXCR7 allows adrenomedullin to run rampant, triggering the development of an enlarged heart and the overgrowth of the lymphatic vessels that traffic immune cells and fluids throughout the body.
The study, published September 8 in the journal Developmental Cell, reveals that CXCR7 binds to the ligand adrenomedullin. The ...
UNC researchers find new genetic target for a different kind of cancer drug
2014-09-08
CHAPEL HILL, NC – Researchers from the UNC School of Medicine have discovered that the protein RBM4, a molecule crucial to the process of gene splicing, is drastically decreased in multiple forms of human cancer, including lung and breast cancers. The finding, published today in the journal Cancer Cell, offers a new route toward therapies that can thwart the altered genetic pathways that allow cancer cells to proliferate and spread.
"Historically, scientists haven't targeted the proteins in cancer cells that are involved in gene splicing," said Zefeng Wang, PhD, associate ...
[1] ... [3358]
[3359]
[3360]
[3361]
[3362]
[3363]
[3364]
[3365]
3366
[3367]
[3368]
[3369]
[3370]
[3371]
[3372]
[3373]
[3374]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.