Study finds wide gap in compensation from '07 South Korean oil spill
2014-09-03
Although nearly eight years have passed since a major oil spill in South Korea, compensation and recovery efforts appear to be far from satisfactory, and the affected communities continue to suffer the effects of the disaster.
UT Dallas' Dr. Dohyeong Kim, second-year doctoral student Soojin Min and two Korean scholars have found a considerable gap between the economic loss claimed by residents and the compensation they received after the Hebei Spirit oil spill. Only 11 percent of the claims were approved for compensation.
"I was surprised," said Kim, the lead author ...
For kids with both asthma and obesity, which came first?
2014-09-03
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (September 3, 2014) – For years, doctors have known that there is a link between childhood obesity and asthma, but have found it difficult to determine which condition tends to come first, or whether one causes the other.
An article published in the September issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), suggests it is more probable that childhood obesity contributes to asthma, although the connection is complex and has many factors.
"The relationship ...
You may have to watch what your fruits and veggies eat
2014-09-03
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (September 3, 2014) – People with food allergies always have to watch what they eat. Now, they may have to watch what their fruits and vegetables eat, as it seems it's possible to have an allergic reaction to antibiotic residues in food.
An article published in the September issue of Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), examines the case of a 10 year-old girl who had an anaphylactic (severely allergic) reaction after eating blueberry pie. Although ...
Brown marmorated stink bug biology and management options described in open-access article
2014-09-03
The brown marmorated stink bug (Halyomorpha halys) is an invasive, herbivorous insect species that was accidentally introduced to the United States from Asia. First discovered in Allentown, Pennsylvania in 1996, it has since been found in at least 40 states in the U.S. as well as Canada, Switzerland, France, Germany, Italy, and Lichtenstein.
In North America, it has become a major agricultural pest across a wide range of commodities. The insect is capable of eating more than 100 different plant species, and in 2010 it caused $37 million worth of damage to apples alone.
Now ...
Cosmic forecast: Dark clouds will give way to sunshine
2014-09-03
Lupus 4 is located about 400 light-years away from Earth, straddling the constellations of Lupus (The Wolf) and Norma (The Carpenter's Square). The cloud is one of several affiliated dark clouds found in a loose star cluster called the Scorpius–Centaurus OB association. An OB association is a relatively young, yet widely dispersed grouping of stars [1]. The stars likely had a common origin in a gigantic cloud of material.
Because the association, and its Lupus clouds, form the closest such grouping to the Sun, they are a prime target for studying how stars grow up together ...
Scientists discover how to 'switch off' autoimmune diseases
2014-09-03
Scientists have made an important breakthrough in the fight against debilitating autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis by revealing how to stop cells attacking healthy body tissue.
Rather than the body's immune system destroying its own tissue by mistake, researchers at the University of Bristol have discovered how cells convert from being aggressive to actually protecting against disease.
The study, funded by the Wellcome Trust, is published today [03 September] in Nature Communications.
It's hoped this latest insight will lead to the widespread use of antigen-specific ...
Unplanned births out-of-hospital increases risk of infant mortality
2014-09-03
New research reveals that unplanned births out-of-hospital in Norway are associated with higher infant mortality. The findings published in Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica, a journal of the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology, indicate that young women who have given birth at least once before (multiparous) and those living in remote areas are more likely to have unplanned deliveries, which may increase the risk of death in newborns.
In 2013, close to 60,000 babies were born in Norway according to the Statistics Norway. The country ...
Around 1 in 10 UK women has dry eye disease, requiring artificial tears
2014-09-03
The symptoms of dry eye disease include the sensation of grit in the eye, frequently accompanied by itching, burning and visual disturbance. The causes are poorly understood.
The researchers base their findings on almost 4000 women aged 20 to 87 (average age 57) from the TwinsUK cohort, drawn from the registry held at St Thomas' Hospital in London.
This cohort is widely regarded as representative of the UK general population, and has been used to look at a wide range of diseases and genetic traits over the years.
The prevalence of dry eye disease, and the frequency and ...
Stillbirth gap closing between indigenous and non-indigenous women, shows Australian study
2014-09-03
The gap in stillbirth rates between indigenous and non-indigenous women in Queensland, Australia, is closing, however indigenous women are still at risk of stillbirth due to preventable causes, find researchers in a new study published today (3 September) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
The Australian study used data from the Queensland Perinatal Data Collection and looked at 881,211 singleton births from 1995 to 2011. It aimed to assess the differences in stillbirth rates over time among indigenous (Australian Aboriginal and Torres ...
Estrogen increases cannabis sensitivity
2014-09-03
PULLMAN, Wash. - Smoking today's concentrated pot might be risky business for women, according to new research from Washington State University. The study is the first to demonstrate sex differences in the development of tolerance to THC.
Psychology professor Rebecca Craft showed that, thanks to their estrogen levels, female rats are at least 30 percent more sensitive than males to the pain-relieving qualities of THC—the key active ingredient in cannabis. Females also develop tolerance to THC more quickly. These sensitivities could increase vulnerability to negative ...
Discharged patients return to the ER because 'better safe than sorry'
2014-09-02
WASHINGTON – Patients who return to the emergency department within a few days of discharge do so principally because they are anxious about their symptoms and have lost trust in other parts of the health care system, according to the results of a study published online today in Annals of Emergency Medicine ("Return Visits to the Emergency Department: The Patient Perspective").
"When asked why they did not follow up as an outpatient, patients reported feeling that their symptoms were too severe to wait until their scheduled appointment or being instructed to return ...
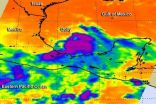
NASA satellites calling here you come again, Tropical Storm Dolly
2014-09-02
Tropical Storm Dolly visited Mexico six years ago, and NASA satellite data is calling "Here you come again," reminiscent of the famous country singer's hit song, as another storm named Dolly heads for a second landfall in Mexico.
In July of 2008, Tropical Storm Dolly made landfall on Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico before making a second and final landfall in south Texas. Now, six years later, Tropical Storm Dolly returns thanks to the six year list of revolving hurricane names, and once again Dolly is making landfall in eastern Mexico. NASA's Aqua satellite caught ...
Residency training predicts physicians' ability to practice conservatively
2014-09-02
LEBANON, NH – Doctors trained in locations with less intensive (and expensive) practice patterns appear to consistently be better at making clinical decisions that spare patients unnecessary and excessive medical care, according to a new study in JAMA Internal Medicine.
"Growing concern about the costs and harms of medical care has spurred interest in assessing physicians' ability to avoid the provision of unnecessary care," said lead author Brenda Sirovich of the VA Outcomes Group and The Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy & Clinical Practice.
Sirovich and colleagues ...
Experiences make you happier than possessions -- Before and after
2014-09-02
To get the most enjoyment out of our dollar, science tells us to focus our discretionary spending on experiences such as travel over material goods. A new Cornell University study shows that the enjoyment we derive from experiential purchases may begin even before we buy.
This research offers important information for individual consumers who are trying to "decide on the right mix of material and experiential consumption for maximizing well-being," said psychology researcher and study author Thomas Gilovich of Cornell University.
Previously, Gilovich and colleagues ...
Diabetes mellitus and mild cognitive impairment: Higher risk in middle age?
2014-09-02
Essen, Germany, September 2, 2014 – In a large population-based study of randomly selected participants in Germany, researchers found that mild cognitive impairment (MCI) occurred twice more often in individuals diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 2. Interestingly, this strong association was only observed in middle-aged participants (50-65 years), whereas in older participants (66-80 years) the association vanished. This study is published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
The concept of MCI describes an intermediate state between normal cognitive aging and dementia. ...
This week From AGU: California earthquake, future Mars rovers, models underestimate ozone
2014-09-02
From AGU's blogs: Earthquake rupture through a U.S. suburb
Observations and mapping by seismologists at the University of California Davis in the hours and days after the August 24 earthquake in northern California are helping scientists understand why the earthquake caused so much damage in the region, according to a post in The Trembling Earth blog, hosted by the American Geophysical Union.
From this week's Eos: Future Mars Rovers: The Next Places to Direct Our Curiosity
Selecting where the next Mars rovers will land involves a series of open-invitation workshops ...
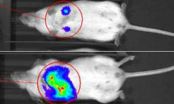
‘Prepped’ by tumor cells, lymphatic cells encourage breast cancer cells to spread
2014-09-02
Breast cancer cells can lay the groundwork for their own spread throughout the body by coaxing cells within lymphatic vessels to send out tumor-welcoming signals, according to a new report by Johns Hopkins scientists.
Writing in the Sept. 2 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe animal and cell-culture experiments that show increased levels of so-called signaling molecules released by breast cancer cells. These molecules cause lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in the lungs and lymph nodes to produce proteins called CCL5 and VEGF. CCL5 attracts tumor ...
Cool calculations for cold atoms
2014-09-02
Chemical reactions drive the mechanisms of life as well as a million other natural processes on earth. These reactions occur at a wide spectrum of temperatures, from those prevailing at the chilly polar icecaps to those at work churning near the earth's core. At nanokelvin temperatures, by contrast, nothing was supposed to happen. Chemistry was expected to freeze up. Experiments and theoretical work have now show that this is not true. Even at conditions close to absolute zero atoms can interact and manage to form chemical bonds.
Within this science of ultracold ...
Enzyme controlling metastasis of breast cancer identified
2014-09-02
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have identified an enzyme that controls the spread of breast cancer. The findings, reported in the current issue of PNAS, offer hope for the leading cause of breast cancer mortality worldwide. An estimated 40,000 women in America will die of breast cancer in 2014, according to the American Cancer Society.
"The take-home message of the study is that we have found a way to target breast cancer metastasis through a pathway regulated by an enzyme," said lead author Xuefeng Wu, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher ...
Study links sex hormone levels in the blood to risk of sudden cardiac arrest
2014-09-02
LOS ANGELES (Sept. 2, 2014) – Measuring the levels of sex hormones in patients' blood may identify patients likely to suffer a sudden cardiac arrest, a heart rhythm disorder that is fatal in 95 percent of patients.
A new study, published online by the peer-reviewed journal Heart Rhythm, shows that lower levels of testosterone, the predominant male sex hormone, were found in men who had a sudden cardiac arrest. Higher levels of estradiol, the major female sex hormone, were strongly associated with greater chances of having a sudden cardiac arrest in both men and women. ...
UO-Berkeley Lab unveil new nano-sized synthetic scaffolding technique
2014-09-02
EUGENE, Ore. -- Scientists, including University of Oregon chemist Geraldine Richmond, have tapped oil and water to create scaffolds of self-assembling, synthetic proteins called peptoid nanosheets that mimic complex biological mechanisms and processes.
The accomplishment -- detailed this week in a paper placed online ahead of print by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences -- is expected to fuel an alternative design of the two-dimensional peptoid nanosheets that can be used in a broad range of applications. Among them could be improved chemical sensors ...
Microphysiological systems will revolutionize experimental biology and medicine
2014-09-02
The Annual Thematic issue of Experimental Biology and Medicine that appears in September 2014 is devoted to "The biology and medicine of microphysiological systems" and describes the work of scientists participating in the Microphysiological Systems Program directed by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and funded in part by the NIH Common Fund. The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are collaborating with the NIH in the program. Fourteen of ...
An uphill climb for mountain species?
2014-09-02
A recently published paper provides a history of scientific research on mountain ecosystems, looks at the issues threatening wildlife in these systems, and sets an agenda for biodiversity conservation throughout the world's mountain regions.
The paper, "Mountain gloom and mountain glory revisited: A survey of conservation, connectivity, and climate change in mountain regions," appears online in the Journal of Mountain Ecology. Authors are Charles C. Chester of Tufts University, Jodi A. Hilty of the Wildlife Conservation Society, and Lawrence S. Hamilton of World Commission ...
Sabotage as therapy: Aiming lupus antibodies at vulnerable cancer cells
2014-09-02
New Haven, Conn. — Yale Cancer Center researchers may have discovered a new way of harnessing lupus antibodies to sabotage cancer cells made vulnerable by deficient DNA repair.
The findings were published recently in Nature's journal Scientific Reports.
The study, led by James E. Hansen, M.D., assistant professor of therapeutic radiology at Yale School of Medicine, found that cancer cells with deficient DNA repair mechanisms (or the inability to repair their own genetic damage) were significantly more vulnerable to attack by lupus antibodies.
"Patients with lupus ...
Seatbelt laws encourage obese drivers to buckle up
2014-09-02
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Obesity is associated with many health risks, including heart disease and diabetes, but University of Illinois researchers have found a possible way to mitigate one often-overlooked risk: not buckling up in the car.
A new study led by Sheldon H. Jacobson, a professor of computer science and of mathematics, found that increasing the obesity rates are associated with a decrease in seatbelt usage. However, these effects can be mitigated when seatbelt laws are in effect.
"Primary seatbelt laws lead to increased use of seatbelts," Jacobson said. "On the ...
[1] ... [3370]
[3371]
[3372]
[3373]
[3374]
[3375]
[3376]
[3377]
3378
[3379]
[3380]
[3381]
[3382]
[3383]
[3384]
[3385]
[3386]
... [8828]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.