MESA heart disease risk score worked well with or without race included
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
A version of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) heart disease risk score that did not include race predicted heart disease risk just as well as the original version that includes race.
The original MESA risk score, developed in 2015[1], combines traditional risk factors, sex and race with a coronary artery calcium score.
The MESA formula without race may be used for people who identify with more than one racial or ethnic group or those who prefer not to disclose their race or ethnicity.
Note: The study featured in this ...
Bystander CPR up to 10 minutes after cardiac arrest may protect brain function
2024-11-11
This news release contains updated information and data not included in the abstract.
Research Highlights:
The sooner a lay rescuer (bystander) starts cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on a person having a cardiac arrest at home or in public, up to 10 minutes after the arrest, the better the chances of survival and brain protection, according to an analysis of nearly 200,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrest cases in the U.S. from 2013 to 2022.
Among the study’s findings, people who received CPR within two minutes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had 81% higher odds of survival to release from the hospital ...
911 dispatcher assistance improved chances of receiving bystander CPR
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
A study of nearly 2,400 cardiac arrest cases in North Carolina found that when emergency dispatchers (telecommunicators) provided cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) instructions to 911 callers, people were more likely to provide aid for both men and women.
The study’s findings indicate that when a telecommunicator provided assistance to callers, bystander CPR was performed 44% of the time on women and 40% on men, compared to 9% on women and 11% on men when telecommunicator assistance was not provided.
Researchers found the telecommunicator role critical in instructing bystanders to act quickly, possibly instrumental in reducing sex disparities ...
GLP-1, SGLT2 medications may lower stroke survivor’s risk of future heart attack, stroke
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
In an analysis of more than 7,000 stroke survivors, those who were taking either a GLP1-receptor agonist or an SGLT2 inhibitor medication had a lower risk of a subsequent stroke, heart attack or death compared to peers who were not prescribed the medications during a three-year follow up period.
The analysis used health data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project collected from 2000 to 2022. The first GLP-1 medication was prescribed beginning in 2006, and the authors included cases beginning in 2000 to increase the power of the study, they noted.
Note: The study featured in this news release ...
TYK2 transforms tau from ‘good guy’ to a ‘bad guy’ that contributes to Alzheimer’s disease
2024-11-11
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital and collaborating institutions discovered that the enzyme TYK2 transforms the normal protein tau into one that accumulates in the brain and contributes to the development of Alzheimer’s disease in animal models. Published in Nature Neuroscience, the study suggests that partially restraining TYK2 could be a strategy to reduce tau levels and toxicity.
“Many studies have shown that the accumulation ...
Elephant seal colony declines one year after avian flu outbreak
2024-11-11
The sounds of barking elephant seals are again in the air along the breeding grounds of Península Valdés, Argentina—but it’s quieter. Almost exactly a year after a massive outbreak of H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza killed more than 17,000 elephant seals, including about 97% of their pups, scientists estimate that only about a third of the elephant seals normally expected here returned.
“It’s beautiful to walk the beaches now and hear elephant seals again,” said Marcela Uhart, director of the Latin America Program at the UC Davis Karen C. Drayer Wildlife Health Center within ...
While more is better, even moderate amounts of exercise may reduce risk for common heart condition
2024-11-11
Adding an extra hour every week of physical activity may lower the chance of developing the most common type of irregular heartbeat (arrythmia) by 11%, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the investigation focused on atrial fibrillation, a condition in which the heart’s upper two chambers beat rapidly and irregularly instead of at a consistent pace. If left untreated, this can lead to stroke, heart failure, and other issues. While past studies have linked exercise to reduced risk of this type of arrhythmia, nearly all of these analyses have relied on the participants’ ...
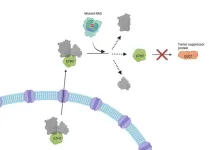
Researchers uncover new role of mutant proteins in some of the deadliest cancers
2024-11-11
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have discovered a new way in which RAS genes, which are commonly mutated in cancer, may drive tumor growth beyond their well-known role in signaling at the cell surface. Mutant RAS, they found, helps to kick off a series of events involving the transport of specific nuclear proteins that lead to uncontrolled tumor growth, according to a study published November 11, 2024, in Nature Cancer.
RAS genes are the second most frequently mutated genes in cancer, and mutant RAS proteins are key drivers of some of the deadliest cancers, ...
Patients may become unnecessarily depressed by common heart medicine
2024-11-11
All patients who have had a heart attack are typically treated using beta blockers. According to a Swedish study conducted earlier this year, this drug is unlikely to be needed for those heart patients who have a normal pumping ability. Now a sub-study at Uppsala University shows that there is also a risk that these patients will become depressed by the treatment.
“We found that beta blockers led to slightly higher levels of depression symptoms in patients who had had a heart attack but were not suffering from heart failure. At the same time, beta blockers have no life-sustaining function for this group of patients,” says Philip Leissner, a doctoral student in cardiac ...
Largest T cell clinical trial in solid tumors heralds new era in precision immunotherapy
2024-11-11
The largest ever clinical trial of T cell therapy (a type of cell-based immunotherapy) for solid tumours has been completed.
Led by a Singapore clinician-investigator, the global, international, multisite trial recruited 330 advanced nasopharyngeal (NPC) cancer patients in 23 sites across Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Taiwan and the United States.
The trial did not show an overall survival benefit for the entire patient cohort but a subset analysis combining outcomes of US, Singapore and Taiwanese sites, showed better progression free survival ...
Call for applications: Participation in the 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum for Outstanding Young Researchers in Mathematics and Computer Science
2024-11-11
The application process for the 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum has begun!
Young researchers in mathematics and computer science from all over the world can apply for one of the 200 exclusive spots to participate in the Heidelberg Laureate Forum (HLF), an annual networking conference. The HLF offers all accepted young researchers the unique opportunity to interact with the laureates of the most prestigious prizes in the fields of mathematics and computer science. Traditionally, the recipients of the Abel Prize, the ACM A.M. Turing Award, the ACM Prize in Computing, ...
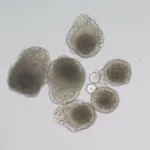
A milestone for reproductive medicine: Producing viable eggs from undeveloped oocytes through In vitro technology
2024-11-11
Mature egg cells, or oocytes, are essential for fertilization in assisted reproductive technologies. However, some ‘denuded’ oocytes, or those lacking the protective granulosa cell layer, fail to mature. Now, in a new study by researchers at Shinshu University, the team has developed a method to culture mature oocytes from these denuded oocytes in the lab. This innovative approach holds promise for overcoming significant challenges in reproductive science, marking a major advancement in fertility research.
Assisted ...
Vast majority of Trump voters believe American values and prosperity are ‘under threat’
2024-11-11
Almost nine out of ten voters who supported Donald Trump for US President believe that America’s values, traditions and future economic prosperity are under threat – double the number of Kamala Harris supporters.
This is according to new data from Cambridge University’s Political Psychology lab, who worked with YouGov to conduct an opinion poll of US voters shortly before the election.*
Some 89% of Trump voters agree that “American values and beliefs are being undermined and cherished traditions are under threat” compared ...
Scientists investigate if red grape chemical can keep bowel cancer at bay
2024-11-11
Cancer Research UK-funded scientists are finding out if an ingredient commonly found in grape juice and wine could keep bowel cancer at bay.
Resveratrol – a naturally occurring ingredient found in grapes, blueberries, raspberries and peanuts – will be tested as a potential cancer prevention drug as part of the Cancer Research UK-funded COLO-PREVENT trial.
The trial is led from the University of Leicester and the National Institute for Health and Social Care Research (NIHR) Leicester Biomedical Research Centre.
The trial ...
The refrigerator as a harbinger of a better life
2024-11-09
To get a good sense of a country’s level of development, you need to look at the items people have in their homes, according to economists Rutger Schilpzand and Jeroen Smits from Radboud University. Research on low- and middle-income countries often focuses on income, health or education, but that doesn’t tell you the full story of a country’s situation. ‘That’s why, for the first time, we are mapping out how the material wealth of households is developing,’ Schilpzand explains. The researchers coin this material wealth growth for households the 'domestic transition'. ...
Windfall profits from oil and gas could cover climate payments
2024-11-09
A central issue at the UN Climate Change Conference, set to start on November 11, will be the negotiations on new payments from industrialized nations to poorer countries. However, the question of whether and how these payments will be financed remains highly controversial. The study by an international team of researchers, with participation by the Technical University of Munich (TUM), has now revealed: The windfall profits alone taken in by oil and gas companies due to the 2022 energy crisis would have been sufficient to cover the existing commitments of the industrialized nations for nearly five years. The researchers ...
Heartier Heinz? How scientists are learning to help tomatoes beat the heat
2024-11-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — By studying tomato varieties that produce fruit in exceptionally hot growing seasons, biologists at Brown University identified the growth cycle phase when tomatoes are most vulnerable to extreme heat, as well as the molecular mechanisms that make the plants more heat tolerant.
The discovery, detailed in a study in Current Biology, could inform a key strategy to protect the food supply in the face of climate instability, the researchers said. Agricultural productivity is particularly vulnerable to climate change, the study noted, and rising temperatures are predicted to reduce crop yields by 2.5% to 16% for every ...
Breaking carbon–hydrogen bonds to make complex molecules
2024-11-08
A team of scientists led by Caltech and Emory University has synthesized a highly complex natural molecule using a novel strategy that functionalizes normally nonreactive bonds, called carbon–hydrogen (C–H) bonds. The work demonstrates a new category of reactions that organic chemists can consider as they work to create natural products that could be used in pharmaceuticals or new materials, or to produce organic chemicals in more sustainable ways.
"This work moves the field forward by showing the power of C–H functionalization," says ...
Sometimes you're the windshield: Utah State University researcher says vehicles cause significant bee deaths
2024-11-08
LOGAN, UTAH, USA -- When a large mammal such as a deer or a moose is struck by a motor vehicle, the damage is usually dramatic. To reduce these unfortunate events, transportation officials have teamed with wildlife researchers to place warning signs, and to construct wildlife underpasses and overpasses, to mitigate mishaps along animal migration paths.
In contrast, collisions with much smaller bees often go unnoticed or are perceived by motorists as simply an annoying splat on a windshield. The significance, Utah State University ...
AMS Science Preview: Turbulence & thunderstorms, heat stress, future derechos
2024-11-08
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form.
Below is a selection of articles published early online recently. Some articles are open-access; to view others, members of the media can contact kpflaumer@ametsoc.org for press login credentials.
JOURNAL ARTICLES
A New Heat Stress Index For Climate Change Assessment
Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society
Heat Index may dramatically underestimate heat stress in extreme temperatures. This work compares the ...
Study of mountaineering mice sheds light on evolutionary adaptation
2024-11-08
Teams of mountaineering mice are helping advance understanding into how evolutionary adaptation to localized conditions can enable a single species to thrive across diverse environments.
In a study led by Naim Bautista, a postdoctoral researcher in Jay Storz’s lab at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, the team took highland deer mice and their lowland cousins on a simulated ascent to 6,000 meters. The “climb” ventured from sea level and the mice reached the simulated summit seven weeks later. Along the way, Bautista tracked how the mice responded to cold stress at progressively lower oxygen levels.
“Deer ...
Geologists rewrite textbooks with new insights from the bottom of the Grand Canyon
2024-11-08
LOGAN, UTAH, USA – Any boomer, gen xer, millennial, gen zer or alpha who’s studied geology has likely gained foundational knowledge from Edwin Dinwiddie McKee’s landmark studies of the Grand Canyon’s sedimentary record – even if they don’t readily recognize McKee’s name.
The legendary scientist, who lived from 1906-1984, studied and documented the stratigraphy and sedimentation of Colorado Plateau geology, especially the Grand Canyon’s Cambrian Tonto Group, for more than 50 years. His time-tested ...
MSU researcher develops promising new genetic breast cancer model
2024-11-08
A Michigan State University researcher’s new model for studying breast cancer could help scientists better understand why and where cancer metastasizes.
Professor https://directory.natsci.msu.edu/Directory/Profiles/Person/103559 who teaches in the MSU Department of Physiology, has been researching the E2F5 gene, of which little is known, and its role in the development of breast cancer. Based on findings from Andrechek’s lab, the loss of E2F5 results in altered regulation of Cyclin D1, a protein linked to metastatic breast tumors after long ...
McCombs announces 2024 Hall of Fame inductees and rising stars
2024-11-08
AUSTIN, Texas — Friends and distinguished alumni of the McCombs School of Business at The University of Texas at Austin inducted four alumni into the school’s Hall of Fame on Nov. 7 at the AT&T Hotel and Conference Center. This year’s honorees are Christopher Bake, BBA ’88; Ray Brimble, B.A. ’74; Bennett Glazer, BBA ’68; and Brien Smith, BBA ’79, MPA '81. McCombs Dean Lillian Mills also recognized 2024 Rising Stars Simeon Bochev, MSF ’13; Michael Ginnings, BBA ’09; and Gerardo Guardado, MBA ’10.
The ...
Stalling a disease that could annihilate banana production is a high-return investment in Colombia
2024-11-08
There’s no cure for a fungal disease that could potentially wipe out much of global banana production. Widespread adoption of cement paths, disinfection stations, and production strategies could net 3-4 USD of benefits for each dollar invested in Colombia.
Hundreds of millions of dollars in banana exports from Colombia are at risk due to a fungal disease best known as Tropical Race 4 (TR4). First detected in Asia in the 1990s, the Fusarium fungus that causes the disease arrived in Colombia in 2019, completing its inevitable global spread to South America, the last major banana production continent that remained TR4-free. Researchers are confident ...
[1] ... [839]
[840]
[841]
[842]
[843]
[844]
[845]
[846]
847
[848]
[849]
[850]
[851]
[852]
[853]
[854]
[855]
... [8835]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.