The secrets of fossil teeth revealed by the synchrotron: a long childhood is the prelude to the evolution of a large brain
2024-11-13
The secrets of fossil teeth revealed by the synchrotron: a long childhood is the prelude to the evolution of a large brain
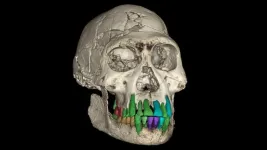
Could social bonds be the key to human big brains? A study of the fossil teeth of early Homo from Georgia dating back 1.77 million years reveals, thanks to the European Synchrotron (ESRF) in Grenoble, a prolonged childhood despite a small brain and an adulthood comparable to that of the great apes. This discovery suggests that an extended childhood, combined with cultural transmission ...
Obesity-fighting drugs may reduce alcohol consumption in individuals with alcohol use disorder
2024-11-13
A new joint study by the University of Eastern Finland and Karolinska Institutet in Sweden found that the GLP-1 agonists semaglutide and liraglutide, which are used for treating diabetes and obesity, were associated with fewer hospitalisations among individuals with alcohol use disorder, AUD. Fewer hospitalisations were observed for alcohol related causes, substance use related causes, and for physical illnesses. However, no association was observed for hospitalisations due to attempted suicide.
Effective treatments for alcohol dependence exist; however, they remain underused and are not effective, or suitable, for all patients with alcohol or substance use disorder. Previous ...
Does AI improve doctors’ diagnoses? Study puts it to the test
2024-11-13
With hospitals already deploying artificial intelligence to improve patient care, a new study has found that using Chat GPT Plus does not significantly improve the accuracy of doctors’ diagnoses when compared with the use of usual resources.
The study, from UVA Health’s Andrew S. Parsons, MD, MPH and colleagues, enlisted 50 physicians in family medicine, internal medicine and emergency medicine to put Chat GPT Plus to the test. Half were randomly assigned to use Chat GPT Plus to diagnose complex cases, while the other half relied on conventional methods such as medical reference sites (for example, UpToDate©) and Google. The researchers then compared the resulting ...
Extreme weather accelerates nitrate pollution in groundwater
2024-11-13
Extreme weather spurred by climate change, including droughts and heavy rains, may increase the risk of nitrates from fertilizers ending up in groundwater, according to a recent study from researchers at the University of California, Davis. The study found heavy rains after a drought caused nitrates to seep 33 feet under farm fields in as little as 10 days. The study was published in Water Resources Research.
“The conventional wisdom was that it could take several weeks to years for nitrates to move from the crop root zones to reach groundwater,” said corresponding author Isaya Kisekka, a professor in the Departments ...
Burden of liver cancer attributable to hepatitis B and alcohol globally, in China, and for five sociodemographic index regions from 1990 to 2021
2024-11-13
Background and Aims
Liver cancer is a digestive system malignancy that poses a significant public health challenge globally. This study aimed to analyze and compare the epidemiological trends of liver cancer attributed to hepatitis B (LCHB) and alcohol use (LCAL) over the past 32 years.
Methods
Data on mortality and disability-adjusted life years for LCHB and LCAL in China, globally, and across five sociodemographic index regions were obtained from the Global Burden of Disease 2021 database and comprehensively ...
Lehigh partners with North Carolina A&T to enhance flood damage mapping with AI and advanced radar
2024-11-13
One only needs to glance at the news, social media, or even just out the window to understand the devastation caused by flooding. Recent back-to-back major hurricanes have brought catastrophic rainfall that has devastated communities across the southeastern United States.
With climate change, experts predict these extreme weather events will increasingly become the norm. Among the many ways that researchers are devising strategies to protect and assist vulnerable areas, one such effort involves increasing the speed and accuracy of damage assessments.
“Research ...
2024 AAAS Kavli Science Journalism Award winners named
2024-11-13
Stories on the discovery of vital fluid-transport systems in the human body are among the winners of the 2024 AAAS Kavli Science Journalism Awards. Winning journalists also did immersive stories on scientists and physicians at work – in the field, in the lab and in the emergency room.
Independent panels of science journalists select the winners of the awards, which are administered by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and endowed by The Kavli Foundation. There is a Gold Award ($5,000) and Silver Award ($3,500) for each of the eight categories. The global awards program drew entries ...
Collaborative of prominent academic institutions launches groundbreaking healthcare AI challenge
2024-11-13
Mass General Brigham AI is hosting the Healthcare AI Challenge, a multi-institutional virtual, interactive series of events where healthcare professionals can explore and assess the latest AI healthcare technologies in real-world healthcare scenarios.
The Healthcare AI Challenge Collaborative is launching with a diverse set of healthcare institutions and their healthcare professionals, including Mass General Brigham; Emory Healthcare; the Department of Radiology at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health; and the Department of Radiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine. The American College of Radiology (ACR), ...
American Federation for Aging Research announces 2024 AFAR grants for junior faculty
2024-11-13
NEW YORK, NY— The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) is pleased to announce the recipients of its 2024 AFAR Grants for Junior Faculty. The AFAR Grants for Junior Faculty program provides up to $150,000 for a one- to two-year award to junior faculty (MDs and PhDs) to conduct research that will serve as the basis for longer term research efforts on the biology of aging. The major goal of this program is to assist in the development of the careers of early career investigators committed to pursuing careers in aging research. Selected through ...
Potential single-dose smallpox and mpox vaccine moves forward
2024-11-13
Highlights:
An FDA-approved vaccine for smallpox and mpox is effective but causes side effects. The other requires multiple doses.
An experimental single-dose vaccine uses the horsepox virus to harness the benefits of both strategies.
Previous studies suggest that inoculation with horsepox elicits an antibody response to mpox and provides 100% protection in animal models.
New data show that the horsepox virus is significantly more attenuated, or weakened, compared to the virus used in the FDA-approved live virus vaccine.
Washington, D.C.—Vaccines that prevent smallpox and mpox come in 2 varieties. One uses a single shot of a live virus but ...
Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute names Spark Grant recipients
2024-11-13
The Mass General Brigham Gene and Cell Therapy Institute, a hub of innovation dedicated to accelerating groundbreaking research, conducting clinical trials and developing FDA-approved treatments, today announced four winning project groups, consisting of seven individuals, of its second annual Spark Grant program. The program was created to fund gene and cell therapy projects by Mass General Brigham investigators that demonstrate tangible advancements towards clinical applications and commercialization outcomes, including licensing, partnerships, or new company creation. A total of $1,150,000 ...
New discovery may lead to more effective treatment for cardiovascular disease
2024-11-13
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have identified a new target to treat atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque clogs arteries and causes major cardiac issues, including stroke and heart attack.
In a new study, published in the journal Cell Reports, they identified an inflammation-reducing molecule—called itaconate (ITA)—that could be the foundation of a new approach to treat such a common and deadly disease.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for ...
Developing advanced recycling technology to restore spent battery cathode materials
2024-11-13
A research team led by Dr. Jung-Je Woo at the Gwangju Clean Energy Research Center of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) has successfully developed a cost-effective and eco-friendly technology for recycling cathode materials* from spent lithium-ion batteries.
*Cathode Materials: Materials that play a crucial role in generating electricity by storing and releasing lithium ions during battery charging and discharging.
With the recent rise in electric vehicles and mobile devices, managing spent batteries has become a critical global challenge. By 2040, the number of decommissioned electric vehicles is expected to exceed 40 million*, leading ...
An advance toward inhalable mRNA medications, vaccines
2024-11-13
Most people don’t enjoy getting shots for treatments or vaccines. So, researchers are working to create more medicines, such as those made from messenger RNA (mRNA), that can be sprayed and inhaled. A study in the Journal of the American Chemical Society reports steps toward making inhalable mRNA medicines a possibility. Researchers outline their improved lipid-polymer nanoparticle for holding mRNA that is stable when nebulized and successfully delivers aerosols (liquid droplets) in mice’s lungs.
mRNA ...
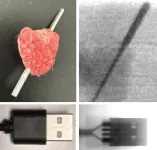
A step toward safer X-rays with new detector technology
2024-11-13
X-rays are a common component of diagnostic testing and industrial monitoring, used for everything from monitoring your teeth to scanning your suitcase at the airport. But the high-energy rays also produce ionizing radiation, which can be dangerous after prolonged or excessive exposures. Now, researchers publishing in ACS Central Science have taken a step toward safer X-rays by creating a highly sensitive and foldable detector that produces good quality images with smaller dosages of the rays.
“This advancement reduces detection limits and paves the way for safer and more energy-efficient medical imaging and industrial monitoring,” says Omar F. Mohammed, ...
On the origin of life: How the first cell membranes came to exist
2024-11-13
Few questions have captivated humankind more than the origin of life on Earth. How did the first living cells come to exist? How did these early protocells develop the structural membranes necessary for cells to thrive and assemble into complex organisms?
New research from the lab of University of California San Diego Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry Neal Devaraj has uncovered a plausible explanation involving the reaction between two simple molecules. This work appears in Nature Chemistry.
Life on Earth ...
New evidence-based information from NCCN offers tangible and moral support for people trying to quit smoking
2024-11-13
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [November 13, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers—today announced the publication of a new patient guideline designed to provide critical support and guidance for individuals with cancer who are seeking to quit smoking. Continued smoking elevates the risk of developing additional cancers, reduces the effectiveness of treatment, exacerbates treatment side effects, and is associated with shorter survival. The new NCCN Guidelines for Patients®: Quitting Smoking explains how to best use the tools that exist to help anyone quit ...
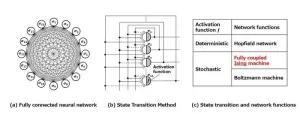
Solving complex problems faster: Innovations in Ising machine technology
2024-11-13
Computers are essential for solving complex problems in fields, like scheduling, logistics, and route planning, but traditional computers struggle with large-scale combinatorial optimization, as they can’t efficiently process vast numbers of possibilities. To address this, researchers have explored specialized systems.
One such system is the Hopfield network, a significant artificial intelligence breakthrough from 1982, proven in 1985 to solve combinatorial optimization by representing solutions as energy levels and naturally finding the lowest energy, or optimal, solution. ...
Grief-specific cognitive behavioral therapy vs present-centered therapy
2024-11-13
About The Study: This randomized clinical trial demonstrates that cognitive behavioral therapy for prolonged grief was superior to present-centered therapy after treatment and at follow-up with regard to comorbid symptoms. Both treatments were shown to be effective and acceptable, showing the potential for dissemination and increasing patient choice.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rita Rosner, PhD, email rita.rosner@ku.de.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
New species discovered with refined DNA technology
2024-11-13
Sometimes plants are so similar to each other that the methods developed by 18th century scientist Carl Linnaeus for identifying species are not enough. In a thesis from the University of Gothenburg, completely new species of daisies have been discovered when analysed using modern DNA technology.
There are currently estimated to be around 8.7 million different species on Earth, of which around 2.2 million are found in the oceans. Many species can be identified in the classical way, by their physical characteristics, the morphology. For over a decade, botanists and zoologists have also been using DNA sequencing to more accurately identify species. ...
C-PATH announces Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD) initiative
2024-11-13
INFORMATION EMBARGOED UNTIL WEDNESDAY, NOV. 13, 2024, 7 a.m. ET
C-Path Announces Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD) Initiative
C-Path expands its worldwide leadership in accelerating drug development in neurology; seeks additional collaborators to broaden impact.
TUCSON, Ariz., November 13, 2024 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) today announced a landmark initiative, Gender Equitable Medicines for Parkinson's Disease (GEM-PD), dedicated to globally ...
Faster flowing glaciers could help predict nearby volcanic activity
2024-11-13
Glaciers that are within three miles of a volcano move nearly 50% quicker than average, a new study has found, which could help create early warning of future eruptions.
In a new article published in Communications Earth & Environment today, researchers from the University of Aberdeen, University of Birmingham and Manchester Metropolitan University analysed velocity data from 85% of the world’s approximately 217,000 glaciers. After controlling for factors such as climate, ice thickness and surface slope, the team found that glaciers near active volcanoes typically flowed 46% faster than other glaciers.
Glaciers ...
MIT engineers make converting CO2 into useful products more practical
2024-11-13
As the world struggles to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, researchers are seeking practical, economical ways to capture carbon dioxide and convert it into useful products, such as transportation fuels, chemical feedstocks, or even building materials. But so far, such attempts have struggled to reach economic viability.
New research by engineers at MIT could lead to rapid improvements in a variety of electrochemical systems that are under development to convert carbon dioxide into a valuable commodity. ...
Primary care professionals key to helping people achieve & maintain heart health
2024-11-13
Statement Highlights:
A new scientific statement outlines the role of primary care professionals in helping their patients achieve Life’s Essential 8, the key measures for improving and maintaining cardiovascular health defined by the American Heart Association.
The new statement highlights how primary care clinicians can help patients follow and maintain the Association’s Life’s Essential 8 health metrics for optimal cardiovascular health, which includes four health behaviors (diet, physical activity, nicotine exposure and sleep) and four health ...
Early detection, intensive treatment critical for high-risk patients with Kawasaki Disease
2024-11-13
Embargoed until 4:00 a.m. CT/5:00 a.m. ET Wed., Nov. 13, 2024
DALLAS, Nov. 13, 2024 — Advances in cardiac imaging techniques and risk categorization have led to improvements in diagnosis, initial treatment and long-term management of patients with Kawasaki Disease, according to a new scientific statement published today in the American Heart Association’s flagship, peer-reviewed journal Circulation.
The new statement, “Update on Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease,” summarizes the data published since the 2017 American Heart Association Scientific Statement ...
[1] ... [833]
[834]
[835]
[836]
[837]
[838]
[839]
[840]
841
[842]
[843]
[844]
[845]
[846]
[847]
[848]
[849]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.