New drug targets for Alzheimer’s identified from cerebrospinal fluid
2024-11-14
A multitude of genes have been linked to the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Specifically how those genes might influence the progression of neurodegeneration remains something of a black box though, in part because of the challenges of examining in molecular detail the brain of a living patient.
Using cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collected from living patients, a team of researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has for the first time linked disease-related proteins and genes to identify specific cellular pathways responsible for Alzheimer’s ...
Neuro-oncology experts reveal how to use AI to improve brain cancer diagnosis, monitoring, treatment
2024-11-14
INDIANAPOLIS — An international, multidisciplinary team of leading neuro-oncology researchers and clinicians has released new recommendations for good clinical practice — a set of guidelines that helps ensure clinical trial results are reliable, and patients are protected — regarding the use of artificial intelligence methods to more accurately diagnose, monitor and treat brain cancer patients.
The team recently published two companion policy reviews in The Lancet Oncology, on behalf of the ...
Argonne to explore novel ways to fight cancer and transform vaccine discovery with over $21 million from ARPA-H
2024-11-14
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory will use its world-leading capabilities in artificial intelligence (AI) and high performance computing to research novel ways to fight cancer and transform vaccine discovery.
The two awards, totaling up to $21.7 million, are from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H), part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Established in 2022, ARPA-H’s mission is to accelerate transformative ...
Firefighters exposed to chemicals linked with breast cancer
2024-11-14
It’s well documented that firefighters have significantly higher rates of cancer than the general population, and these elevated rates have been associated with exposures to toxic chemicals on the job. However, most research on cancer in firefighters has been done in men and less is known about the risks in women.
Now a new study by Silent Spring Institute has identified multiple chemical exposures that firefighters face on the job that could increase their risk of developing breast cancer.
“With more and more women entering the profession, it’s important to understand the impact of workplace exposures on their health so that we can inform policies to reduce ...
Addressing the rural mental health crisis via telehealth
2024-11-14
The Medical University of South Carolina has been awarded $1.75 million from the Health Resources and Services Administration to develop and test the effectiveness and sustainability of the SC Rural Telehealth-enabled Collaborative Care Network (SC-RTECC). The SC-RTECC will deliver psychiatric collaborative care management to 1500 primary care patients over a five-year period in seven diverse, rural, underserved South Carolina counties.
The goal of the project is to test whether telehealth can be used to deliver psychiatric collaborative care management efficiently and sustainably at rural primary care clinics in South Carolina.
The project will be led by Ryan ...
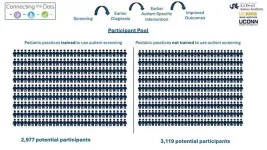
Standardized autism screening during pediatric well visits identified more, younger children with high likelihood for autism diagnosis
2024-11-14
New research from Drexel University’s A.J. Drexel Autism Institute found that the use of standardized autism screening during pediatric well-child visits identifies more children with high autism likelihood at a younger age, including those presenting with more subtle symptoms. This is the first large-scale, randomized trial to test the impact of standardized autism screening on early detection of autism in pediatric primary care.
Recently published in the Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychology, the multi-site ...
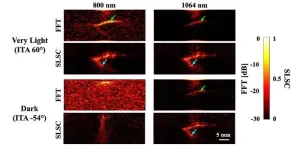
Researchers shed light on skin tone bias in breast cancer imaging
2024-11-14
Breast cancer is a major health concern worldwide, and early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Traditional imaging methods, such as mammography, have limitations, especially for women with dense breast tissue. Photoacoustic imaging, which combines light and sound to create detailed images of breast tissue, offers a promising alternative. However, recent research has highlighted a significant challenge: skin tone bias.
A team of researchers from Johns Hopkins University recently investigated how skin tone affects the visibility of breast cancer targets in photoacoustic imaging. As reported in Biophotonics Discovery, the study focused on three image ...
Study finds humidity diminishes daytime cooling gains in urban green spaces
2024-11-14
Urban green spaces provide shade for city dwellers facing rising temperatures brought on by climate change, but how much relief from the heat island effect do they provide when humidity is factored in?
The temperature and humidity effect cancel each other out during daylight hours, but green spaces provide a net reduction in humid heat at night, according to a new study in Nature Cities, co-authored by Yale School of the Environment doctoral student Yichen Yang and Xuhui Lee, Sara Shallenberger Brown Professor of Climate Science.
"When it comes to urban ...
Tennessee RiverLine secures $500,000 Appalachian Regional Commission Grant for river experience planning and design standards
2024-11-14
The Tennessee RiverLine, an initiative of University of Tennessee Extension, has been awarded a $500,000 Area Development grant from the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) and Tennessee Department of Economic and Community Development to support the development of comprehensive Planning and Design Standards. These standards will help accelerate the creation of new river experience amenities along the 652-mile stretch of the Tennessee River, benefitting residents and visitors throughout the region.
The 18-month project will be led by a professional ...
AI tool ‘sees’ cancer gene signatures in biopsy images
2024-11-14
To determine the type and severity of a cancer, pathologists typically analyze thin slices of a tumor biopsy under a microscope. But to figure out what genomic changes are driving the tumor’s growth — information that can guide how it is treated — scientists must perform genetic sequencing of the RNA isolated from the tumor, a process that can take weeks and costs thousands of dollars.
Now, Stanford Medicine researchers have developed an artificial intelligence-powered computational program that can predict the activity of thousands of genes within tumor cells based only on standard microscopy images of the biopsy. The tool, described online in Nature Communications Nov. 14, ...
Answer ALS releases world's largest ALS patient-based iPSC and bio data repository
2024-11-14
Answer ALS Releases World's Largest ALS Patient-Based iPSC and Bio Data Repository
Unprecedented resource, created with Cedars-Sinai, to accelerate ALS research and drive development of targeted therapies globally
NEW ORLEANS, [November 14, 2024] — In a landmark continuing collaboration, Answer ALS and Cedars-Sinai have announced the completed availability of the largest amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patient-based induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) and bio data repository. The repository encompasses biological and clinical data from nearly 1,000 ALS patients, offering an unprecedented resource for global ...
2024 Joseph A. Johnson Award Goes to Johns Hopkins University Assistant Professor Danielle Speller
2024-11-14
WASHINGTON, Nov. 14, 2024 – AIP and the National Society of Black Physicists congratulate Danielle Speller as the winner of the 2024 Joseph A. Johnson Award for Excellence. Jessica Esquivel is also being recognized with an Honorable Mention.
The Johnson Award, now in its fifth year, is given jointly by AIP and NSBP to recognize early-career scientists who demonstrate scientific ingenuity and impactful mentorship and service—the core values of NSBP founder Joseph A. Johnson.
“Dr. Speller not only ...
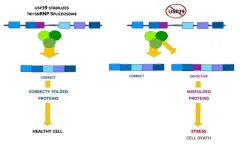
Slow editing of protein blueprints leads to cell death
2024-11-14
FRANKFURT. Genes contain the essential building instructions for life, guiding cells on which amino acids to assemble in what sequence to produce specific proteins. The human genome codes for about 20,000 such instructions. “Nevertheless, our cells can produce several hundred thousand different proteins,” explains Prof. Ivan Đikić from the Institute of Biochemistry II at Goethe University Frankfurt.
This diversity is enabled by a process known as “splicing.” When a cell requires a protein, it generates a copy of the relevant instructions in the cell nucleus. During splicing, this transcript undergoes modification: a cellular editing complex, the spliceosome, ...
Industrial air pollution triggers ice formation in clouds, reducing cloud cover and boosting snowfall
2024-11-14
Pollution from industrial hotspots can trigger ice formation in supercooled clouds, altering their reflective properties and increasing regional snowfall, according to a new study. The findings shed light on poorly understood impacts of anthropogenic aerosols on climate and could help improve climate modeling and mitigation strategies. The impact of human-generated aerosols (tiny air pollution particles) on climate, particularly in counteracting greenhouse gas-induced warming, remains uncertain. These aerosols, in addition to influencing cloud formation as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), may also act as ice-nucleating particles (INPs), crucial for ice formation in supercooled ...
Emerging alternatives to reduce animal testing show promise
2024-11-14
In a Policy Forum, Chad Nelson and colleagues highlight the efforts of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in advancing alternative methods to reduce animal testing for regulatory use. Animal studies have been crucial for advancing disease understanding, developing therapies, and assessing the safety and effectiveness of consumer products. However, reducing animal use and developing effective alternatives is an ongoing priority. Although advances in biology, engineering, and artificial intelligence offer new opportunities to improve product safety assessments, these technologies require extensive development to meet regulatory ...
Presenting Evo – a model for decoding and designing genetic sequences
2024-11-14
A new study presents “Evo” – a machine learning model capable of decoding and designing DNA, RNA, and protein sequences, from molecular to genome scale, with unparalleled accuracy. Evo’s ability to predict, generate, and engineer entire genomic sequences could change the way synthetic biology is done. “The ability to predict the effects of mutations across all layers of regulation in the cell and to design DNA sequences to manipulate cell function would have tremendous diagnostic and therapeutic implications for disease,” writes Christina Theodoris ...
Global plastic waste set to double by 2050, but new study offers blueprint for significant reductions
2024-11-14
Without intervention, global plastic waste could double by 2050, a new machine learning study predicts. However, according to simulations by the study’s authors, a mix of policy interventions could cut plastic waste by more than 90% and it could cut plastics-related emissions by a third. With UN treaty negotiations underway, these findings provide a crucial blueprint for tackling the plastic crisis. Plastic production has increased relentlessly for decades, leading to surging plastic waste generation and environmental mismanagement. As plastic ...
Industrial snow: Factories trigger local snowfall by freezing clouds
2024-11-14
Anthropogenic aerosols, tiny solid and liquid air pollution particles, have masked a fraction of global warming caused by anthropogenic greenhouse gases. Climate researchers have known for decades that anthropogenic aerosols perturb liquid clouds by enabling the formation of a larger number of cloud droplets, making clouds brighter. A new landmark study led by the University of Tartu suggests that anthropogenic aerosols may also influence clouds by converting cloud droplets to ice at temperatures below zero degrees Celsius.
Powerplant Snow
Using satellite observations, climate researchers discovered unique plumes of ice clouds and reduced cloud cover downwind of industrial hot spots ...
Backyard birds learn from their new neighbors when moving house
2024-11-14
Scientists have found a trigger for social learning in wild animals. An experiment on great tits has pinpointed a single factor—immigration—that can cause birds to pay close attention to others, leading them to rapidly adopt useful behaviors. The study is the first to provide experimental support of a long-held assumption that immigrants should strategically use social learning. The study, conducted by scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior (MPI-AB) and the Cluster of Excellence Collective Behaviour at the University of Konstanz in Germany, is published November 14 in PLOS Biology.
Many animals that live in groups learn from one another, but few ...
New study in Science finds that just four global policies could eliminate more than 90% of plastic waste and 30% of linked carbon emissions by 2050
2024-11-14
Berkeley, CA/Santa Barabara, CA (14 November 2024) — A new study released in Science today determines that just four policies can reduce mismanaged plastic waste — plastic that isn’t recycled or properly disposed of and ends up as pollution — by 91% and plastic-related greenhouse gasses by one-third. The policies are: mandate new products be made with 40% post-consumer recycled plastic; cap new plastic production at 2020 levels; invest significantly in plastic waste management — such as landfills and waste collection services; and implement a small fee on plastic packaging. ...
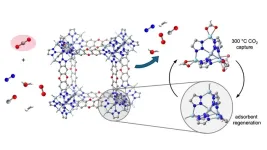
Breakthrough in capturing 'hot' CO2 from industrial exhaust
2024-11-14
Industrial plants, such as those that make cement or steel, emit copious amounts of carbon dioxide, a potent greenhouse gas, but the exhaust is too hot for state-of-the-art carbon removal technology. Lots of energy and water are needed to cool the exhaust streams, a requirement that has limited adoption of CO2 capture in some of the most polluting industries.
Now, chemists at the University of California, Berkeley, have discovered that a porous material can act like a sponge to capture CO2 at temperatures close to those of many industrial exhaust streams. ...
New discovery enables gene therapy for muscular dystrophies, other disorders
2024-11-14
Gene therapy can effectively treat various diseases, but for some debilitating conditions like muscular dystrophies there is a big problem: size. The genes that are dysfunctional in muscular dystrophies are often extremely large, and current delivery methods can’t courier such substantial genetic loads into the body. A new technology, dubbed “StitchR,” surmounts this obstacle by delivering two halves of a gene separately; once in a cell, both DNA segments generate messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that join seamlessly together to restore expression of a protein that is missing or inactive in disease.
Published in ...
Anti-anxiety and hallucination-like effects of psychedelics mediated by distinct neural circuits
2024-11-14
New research suggests that it could be possible to separate treatment from hallucinations when developing new drugs based on psychedelics. The anti-anxiety andhallucination-inducing qualities of psychedelic drugs work through different neural circuits, according to research using a mouse model. The work is published Nov. 15 in Science.
The research shows that decoupling the beneficial effects of psychedelics from their hallucinogenic effects isn’t just a matter of chemical compound design. It’s a matter of targeted neural circuitry.
“In the past, we did this using chemistry by making new compounds, but here we focused on identifying the circuits responsible ...
How do microbiomes influence the study of life?
2024-11-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Microorganisms — bacteria, viruses and other tiny life forms — may drive biological variation in visible life as much, if not more, than genetic mutations, creating new lineages and even new species of animals and plants, according to Seth Bordenstein, director of Penn State’s One Health Microbiome Center, professor of biology and entomology, and the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Endowed Chair in Microbiome Sciences. Bordenstein and 21 other scientists from around the world published a paper in the leading journal Science, summarizing research that they said drives a deeper understanding of biological ...
Plant roots change their growth pattern during ‘puberty’
2024-11-14
Ghent, November 15, 2024 – Understanding how roots grow can help us develop plants that, for example, are more resistant to drought. Research by Prof. Bert De Rybel’s team (VIB-UGent), in collaboration with the VIB Screening Core and Ghent University, uncovers how roots go through a puberty phase, which could have important implications for developing climate-resilient agriculture. Their work appears in Science.
Plant puberty
Plants, like all living organisms, transition through various developmental stages, starting as a seed, becoming a shoot, and eventually a full-grown, fertile plant. They even go through a sort of ‘puberty’ ...
[1] ... [829]
[830]
[831]
[832]
[833]
[834]
[835]
[836]
837
[838]
[839]
[840]
[841]
[842]
[843]
[844]
[845]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.