Breaking free from negative thoughts using a scientifically gamified app
2024-11-11
(Toronto, November 11, 2024) A new study published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research by JMIR Publications reveals promising results from a digital health intervention that is based on a decade of research at Harvard Medical School and designed to alleviate depressive symptoms. The study, titled "Facilitating Thought Progression to Reduce Depressive Symptoms: Randomized Controlled Trial," found that participants experienced substantial reduction of depressive symptoms by using a gamified mobile app focused on disrupting ruminative thinking.
Led by Prof. Moshe Bar and colleagues, the research ...
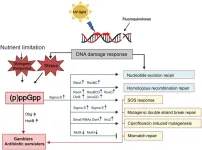
The emerging role of (p)ppGpp in DNA repair and associated bacterial survival against fluoroquinolones
2024-11-11
Bacteria frequently encounter adverse environmental conditions, such as nutrient scarcity and antibiotic exposure, which can induce DNA damage. Efficient DNA repair mechanisms are essential for bacterial survival, particularly under such stress conditions. A critical player in these processes is the signaling molecule (p)ppGpp, a phosphorylated guanosine synthesized by bacteria during periods of stress. Initially discovered in Escherichia coli under amino acid starvation, (p)ppGpp is now recognized for its broader roles in modulating cellular functions essential for DNA repair and stress response. By regulating diverse cellular processes, (p)ppGpp not ...
People with fewer resources seen as less trustworthy across cultures, new research shows
2024-11-11
New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science identifies a widespread stereotype linking wealth to perceived trustworthiness across diverse cultures. The research, led by Mélusine Boon-Falleur from the Center for Research on Social Inequalities at Sciences Po in Paris, shows that individuals with fewer material resources are consistently viewed as less trustworthy.
The study, conducted across eight countries including Brazil, Colombia, Democratic Republic of Congo, India, France, Nigeria, Philippines, and the United Kingdom, employed a novel method to uncover stereotypes while avoiding social desirability bias.
"People ...
Inland Delaware watersheds impaired by human waste
2024-11-11
Highlights:
Delaware watersheds show high microbial impairment.
Researchers collected samples from Delaware waters over 2 years and identified microbial DNA signatures present in the water.
The findings suggest that both treated and untreated human waste are the culprit, likely due to infrastructural issues.
Washington, D.C.—Delaware has numerous inland waterways with high microbial impairment from unknown sources. Now, a new study suggests that human waste, both treated and untreated, is responsible for the waterway impairment in these Delaware watersheds. The study was published in Applied and Environmental Microbiology, ...
Study on the ideas and methods of bloodletting therapy in the treatment of heat stroke
2024-11-11
Heat stroke is primarily classified into exertional and non-exertional forms. Exertional heat stroke results from strenuous physical activity in high heat, while non-exertional heat stroke typically affects those exposed to extreme heat without engaging in significant physical exertion. Symptoms include elevated body temperature, impaired consciousness, headaches, muscle spasms, and, in severe cases, cardiovascular overload, cerebral hypoxia, and organ failure. Western medicine’s primary treatments include cooling methods, rehydration, and pharmacological interventions like dexamethasone ...
New measures of patient well-being can be applied readily in clinical care
2024-11-11
Waltham — November 11, 2024 — Two measures of patient well-being, designed for use in busy clinical settings, are described in a Perspective piece in a supplement to Medical Care, the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The Medical ...
New study links historical redlining to delays in HIV treatment
2024-11-11
A new study from Tulane University finds that historical race-based lending practices are still impacting health today, linking these discriminatory policies to delays in effective HIV treatment within affected neighborhoods.
The lending practice, called redlining, was abolished in 1968. Yet, those living in once historically redlined neighborhoods experience 15% longer delays in achieving viral suppression of HIV compared to those in non-redlined areas, according to the study published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
The disparity can impact both individual ...
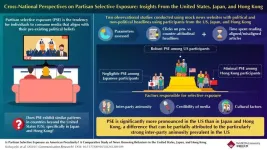
Understanding causes of echo chambers: Political news selective exposure across countries
2024-11-11
In our digital age, with easy access to a vast array of information, one would think that readers would naturally be exposed to a wide range of perspectives. However, the opposite seems to be happening, especially in countries like the United States (US), where people often seek out news that reinforces their existing beliefs and avoid content that challenges them. This tendency, known as partisan selective exposure, has been linked to increasing divides and tensions between different ideological groups. But is ...
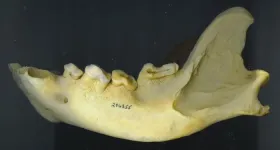
New study reveals unique adaptations of jaw function and tooth wear in hypercarnivores
2024-11-11
A new study led by Dr. Jack Tseng and published in PeerJ Life & Environment has shed light on the intricate relationship between tooth wear and jaw mechanics in highly carnivorous mammals, known as hypercarnivores. As mammalian teeth do not regenerate, these animals often face declining bite efficiency as their teeth wear down over time. This research explores how different hypercarnivorous species, including scavengers, meat specialists, and bone-cracking predators, adapt biomechanically and possibly behaviorally to manage the challenges posed by tooth wear.
The ...
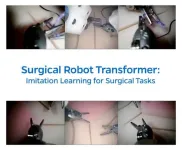
Robot that watched surgery videos performs with skill of human doctor
2024-11-11
A robot, trained for the first time by watching videos of seasoned surgeons, executed the same surgical procedures as skillfully as the human doctors.
The successful use of imitation learning to train surgical robots eliminates the need to program robots with each individual move required during a medical procedure and brings the field of robotic surgery closer to true autonomy, where robots could perform complex surgeries without human help.
“It’s really magical to have this model and all we do is feed it camera input and it can predict the robotic ...
“Emotional contagion” a factor in senior’s mental health
2024-11-11
Madeleine and Paul are sitting on a park bench. As she tells Paul about her financial worries and how she’s been struggling for months to make ends meet, Madeleine’s eyes well with tears. Paul is moved by her distress; her woes resonate with him and heighten his own fears. His heart grows heavy and his own eyes become moist, too.
What’s going on? A kind of behavioural mirroring, what psychologists call “emotional contagion.”
“Just as some people are more likely to catch a respiratory virus through close contact, others are more susceptible to ‘catching’ the emotions of the people around them,” explained Marie-Josée ...
Fear of another heart attack may be a major source of ongoing stress for survivors
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
Fear of another heart attack was a significant ongoing contributor to how heart attack survivors perceive their health, according to a new study.
While anxiety and depression are recognized as common conditions after a heart attack, they did not explain the impact of fear of recurrence in this study.
The researchers suggest that fear of another heart attack should be evaluated and addressed separately from depression and anxiety.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts presented at the American ...
Let’s talk about sex: Heart patients want guidance from health care professionals
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
A small survey of adults aged 30 to 89 (average age of 65) in Sweden who have heart conditions found that there is a significant difference between the sexual health information they seek and what is provided to them by their health care professionals and the health care system.
Despite 76% of patients with heart conditions reporting that sexual health affects their mood and well-being, only 5% received information or counseling about sexual health.
Researchers suggest health care professionals adjust their patient care practices to ensure that discussing sexual health becomes a standard and respected topic in health ...
Heart disease more common in past redlined areas linked to limited access to healthy foods
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
Heart disease, Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure and obesity were more common and linked to reduced access to healthy food among people who lived in neighborhoods previously subjected to structural racism-based policies that limited home ownership — an outlawed practice known as redlining.
Researchers say testing interventions to help improve access to healthy food or boost social and economic resources could mitigate the still-present impact of outdated policies like redlining.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts presented at American Heart Association’s scientific meetings are not peer-reviewed, and the ...
Heart disease could hit up to 28 years sooner for people with CKM syndrome
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
Scientists conducted a simulation study to estimate the impact of cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) syndrome on cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk prediction.
The study found that adults with chronic kidney disease would have elevated CVD risk eight years earlier than those without the disease. In addition, people with Type 2 diabetes would have an elevated CVD risk about a decade sooner than those without it.
Among adults with both Type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease, women ...
MESA heart disease risk score worked well with or without race included
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
A version of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) heart disease risk score that did not include race predicted heart disease risk just as well as the original version that includes race.
The original MESA risk score, developed in 2015[1], combines traditional risk factors, sex and race with a coronary artery calcium score.
The MESA formula without race may be used for people who identify with more than one racial or ethnic group or those who prefer not to disclose their race or ethnicity.
Note: The study featured in this ...
Bystander CPR up to 10 minutes after cardiac arrest may protect brain function
2024-11-11
This news release contains updated information and data not included in the abstract.
Research Highlights:
The sooner a lay rescuer (bystander) starts cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on a person having a cardiac arrest at home or in public, up to 10 minutes after the arrest, the better the chances of survival and brain protection, according to an analysis of nearly 200,000 out-of-hospital cardiac arrest cases in the U.S. from 2013 to 2022.
Among the study’s findings, people who received CPR within two minutes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest had 81% higher odds of survival to release from the hospital ...
911 dispatcher assistance improved chances of receiving bystander CPR
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
A study of nearly 2,400 cardiac arrest cases in North Carolina found that when emergency dispatchers (telecommunicators) provided cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) instructions to 911 callers, people were more likely to provide aid for both men and women.
The study’s findings indicate that when a telecommunicator provided assistance to callers, bystander CPR was performed 44% of the time on women and 40% on men, compared to 9% on women and 11% on men when telecommunicator assistance was not provided.
Researchers found the telecommunicator role critical in instructing bystanders to act quickly, possibly instrumental in reducing sex disparities ...
GLP-1, SGLT2 medications may lower stroke survivor’s risk of future heart attack, stroke
2024-11-11
Research Highlights:
In an analysis of more than 7,000 stroke survivors, those who were taking either a GLP1-receptor agonist or an SGLT2 inhibitor medication had a lower risk of a subsequent stroke, heart attack or death compared to peers who were not prescribed the medications during a three-year follow up period.
The analysis used health data from the Rochester Epidemiology Project collected from 2000 to 2022. The first GLP-1 medication was prescribed beginning in 2006, and the authors included cases beginning in 2000 to increase the power of the study, they noted.
Note: The study featured in this news release ...
TYK2 transforms tau from ‘good guy’ to a ‘bad guy’ that contributes to Alzheimer’s disease
2024-11-11
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital and collaborating institutions discovered that the enzyme TYK2 transforms the normal protein tau into one that accumulates in the brain and contributes to the development of Alzheimer’s disease in animal models. Published in Nature Neuroscience, the study suggests that partially restraining TYK2 could be a strategy to reduce tau levels and toxicity.
“Many studies have shown that the accumulation ...
Elephant seal colony declines one year after avian flu outbreak
2024-11-11
The sounds of barking elephant seals are again in the air along the breeding grounds of Península Valdés, Argentina—but it’s quieter. Almost exactly a year after a massive outbreak of H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza killed more than 17,000 elephant seals, including about 97% of their pups, scientists estimate that only about a third of the elephant seals normally expected here returned.
“It’s beautiful to walk the beaches now and hear elephant seals again,” said Marcela Uhart, director of the Latin America Program at the UC Davis Karen C. Drayer Wildlife Health Center within ...
While more is better, even moderate amounts of exercise may reduce risk for common heart condition
2024-11-11
Adding an extra hour every week of physical activity may lower the chance of developing the most common type of irregular heartbeat (arrythmia) by 11%, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health, the investigation focused on atrial fibrillation, a condition in which the heart’s upper two chambers beat rapidly and irregularly instead of at a consistent pace. If left untreated, this can lead to stroke, heart failure, and other issues. While past studies have linked exercise to reduced risk of this type of arrhythmia, nearly all of these analyses have relied on the participants’ ...
Researchers uncover new role of mutant proteins in some of the deadliest cancers
2024-11-11
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators have discovered a new way in which RAS genes, which are commonly mutated in cancer, may drive tumor growth beyond their well-known role in signaling at the cell surface. Mutant RAS, they found, helps to kick off a series of events involving the transport of specific nuclear proteins that lead to uncontrolled tumor growth, according to a study published November 11, 2024, in Nature Cancer.
RAS genes are the second most frequently mutated genes in cancer, and mutant RAS proteins are key drivers of some of the deadliest cancers, ...
Patients may become unnecessarily depressed by common heart medicine
2024-11-11
All patients who have had a heart attack are typically treated using beta blockers. According to a Swedish study conducted earlier this year, this drug is unlikely to be needed for those heart patients who have a normal pumping ability. Now a sub-study at Uppsala University shows that there is also a risk that these patients will become depressed by the treatment.
“We found that beta blockers led to slightly higher levels of depression symptoms in patients who had had a heart attack but were not suffering from heart failure. At the same time, beta blockers have no life-sustaining function for this group of patients,” says Philip Leissner, a doctoral student in cardiac ...
Largest T cell clinical trial in solid tumors heralds new era in precision immunotherapy
2024-11-11
The largest ever clinical trial of T cell therapy (a type of cell-based immunotherapy) for solid tumours has been completed.
Led by a Singapore clinician-investigator, the global, international, multisite trial recruited 330 advanced nasopharyngeal (NPC) cancer patients in 23 sites across Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Taiwan and the United States.
The trial did not show an overall survival benefit for the entire patient cohort but a subset analysis combining outcomes of US, Singapore and Taiwanese sites, showed better progression free survival ...
[1] ... [827]
[828]
[829]
[830]
[831]
[832]
[833]
[834]
835
[836]
[837]
[838]
[839]
[840]
[841]
[842]
[843]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.