New study links air pollution with higher rates of head and neck cancer
2024-11-12
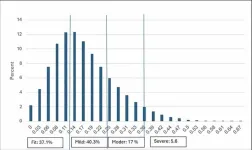
DETROIT — A recent study published in the journal Scientific Reports correlates higher levels of pollutant particulate matter to higher occurrences of head and neck aerodigestive cancer.
The article, "Air Pollution Exposure and Head and Neck Cancer Incidence," is the work of a multi-institutional collaboration with researchers from Wayne State University, Johns Hopkins University and Mass General Brigham.
The study was led by John Cramer, Ph.D., associate professor of otolaryngology, and John Peleman, M.D., medical resident in the Department of Otolaryngology, in the Wayne State University School of Medicine. They collaborated with Mass General Brigham, an integrated ...
LSU researchers excavate earliest ancient Maya salt works
2024-11-12
The team was led by LSU Alumni Professor Heather McKillop, who first discovered wooden buildings preserved there below the sea floor, along with associated artifacts, and the only ancient Maya wooden canoe paddle in 2004.
Her key collaborator, Assistant Professor Elizabeth Sills at the University of Texas at Tyler, began working with McKillop as a master’s student and then as a doctoral student at LSU.
Since their initial discovery of wood below the sea floor in Belize, the team has uncovered an extensive pattern of sites that include “salt kitchens” for boiling ...
Building a diverse wildland fire workforce to meet future challenges
2024-11-12
Every year around this time, California’s wildland firefighters hold their breath as hot, dry winds threaten to spread flames across the state. As such conflagrations grow in size and severity throughout the Western U.S., the strain on fire managers has intensified. A new report from Stanford University’s Climate and Energy Policy Program provides a blueprint for fostering a more inclusive, diverse and well-supported workforce to meet the increasing need for fire mitigation and management.
“The wellbeing of the wildland fire workforce has ...
MBARI researchers discover remarkable new swimming sea slug in the deep sea
2024-11-12
MBARI researchers have discovered a remarkable new species of sea slug that lives in the deep sea. Bathydevius caudactylus swims through the ocean’s midnight zone with a large gelatinous hood and paddle-like tail, and lights up with brilliant bioluminescence. The team published a description of the animal, nicknamed the “mystery mollusc,” in the journal Deep-Sea Research Part I.
“Thanks to MBARI’s advanced underwater technology, we were able to prepare the most comprehensive description of a deep-sea animal ever made. We’ve ...
Decentralized social media ‘increases citizen empowerment’, says Oxford study
2024-11-12
Researchers from the Oxford Martin Programme on Ethical Web and Data Architectures (University of Oxford) have reported findings from a paper exploring the motivations and challenges in running decentralised social media such as Mastodon, concluding such platforms offer potential for increased citizen empowerment in this digital domain.
In their study, presented at the 27th ACM SIGCHI Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work & Social Computing (CSCW) today, the researchers interviewed 16 administrators of Mastodon servers (otherwise known as instances), including those supporting marginalised and stigmatised communities. Their ...
Validating an electronic frailty index in a national health system
2024-11-12
“The classification of patients according to their level of frailty allows us to adjust prevention programs and focus our limited resources on the right action for the right person.”
BUFFALO, NY- November 12, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science), on October 24, 2024, Volume 16, Issue 20, titled, "Development and validation of an electronic frailty index in a national health ...
Combination approach shows promise for treating rare, aggressive cancers
2024-11-12
A research team led by UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center investigators has shown that that combining pembrolizumab, an immunotherapy drug, with standard chemotherapy can improve treatment outcomes for patients with small cell bladder cancer and small cell/neuroendocrine prostate cancer.
Small cell carcinomas can arise in various tissues—including the bladder, prostate, lung, ovaries and breast—and are known for their rapid progression, tendency to relapse after initial treatment and poor overall survival ...
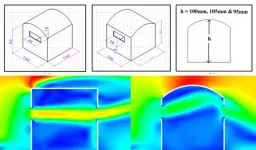
Raise the roof: How to reduce badminton birdie drift
2024-11-12
WASHINGTON, Nov. 12, 2024 – Indoor badminton courts are often used for high-stakes tournaments, but even an enclosed court can affect the path of a birdie.
The airflow from a court’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system and cross ventilation plays a significant role in badminton. The lightweight feathered birdie passed between the players can be affected by low wind speed in the stadium. This is known as wind drift and has been at the center of multiple tournament controversies. While shutting ...
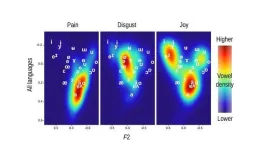
Ouch! Commonalties found in pain vocalizations and interjections across cultures
2024-11-12
WASHINGTON, Nov. 12, 2024 – There are an estimated 7,000 languages spoken worldwide, each offering unique ways to express human emotion. But do certain emotions show regularities in their vocal expression across languages?
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, an interdisciplinary team of linguists and bioacousticians led by Maïa Ponsonnet, Katarzyna Pisanski, and Christophe Coupé explored this by comparing expressive interjections (like “wow!”) ...
Income-related disparities in mortality among young adults with type 2 diabetes
2024-11-12
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1.2 million individuals ages 20 to 79 in South Korea, the risk of mortality with low income was most prominent among individuals with type 2 diabetes ages 20 to 39. These findings highlight the need for socioeconomic support to reduce income-related health disparities in younger individuals.
Corresponding authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Sin Gon Kim, MD, PhD (k50367@korea.ac.kr) and Nam Hoon Kim, MD, PhD (pourlife@korea.ac.kr).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Medical board discipline of physicians for spreading medical misinformation
2024-11-12
About The Study: The frequency of discipline for physician-spread misinformation observed in this cross-sectional study was quite low despite increased salience and medical board warnings since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic about the dangers of physicians spreading falsehoods. These findings suggest a serious disconnect between regulatory guidance and enforcement and call into question the suitability of licensure regulation for combatting physician-spread misinformation.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Richard S. Saver, J.D., ...
First-ever randomized clinical trial uses telehealth for suicide prevention
2024-11-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Suicide remains a pressing public health concern. An estimated 703,000 people die by suicide each year worldwide, according to The World Health Organization. In 2022, there were 49,449 suicides in the United States.
A new study found that brief cognitive behavioral therapy for suicide prevention – when delivered remotely via video telehealth – reduces suicide attempts and suicidal ideation.
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine led the study that is published online in the journal JAMA Network Open.
The randomized clinical ...
DNA packaging directly affects how fast DNA is copied in cells
2024-11-12
Researchers from the Mattiroli group have found that the way DNA is packaged in cells can directly impact how fast DNA itself is copied during cell division. They discovered that DNA packaging sends signals through an unusual pathway, affecting the cell’s ability to divide and grow. This opens up new doors to study how the copying of the DNA and its packaging are linked. These findings, published in Molecular Cell, may help scientists to find therapies and medicines for diseases such as cancer in the future.
Chromatin as a guide
Every day, our cells divide. Each time they need to copy both their DNA and the structure in which the DNA is packed. This packaging, ...
Scientists develop advanced catalyst for self-driven seawater splitting with enhanced chloride resistance
2024-11-12
Seawater electrolysis has long been seen as a promising pathway for sustainable hydrogen production but has faced significant limitations due to chloride ion (Cl⁻) corrosion, which can degrade a catalyst's performance.
Now scientists from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, along with their collaborators, have developed an efficient electrocatalyst called Co-N/S-HCS that demonstrates remarkable activity and stability in ...
City of Hope researchers discover why taking a mushroom supplement slows or prevents prostate cancer from getting worse
2024-11-12
LOS ANGELES — Researchers at City of Hope®, one of the largest and most advanced cancer research and treatment organizations in the United States, ranked among the nation’s top 5 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report and a national leader in providing cancer patients with best-in-class, integrated supportive care programs, now understand why taking an investigational white button mushroom supplement shows promise in slowing and even preventing prostate cancer from spreading among men who joined ...
Montefiore Einstein’s Marina Konopleva joins Break Through Cancer TeamLab in fight against acute myelogenous leukemia
2024-11-12
November 12, 2024—(BRONX, NY)— Marina Konopleva, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Leukemia Program and co-director of the Blood Cancer Institute at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center (MECCC), has joined forces with Break Through Cancer, a collaborative medical research foundation that supports teams of scientists as they advance treatments for some of the world’s deadliest cancers. Dr. Konopleva will play a pivotal role in the Eradicating Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Acute ...
Early treatment for nerve tumors prevents serious problems, study finds
2024-11-12
Patients with a small cranial nerve tumor that can cause hearing loss, vertigo, imbalance and ringing in the ears have typically been watched rather than proactively treated, as the risks of early intervention were thought to outweigh the benefits. However, even those patients benefit significantly from non-invasive stereotactic radiosurgery, a multicenter, international study led by UVA Health physicians has found.
Doctors typically treat larger forms of the tumors, called vestibular schwannomas, while taking a “watch and wait” approach ...
Study: Student absenteeism crisis may be hurting teacher job satisfaction
2024-11-12
Washington, November 12, 2024—As student absenteeism reaches record highs in schools across the United States, new research finds that student absences are linked to lower teacher job satisfaction, raising concerns that this may exacerbate growing teacher shortages. The findings were published today in Educational Researcher, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Educational Research Association.
The study, by Michael Gottfried and Colby Woods at the University of Pennsylvania, and Arya Ansari at The Ohio State University, is the first ...
Medicaid enrollment continuity tied to lymphoma stage at diagnosis
2024-11-12
(WASHINGTON, November 12, 2024) – Continuous enrollment in Medicaid was associated with a lower rate of a late-stage lymphoma diagnosis in children and adolescents/young adults (AYAs). However, fewer than half of Medicaid-insured patients in these age ranges were continuously enrolled before diagnosis, according to a study published today in Blood Advances.
Lymphoma – which is divided into two types, Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) – is a cancer of the lymphatic system and ...
INSEAD launches free Negotiation Course for the World
2024-11-12
If knowledge is power, empowering the world with the art and science of negotiation offers even more far-reaching benefits – a more peaceful and prosperous world, according to the INSEAD Negotiation and Conflict Management Collaborative (NCMC).
The Negotiation Course for the World (NCW) is a pioneering effort by the NCMC to make quality negotiation teaching materials and expertise accessible to all, and in so doing, democratise negotiation education. “It is an integral part of the NCMC’s mandate to bring scholars and practitioners together to collaborate on research and education on negotiation and conflict management,” said Roderick Swaab, Professor ...
Wyss Institute’s iNodes team receives ARPA-H Sprint for Women’s Health award to advance the first implantable immune organs to treat ovarian cancer
2024-11-12
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Ovarian cancer is more deadly than any other type of female reproductive organ cancer. It is estimated that in 2024, in the U.S. alone, more than 12,000 women will die from the disease because available therapies are not effective. To help overcome this striking deficit in women’s health, ARPA-H has selected a team at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University as an awardee of its Sprint for Women’s Health effort to develop “iNodes” – implantable lymphoid organs containing patients’ immune cells – as an entirely novel form of personalized immunotherapy to treat ovarian ...
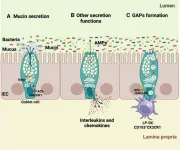
Goblet cells could be the guardians of the gut
2024-11-12
In a recent study, researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have provided new insights into the central role of goblet cells—specialized cells that line the gut—in maintaining a healthy and balanced immune environment within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Led by Dr Fernanda Raya Tonetti, with Dr. Cristina Llorente directing the project and making significant contributions, the study underscores the critical roles of these cells, which act not only as a physical barrier but also ...
Romania’s science journalists join forces on new reporting handbook
2024-11-12
The Balkan Network of Science Journalists and the European Federation for Science Journalism are launching a new science journalism guide, this time in Romanian.
From the Field: A Science Journalist's Handbook is the result of a collective effort by more than 20 Romanian journalists and content creators who dedicated their time and expertise to build a 138-page document designed to help journalists navigate the complex world of science reporting.
The guide was coordinated by science ...
SwRI-led team proposes new solar composition ratios that could reconcile longstanding questions
2024-11-12
SAN ANTONIO — November 12, 2024 — A Southwest Research Institute-led team combined compositional data of primitive bodies like Kuiper Belt objects, asteroids and comets with new solar data sets to develop a revised solar composition that potentially reconciles spectroscopy and helioseismology measurements for the first time. Helioseismology probes the Sun’s interior by analyzing the waves that travel through it, while spectroscopy reveals the surface composition based on the spectral signature produced by each chemical element.
A paper about this research, which ...
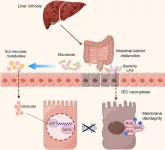
Sodium butyrate inhibits necroptosis by regulating MLKL via E2F1 in intestinal epithelial cells of liver cirrhosis
2024-11-12
Background and Aims
Necroptosis is critical for regulating intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). Butyric acid (BA), produced during intestinal microbial metabolism, protects the intestinal epithelial barrier. However, whether necroptosis occurs in IECs during liver cirrhosis and whether sodium butyrate (NaB) can regulate necroptosis have not yet been reported. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether IECs undergo necroptosis in cirrhosis and whether NaB can regulate necroptosis and the related regulatory mechanisms.
Methods
Serum levels of RIPK3, MLKL, and Zonulin, as well as fecal BA levels, were measured and correlated in 48 patients with liver cirrhosis ...
[1] ... [823]
[824]
[825]
[826]
[827]
[828]
[829]
[830]
831
[832]
[833]
[834]
[835]
[836]
[837]
[838]
[839]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.