Wayne State University to lead USDA grant to support program training students in ‘smart agriculture’
2024-11-20
DETROIT — A new program supported by a four-year, $749,991 grant from the National Institute of Food and Agriculture of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) will use data to study the future of agriculture and train students to better understand how to keep people fed in an ever-changing world.
The project, “Nonformal Training of Michigan Youth on Intersection of Agriculture and Data Science,” will be led by Sara Masoud, Ph.D., assistant professor of industrial and systems engineering in Wayne State University’s College of Engineering.
Agriculture experts say that arable land per person is projected to decrease by two-thirds of the current available ...
Low-dose oral minoxidil initiation for patients with hair loss an international modified Delphi consensus statement
2024-11-20
Hair loss significantly impacts patients’ quality of life, and it may be nonscarring or scarring. Etiologically, hair loss may be hereditary (androgenetic alopecia [AGA]); related to age; congenital (hair shaft disorders); traction induced; inflammatory (primary scarring alopecia); autoimmune (alopecia areata); or secondary to medical, surgical, or emotional stressors (telogen effluvium), infection (tinea capitis), and certain medica- tions including cancer therapies.
Topical minoxidil is approved by the US Food and Drug Admin- istration (FDA) as an over-the-counter drug designed to treat male pa- tients with AGA (minoxidil, 5% ...
Turning carbon emissions into methane fuel
2024-11-20
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Chemists have developed a novel way to capture and convert carbon dioxide into methane, suggesting that future gas emissions could be converted into an alternative fuel using electricity from renewable sources.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a greenhouse gas that accounts for a large part of Earth’s warming climate, and is produced by power plants, factories and various forms of transportation. Typical carbon capture systems aimed at reducing its presence in the atmosphere work to lower carbon dioxide emissions by isolating CO2 from other gases and converting it to useful products. However, this process is difficult to implement on an industrial scale due to the ...
Friendly social behaviors are contagious for chimpanzees
2024-11-20
Chimpanzees are more likely to engage in play or groom each other if they see others performing these social behaviors first, Georgia Sandars and colleagues at Durham University, U.K. report in a study publishing November 20, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
Whether it’s yawning or keeping watch for predators, many animals — including primates and ravens — find certain behaviors contagious: after seeing another member of their group performing one of these behaviors, they will instinctively perform it too. This ‘behavioral contagion’ is thought to help animal groups reinforce their social bonds and stay in sync. ...
Who is most vulnerable to commercial sexual exploitation?
2024-11-20
Educational achievement, mental health diagnoses, childhood abuse, number of arrests and number of children all play a complex role in shaping a person’s vulnerability to commercial sexual exploitation, how long they are exploited for and how difficult it is to get out. That is one conclusion of a new study published November 20, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Courtney Furlong and Ben Hinnant of Auburn University, U.S.
Commercial sexual exploitation (CSE) occurs when anything of value is given in exchange for a sex act. When CSE involves force, fraud, or coercion, it is termed ...
Florida manatees flourish and flounder alongside human neighbors
2024-11-20
Florida manatees are threatened by human activity, but they’re also doing better than ever, according to a study examining manatee populations since 12,000 BC, published November 20, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Thomas J. Pluckhahn of the University of South Florida and David K. Thulman of George Washington University, Washington DC, U.S.
Florida manatees are an iconic species and also a conservation concern, threatened by environmental change and watercraft collisions. Historical manatee populations are poorly understood, and therefore little is known about the state of manatees before modern human influence, making it difficult for conservationists ...
Manatees might be relatively recent arrivals to Florida, USF study finds
2024-11-20
TAMPA, Fla. (Nov. 20, 2024) – New research suggests that while manatees are an indelible part of Florida’s seascape, they might also be relatively new residents in the Sunshine State.
The findings are detailed in a study co-authored by University of South Florida anthropologist Thomas Pluckhahn and David Thulman, an archaeology professor at George Washington University, and scheduled to publish in PLOS ONE on Nov. 20 at 2 p.m. The embargo will lift at that time.
The paper, “Historical ...
New Durham University study shows friendly social behaviors are contagious for chimpanzees
2024-11-20
-With images and videos-
Researchers from Durham University have uncovered new insights into social contagion in chimpanzees, revealing that these primates are capable of catching friendly behaviours, which may strengthen social bonds and increase group harmony.
The study, conducted at the Chimfunshi Wildlife Orphanage in Zambia, observed two affiliative behaviours—grooming and play—and found that these behaviours can spread among group members in a way that promotes group cohesion.
This groundbreaking study has been published in the journal PLOS ONE, which expands our understanding ...
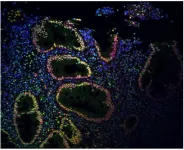
Megapixel fluorescence microscopy through scattering layers made simple
2024-11-20
A team from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem has introduced a new method for megapixel-scale fluorescence microscopy through complex scattering media. This approach resolves high-resolution images from several tens of widefield fluorescence-microscope frames without requiring specialized equipment such as spatial-light modulators or intensive computational processing. By efficiently correcting distortions caused by light scattering, the technique allows for clear imaging of dense and challenging targets. Its compatibility with conventional microscopy setups, coupled with the use of established matrix-based techniques, makes it practical for widespread use.
A recent ...
Over 4 million US adults with chronic liver disease can be grouped into unique risk groups based on barriers to care
2024-11-20
People with chronic liver disease can be categorized into four distinct risk groups based on the different barriers they face in obtaining outpatient care, barriers that increase their odds of requiring hospitalization, a new UCLA study finds.
The findings, to be published November 20 in the peer-reviewed PLOS ONE, point to the need for interventions aimed at reducing possibly avoidable hospitalizations among the highest-risk people with chronic liver disease (CLD). Previous research has found that people with CLD on average need more hospital-based care than those with other chronic diseases.
About ...
Robot flies like a bird
2024-11-20
Have you ever wondered why an airplane has a vertical tailfin? The plane needs it to stabilize its flight. Since flying without a vertical tail is much more energy-efficient, the aviation industry has worked hard to accomplish this – so far without much success. However, birds don’t need a vertical fin, which raises the question: how do they do it?
David Lentink, Professor of Biomimetics at the University of Groningen, has developed a robotic bird model with real pigeon feathers to show how they do it. In previous work, he found that birds continuously ...
Won’t you be mine? Neighborly networking may motivate local climate action
2024-11-20
Individual motivation to act against climate change outweighs the impact of hyperlocal collective intentions, though both approaches are worth strengthening, according to a survey of nine European neighborhoods published Nov. 20, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS Climate by Christian A. Klöckner from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology and colleagues.
Western society contests the individual versus collective responsibility to combat climate change. But do people feel more motivated to act individually (e.g., making waste-free purchasing choices) or in tandem with others (e.g., protesting or completing ...
Mental health issues are "prevalent and troubling" among forcibly displaced children and young people, per scoping review which finds PTSD, anxiety and depression to be most common conditions
2024-11-20
Mental health issues are "prevalent and troubling" among forcibly displaced children and young people, per scoping review which finds PTSD, anxiety and depression to be most common conditions.
+++++
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000076
Article Title: Mental health issues of children and young people displaced by conflict: A scoping review
Author Countries: Nigeria, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
How nerve stimulation could ease inflammatory bowel disease
2024-11-20
Researchers at Duke University School of Medicine have found that tapping into the nervous system could help reduce the gut inflammation that drives inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
A new study led by Luis Ulloa, PhD, and Wei Yang, PhD, reveals how electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve—a major nerve connecting the brain and gut—may combat the stress-related inflammation that worsens IBD symptoms.
Published in Science Translational Medicine, the study showed that vagus nerve stimulation in stressed mice with colitis, a form of IBD, reduced inflammation, improved symptoms, ...
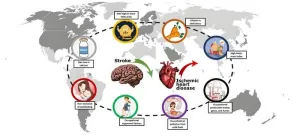
The factors behind the shifting trends of ischemic heart disease and stroke
2024-11-20
Incidence of stroke and ischemic heart disease are declining around the world, except for in a handful of regions, according to research in the open access journal PLOS Global Public Health. Wanghong Xu of Fudan University and colleagues find that in East and West Sub-Saharan Africa, East and Central Asia and Oceania, ischemic heart disease is increasing, which may be attributed to eight factors that include diet, high BMI, household air pollution and more.
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, and ischemic heart disease and stroke ...
How educational attainment may impact memory and dementia risk later in life
2024-11-20
Historical policies shaping educational attainment have enduring benefits for later life memory and risk of dementia, according to a study led by a Rutgers Health researcher.
The study, published in Epidemiology, compared the differences in years of education based on variations in state schooling mandates with cognitive performance outcomes in residents decades later.
“Policies to increase the quantity or quality of schooling now are likely to have long-term benefits on cognitive outcomes,” ...
Growing soybeans has a surprisingly significant emissions footprint, but it’s ripe for reduction
2024-11-20
AMES, Iowa – Over the typical two-year rotation of corn and soybeans most Iowa farmers use, 40% of nitrous oxide emissions are in the soybean year, according to a new study by an Iowa State University research team.
The share of the potent greenhouse gas released during the soybean half of a crop rotation cycle is surprisingly high, given most soybeans fields aren’t treated with nitrogen, said Michael Castellano, agronomy professor and William T. Frankenberger Professor of Soil Science at Iowa State University.
“We’ve just been assuming that legume crops like soybeans don’t have a big emissions footprint because they don’t ...
$6 million grant drives potential treatment for common cause of vision loss toward the clinic
2024-11-20
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), the state’s stem cell agency, has awarded a two-year, $6 million grant to a team at the USC Dr. Allen and Charlotte Ginsburg Institute for Biomedical Therapeutics and the USC Roski Eye Institute advancing a new treatment for one of the leading causes of blindness in older adults. The funding will enable the researchers to conduct preclinical studies needed before launching human trials.
The investigators aim to accelerate progress in fighting dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD), which affects ...
Research aims to roll back contamination caused by toxic tires
2024-11-20
University of Delaware researchers have developed a method for mitigating the decontamination that tires release into the environment at the end of their lifespan.
In a new study published in Nature Chemical Engineering, the team demonstrated a way to upgrade 6PPD – a molecule that provides UV protection to help the rubber found in tires last longer – into safe chemicals. The method would also turn the leftover crumb rubber into aromatics and carbon black, a soot-like material found in everything from pigments to cosmetics to electronics. ...
School social workers an underutilized resource
2024-11-20
Youth in America are experiencing a mental health crisis, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The CDC reports that an increasing number of students are experiencing symptoms of hopelessness, depression, and anxiety, along with thoughts of self-harm.
One thing known to improve mental health among students is increased school connectedness—when students feel that the adults and peers in their school care about them as individuals in addition to their learning ability. Schools are working to improve their connectedness by adding social workers to their staff to help address the mental health concerns of students.
However, ...
Increasing complexity challenges strategic management
2024-11-20
The changes in society and the phenomena surrounding us are becoming more unexpected and interconnected than ever before. This increasing complexity challenges strategic management, making it harder to predict trends and developments. According to a new study from the University of Vaasa, Finland, increased complexity demands new approaches to strategic management.
– In strategic management, it is essential to acknowledge the growth of complexity and understand how to influence complexity ...
Morton Arboretum tree root scientist recognized as top-cited researcher for second straight year
2024-11-20
LISLE, Ill. (Nov. 20, 2024)— For the second year in a row, The Morton Arboretum’s Tree Root Biologist Luke McCormack, Ph.D., has been recognized as one of the most cited and influential researchers worldwide by global information services provider Clarivate’s esteemed annual list of “Highly Cited Researchers.”
The 2024 list, released Nov. 19, includes influential researchers at universities, research institutes and commercial organizations around the world, who have demonstrated significant and broad influence in their research field(s). McCormack, who debuted ...
Scientists show electrical stimulation could be key to healthy tendons
2024-11-20
A new study by researchers at the University of Galway and the University of Limerick suggests that electrical stimulation might be essential for tendons to maintain their health, offering fresh possibilities in tendon repair and regeneration.
The research took place at the CÚRAM Research Centre for Medical Devices, funded through Taighde Éireann – Research Ireland, formerly Science Foundation Ireland.
Tendons resist intense mechanical stress, while facilitating force transmission from muscles to bones. They are also piezoelectric, meaning that when they are stretched, they will produce an electric ...
University Hospitals only health system in northeast Ohio offering FDA-approved KISUNLA™ for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease
2024-11-20
CLEVELAND--University Hospitals Brain Health & Memory Center is now treating patients with KISUNLA™ (donanemab), a Food and Drug Administration-approved medication for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. UH is the only health system in Northeast Ohio currently offering these infusion treatments. Donanemab has shown promise in clinical trials and may be a treatment option for patients with mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease.
“People with Alzheimer’s disease have an abnormal buildup of plaques in their brain ...
Real-world chemists are more diverse than generative AI images suggest
2024-11-20
Asking children “What does a scientist look like?” now results in more illustrations of women and people of color than decades ago. But do generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools also depict the diversity among scientists? Researchers reporting in the Journal of Chemical Education prompted AI image generators for portraits of chemists. They found that none of the collections accurately represents the gender, racial or disability diversity among real chemists today.
Millions of images are being created by generative AI each day. And the output of these tools is only as good as their algorithms and the initial images used to train ...
[1] ... [817]
[818]
[819]
[820]
[821]
[822]
[823]
[824]
825
[826]
[827]
[828]
[829]
[830]
[831]
[832]
[833]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.