New study: Plastics pollution worsen the impacts of all Planetary Boundaries
2024-11-07
“It’s necessary to consider the full life cycle of plastics, starting from the extraction of fossil fuel and the primary plastic polymer production” says lead article writer Patricia Villarrubia-Gómez at Stockholm Resilience Centre.
Plastics are not as safe and inert as previously thought. The new research article written by an international team of researchers uses the planetary boundaries framework to structure the rapidly mounting evidence of the effects of plastics on the environment, health and human wellbeing.
500 million tons of plastics are now produced yearly but only nine percent get recycled globally. Plastics are everywhere: ...
Long-term risks from prostate cancer treatment detailed in new report
2024-11-07
The risks of adverse effects and complications from treatment for prostate cancer are substantial and continue for years after treatment ends. The largest comprehensive analysis reporting long-term risks from such treatment relative to the risks faced by a control group of untreated men has just been published in the journal JAMA Oncology.
In the 12 years following treatment, men whose initial treatment was a prostatectomy (removal of all or part of the prostate) had a risk of urinary or sexual complications ...
Does more virtual care mean more low-value care? Study suggests no
2024-11-07
Before 2024 ends, Congress will decide whether to keep or change rules about telehealth, or let them expire. And even though the decision will focus on Medicare’s payment for virtual patient care, it will likely impact telehealth access for people with other kinds of health insurance too.
Now, a new University of Michigan study suggests that policymakers can rest easier about one of the top worries about telehealth: that virtual care will drive up the use of tests and scans that patients don’t need, wasting money and resources.
In fact, the study shows that low-value care didn’t rise faster at primary care practices that used telehealth the most, compared with those ...
City of Hope Research Spotlight, October 2024
2024-11-07
City of Hope® Research Spotlight offers a glimpse at groundbreaking scientific and clinical discoveries advancing lifesaving cures for patients with cancer, diabetes and other chronic, life-threatening diseases. Each spotlight features research-related news such as recognitions, collaborations and the latest research defining the future of medical treatment.
This roundup highlights the biology behind our sense of smell, real-world data that can be used to refine esophageal cancer treatment guidelines, a potential new approach to treating patients with type 2 diabetes, a new way to target pancreatic cancer ...
Increased focus on comorbidities, socioeconomic factors would help improve health equity for people with COPD
2024-11-07
Miami (November 7, 2024) – Health care providers treating people with COPD also need to focus on the person’s socioeconomic factors, along with considering their additional health conditions or comorbidities, according to a new article. The article is published in the September 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics ...
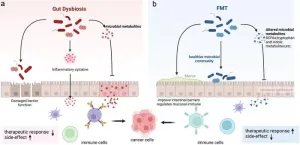
Gut dysbiosis and fecal microbiota transplantation in pancreatic cancer: Current status and perspectives
2024-11-07
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is recognized as one of the most lethal cancers, with an estimated five-year survival rate of approximately 10%. This poor prognosis is largely attributed to the challenges in early diagnosis, aggressive tumor biology, and limited treatment options. Most PDAC cases are diagnosed at advanced stages due to its typically asymptomatic onset, making only a small percentage of patients eligible for potentially curative surgical resection. In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to the role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in PDAC, as ...
Prevalence of unrecognized cognitive impairment in socially and economically vulnerable older adults is high
2024-11-07
INDIANAPOLIS – One of the first studies to investigate the prevalence of unrecognized cognitive impairment among patients seen at Federally Qualified Health Centers, has found that it is ubiquitous, especially among minoritized older adults. These facilities provide primary care and preventive services regardless of ability to pay or health insurance status to more than 30 million patients, including a growing number of older adults.
Early and equitable detection of cognitive impairment can benefit patients and their families. Delaying diagnosis leads to poor health outcomes for patients ...
Men who have sex with men in Europe still vulnerable to hepatitis A and B, highlighting need for public health action and support
2024-11-07
Research analysing European survey data from 113,884 men who have sex with men (MSM) and published in Eurosurveillance indicates that while most MSM have a basic understanding of viral hepatitis, only 44% report having been vaccinated against both hepatitis A and B. The data highlight notable immunisation gaps despite available vaccination and recommendations. Strong public health support and creating an open environment that enables MSM to follow recommendations will be crucial to reduce outbreaks among MSM and eliminate hepatitis B.
Men who have sex with men are more likely to get infected with ...
Cancer genetic risk assessment guidelines expand to meet growing understanding of hereditary risk
2024-11-07
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [November 7, 2024] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®)—an alliance of leading cancer centers focusing on maintaining evidence-based expert consensus driven guidelines for care—announces the publication of the expanded NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast, Ovarian, Pancreatic, and Prostate. This closely follows the recent publication of the expanded NCCN Guidelines® for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Colorectal, Endometrial, and Gastric.
Additional cancer types were added to the title and content for both guidelines. ...
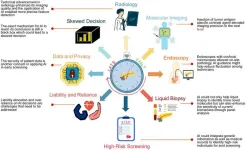
Advances in screening and early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer
2024-11-07
Pancreatic cancer (PC) presents substantial diagnostic challenges due to its aggressive nature and lack of early symptoms, leading to late detection and poor prognosis. According to recent cancer statistics, PC ranks as the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths globally, with increasing incidence, particularly in high-risk regions such as China. Factors such as a shortage of specific and reliable screening markers, along with a lower prevalence in the general population, make effective large-scale screening a formidable tasko assess advancements in diagnostic techniques, artificial intelligence integration, biomarker discoveries, ...
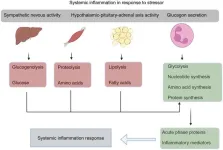
Metabolic dysregulation and metabolite imbalances in acute-on-chronic liver failure: Impact on immune status
2024-11-07
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a life-threatening condition characterized by acute deterioration of liver function in patients with pre-existing chronic liver disease. It is often accompanied by multiorgan failure and systemic inflammation, with high short-term mortality rates. The triggers for ACLF include bacterial infections, acute alcoholic hepatitis, and ischemic hepatitis, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. These systemic inflammatory responses result in immune dysfunction, contributing to the progression of the disease.
Recent research has emphasized the metabolic changes ...
Elite coaches see compassion as a path to better performance
2024-11-07
It may sound like a contradiction to talk about compassion in the competitive world of elite sport. After all, isn't elite sport all about becoming hardened to resistance and adversity?
But this is a false dichotomy, according to a new study that analysed the views of 12 Danish high-performance coaches on the use of compassion in their work with elite athletes.
In fact, there is a broad consensus among the coaches, most of whom are head of national teams, about the benefits of using compassion, says the study's lead author, Emilia Backman from the Department of Psychology, University of Copenhagen.
"All of the high-performance ...
Microplastics impact cloud formation, likely affecting weather and climate
2024-11-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Scientists have spotted microplastics, tiny pieces of plastic smaller than 5 millimeters, in some of the most pristine environments on Earth, from the depths of the Mariana Trench to the snow on Mt. Everest to the mountaintop clouds of China and Japan. Microplastics have been detected in human brains, the bellies of sea turtles and the roots of plants. Now, new research led by Penn State scientists reveals that microplastics in the atmosphere could be affecting weather and climate.
The study, published today (Nov 7) in the journal Environmental Science and Technology: ...
ECOG-ACRIN and PrECOG announce multiple presentations at ASH 2024
2024-11-07
Researchers with the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) and PrECOG, LLC, will present a variety of abstracts that aim to improve treatments for patients with lymphoma and acute leukemias at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Meeting & Exposition. The meeting is set to occur in San Diego, California, and virtually December 7 - 10, 2024.
Promising results from a phase 2 study (PrE0905) in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and new data from the practice-changing E1910 phase ...
Off-the-shelf thermoelectric generators can upgrade CO2 into chemicals. The combination could help us colonize Mars
2024-11-07
Readily available thermoelectric generators operating under modest temperature differences can power CO2 conversion, according to a proof-of-concept study by chemists at the University of British Columbia (UBC).
The findings open up the intriguing possibility that the temperature differentials encountered in an array of environments—from a typical geothermal installation on Earth to the cold, desolate surface of Mars—could power the conversion of CO2 into a range of useful fuels and chemicals.
“The environment ...
What makes human culture unique?
2024-11-07
Why is human culture — the shared body of knowledge passed down across generations — so much more powerful than animal cultures?
“What’s special about our species?” is a question scientists have wrestled with for centuries, and now a scientist at Arizona State University has a new hypothesis that could change the way we perceive ourselves, and the world around us.
“Ten years ago it was basically accepted that it was the ability of human culture to accumulate and evolve that made us special, but new discoveries about animal behavior are challenging these ideas and forcing us to rethink what makes our cultures, ...
Researchers discover dozens of new genes associated with disc herniations
2024-11-07
Lumbar disc herniation is one of the most common structural changes in the lower back and the most common cause of radiating pain, or sciatica, in the leg.
Hereditary risk factors for disc herniations were investigated in a recently published international study led by a University of Oulu research group, utilising data from FinnGen, the Estonian Biobank, and the UK Biobank. The study analyzed the genetic and health data of 829,699 participants.
The study found 41 novel regions of the genome that modify the disease risk for disc herniations, in addition ...
Research shows caterpillar fungus can slow down growth of cancer cells
2024-11-07
New research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus that has shown promise as a possible cancer treatment has revealed how it interacts with genes to interrupt cell growth signals. The discovery is an important step towards developing new drugs for the treatment of the disease.
The research into a chemical produced by a caterpillar fungus has revealed how it may work as a cancer treatment. It interrupts the cell growth signals that are overactive in cancer, an approach that could be less damaging to healthy ...
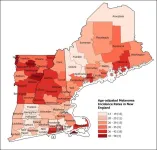
Tanning bed access and usage is driving higher rates of melanoma in specific regions
2024-11-07
Philadelphia, November 7, 2024 – Melanoma accounts for only 1% of skin cancers in the United States but results in the largest number of skin cancer deaths. Investigators evaluated the potential link between the availability and use of tanning beds and the rising rates of melanoma in New England. They found compelling evidence linking tanning bed usage to increased melanoma risk. Their spatial epidemiologic study in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier, provides critical insights to inform public health strategies and reduce melanoma incidence.
The incidence of melanoma in the US has been increasing ...
Mitochondrial dysfunction research transforms mental health: Dr. Ana Andreazza's vision
2024-11-07
Toronto, Canada, 7 November 2024 – From a curious young scientist investigating her grandfather's family wine to a leading expert in mitochondrial health and mental illness, Dr. Ana Cristina Andreazza's journey exemplifies the power of personal motivation in driving scientific innovation. As founder and Scientific Director of the Mitochondrial Innovation Initiative (Mito2i), Dr. Andreazza is revolutionizing our understanding of the connection between cellular energy production and mental health.
In an illuminating Genomic Press Interview, published in Brain Medicine on November 7, 2024, ...
Dr. Nora Volkow shares insights on addiction science and harm reduction in Genomic Press interview
2024-11-07
Bethesda, Maryland, USA, 7 November 2024 – Dr. Nora Volkow's mission to revolutionize addiction treatment began with a deeply personal observation: watching how excessive substance use could profoundly alter a person’s behavior while simultaneously triggering social rejection by others. As the first woman and Hispanic Director of the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Dr. Volkow has dedicated her career to investigating how drugs affect the human brain and how these disruptions contribute to the behavioral/emotional ...
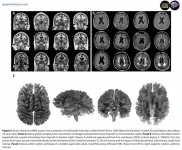
25-year study reveals key factors in healthy brain aging and cognitive performance
2024-11-07
Edinburgh, Scotland, 7 November 2024 – A groundbreaking 25-year research program has unveiled key insights into how our brains age and what factors influence cognitive performance throughout life. The findings, published on 7 November 2024 in Genomic Psychiatry, draw from the Lothian Birth Cohorts (LBC) studies, which uniquely tracked participants' cognitive abilities from childhood through their eighth decade of life.
Professor Ian Deary and Dr. Simon Cox from the University of Edinburgh present remarkable discoveries that challenge conventional wisdom about brain aging. Their research ...
First clinical trial reveals promise of psilocybin treatment for anorexia nervosa
2024-11-07
San Diego, California, 7 November 2024 – In a groundbreaking exploration of psychedelic medicine's potential for treating one of psychiatry's most challenging conditions, researchers at University of California, San Diego (UCSD) provided an analysis and further details of a trial published in Nature Medicine (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10427429/) that had shown how psilocybin therapy affects individuals with anorexia nervosa. In the new peer-reviewed Emerging Topic article in Psychedelics ...
Fabrication of 4-inch wafer-scale heterostructure via PECVD drives AI semiconductor performance innovation!
2024-11-07
As artificial intelligence (AI) technology advances, the demand for higher-performing semiconductors is rapidly growing. The development of new materials and innovative structures to achieve high-performance semiconductors has become crucial. For the first time globally, a 4-inch heterostructure fabrication technology using plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) has been developed. This breakthrough enables the production of low-power, high-performance semiconductors, surpassing the capabilities of traditional silicon-based technology.
The research team led by Senior Researcher Hyeong-U Kim of the Semiconductor Manufacturing Research Center of the ...
Plastic device aids robot-assisted heart surgery
2024-11-07
Robot-assisted heart surgery usually requires an assistant at the operating table to help the surgeon insert the robot arm through a small incision. The assistant has to constantly make sure the surgeon has enough room to operate via the robot arm. For greater independence on the surgeon’s side, an Osaka Metropolitan University-led group has developed a device that can secure the surgical field.
Graduate School of Medicine Professor Toshihiko Shibata and Associate Professor Yosuke Takahashi worked with colleagues and small and ...
[1] ... [832]
[833]
[834]
[835]
[836]
[837]
[838]
[839]
840
[841]
[842]
[843]
[844]
[845]
[846]
[847]
[848]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.