(Press-News.org) For the first time researchers have studied the kind of physical pain that troubles adolescents with different mental health problems.
Professor Marit Sæbø Indredavik at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) thinks that everyone working in the health care system, from medical doctors to psychologists, must be more aware of the chronic pain that can plague young people with mental health woes.
From anxiety to ADHD
The researchers gave a questionnaire to 566 teenagers between 13 and 18 years old, all of whom had conditions ranging from ADHD and depression to anxiety, eating disorders and a range of autistic disorders.
The teens were asked whether or not they had physical pain, and if so, what kind of pain and where it was located. All the youths were participants in a larger health survey conducted by St Olavs Hospital in Trondheim, Norway from 2009-2011.
Seven out of ten answered that they suffered from chronic pain. Among depressed adolescents, the percentage was even higher, with eight out of ten reporting chronic pain, most often musculoskeletal pain. Girls reported having pain more often than boys, no matter their mental health diagnosis.
Must be treated concurrently
"These numbers are so high that the entire support system for children and adolescents needs to be made more aware of the link between physical pain and psychiatric disorders. Physical pain is most common among young people who have conditions such as anxiety and depression, where they tend to be more focused on their problems. This is not a surprise, but it is a clear signal that we need to keep this in mind when treating mental health problems," says Indredavik.
Indredavik is one of the main contributors to the survey, along with PhD candidate Wenche Langfjord Mangerud at NTNU. They both work at NTNU's Regional Centre for Child and Youth Mental Health and Child Welfare. Mangerud emphasizes that physical pain and mental conditions cannot be treated separately.
Hard to cure
"Both anxiety and depression on their own can decrease the quality of life for these adolescents. Now we see that they also suffer from chronic pain. To treat anxiety in a positive way, physical pain must also be treated and vice versa. It is important that treatment in their younger years be effective, so that these problems don't continue into adulthood, as they unfortunately often do," says Mangerud.
She emphasizes that the health care providers must at the very least find out if adolescents also have physical pain. If they do they must receive the right treatment. Their medical doctors should work with physiotherapists.
"Unfortunately there are too few physiotherapists working in child and adolescent psychiatry, but you can find them elsewhere in the health care system. It is important that the health care providers work more closely so that both body and mind are taken care of," says Indredavik.
Mangerud will now study physical activity among adolescents with mental health problems, compared to adolescents who are free from these disorders.
INFORMATION:
The article describing this research was published in BMC Psychiatry and is entitled: Chronic pain and pain-related disability across psychiatric disorders in a clinical adolescent sample, by Wenche L Mangerud, Ottar Bjerkeset, Stian Lydersen and Marit S Indredavik. It can be found at: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-244X/13/272
Depressed girls suffer the most
Adolescents with psychiatric problems are also likely to suffer chronic pain
2014-02-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Earwax: A new frontier of human odor information
2014-02-12
PHILADELPHIA (February 12, 2014) – Scientists from the Monell Center have used analytical organic chemistry to identify the presence of odor-producing chemical compounds in human earwax. Further, they found that the amounts of these compounds differ between individuals of East Asian origin and Caucasians. The findings suggest that human earwax, an easily obtained bodily secretion, could be an overlooked source of personal information.
"Our previous research has shown that underarm odors can convey a great deal of information about an individual, including personal identity, ...
New study explains how dense breast tissue drives the early stages of cancer
2014-02-12
Scientists from The University of Manchester working with IBM Research have identified a key biological mechanism that for the first time explains why women with dense breast tissue are at greater risk of developing breast cancer.
The research, published today in the journal Cell Cycle, has important implications for future cancer prevention and treatment.
Women with higher breast density—detected on mammograms—have more compacted breast tissue and are more likely to develop breast cancer, but until now the reasons for this have been unclear.
Manchester scientists, ...
Strong religious beliefs may drive self-perception of addiction to online pornography
2014-02-12
People who consider themselves very religious and view Internet porn even once may perceive they are addicted, according to a new Case Western Reserve University's psychology study.
"This is one of the first studies to examine the link between perceptions of addiction to online pornography and religious beliefs," said Joshua Grubbs, a doctoral student in psychology and lead author of the study.
The research, "Transgression as Addiction: Religiosity and Moral Disapproval as Predictors of Perceived Addiction to Pornography," will be published today in the journal, Archives ...
Helping preserve independent living
2014-02-12
This news release is available in German. Mr. S. is visually impaired and dependent on a cane since suffering a stroke. Nevertheless, as a 70-yr old living alone, he would rather not move into a care home. Most older people harbor this wish. They want to stay in their own familiar surroundings and continue to live independently for as long as possible. According to data from the German Federal Statistical Office, this applies to 70 percent of seniors. Against better judgment, they are putting their health at risk, for not only does the risk of cardiovascular problems ...
Male Pinterest users are more interested in art than cars
2014-02-12
Male users of Pinterest pin more content about photography, art, design, and home decor than sports, technology and cars, says a new study by researchers at the University of Minnesota and Georgia Tech.
The study revealed that while women and men differed in the types of content they collected and the degree to which they specialized, surprisingly men were not particularly interested in stereotypically male topics.
The most popular topics on Pinterest tend to be of "traditional female" interest including food and drink, crafts, home decor, and women's fashion. While ...
Weight loss program for infrared cameras
2014-02-12
This news release is available in German. We want it cozy and warm in our homes when the thermometer outside gets down into the minus area. Especially with older buildings, however, the money we pay for heat ends up out the window. The fault lies hidden in incorrect insulation, or at spots around windows or ceiling joints that are not sealed. These weak points cannot be perceived from outside – unless you are viewing the building though the lens of an infrared camera. This type of camera is equipped with specialized sensors that distinguish the temperature differences ...
From surf to turf: Archaeologists and chemists trace ancient British diets
2014-02-12
The change by our ancestors from hunter-gathers to farmers is one of the most intensively researched aspects of archaeology. Now a large-scale investigation of British archaeological sites dating from around 4,600 BC to 1,400 AD has examined millions of fragments of bone and analysed over 1,000 cooking pots.
The team, led by Professor Richard Evershed of the University of Bristol's School of Chemistry, developed new techniques in an effort to identify fish oils in the pots. Remarkably, they showed that more than 99 per cent of the earliest farmer's cooking pots lacked ...
Prostate cancer advance could improve treatment options
2014-02-12
Researchers at the University of East Anglia have made an important advance in understanding genetic changes associated with terminal prostate cancer.
Findings published today in the British Journal of Cancer, and funded by the Association for International Cancer Research (AICR), show how a genetic mutation in untreated patients is linked to aggressive cancer later in life. It was previously thought that the mutation only occurred in response to therapy.
The research highlights why relapses could occur in some men following hormone therapy. And it could help identify ...
Mountains, models, salt, sand, and cycles
2014-02-12
Boulder, Colo., USA – Topics in this current batch of Geology articles posted ahead of print include the puzzle of parallel mountain chains; 25 years on the East Pacific Rise; unique episodes in Earth's history; turbidity currents; computer models; Wilson cycles; salt structure beneath the sea bed; the North Scotia Ridge; El Hierro, Canary Islands; sand-sized sub-spherical silica grains; bank pull or bar push; kaolinitic paleosols; Earth's youngest, hottest rocks; 3-D thermo-mechanical numerical models; and the Bohemian Massif.
Open Access Papers:
1. Sublithospheric ...
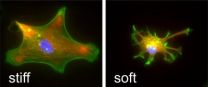
Filling me softly
2014-02-12
Surgical implants are widely used in modern medicine but their effectiveness is often compromised by how our bodies react to them. Now, scientists at the University of Cambridge have discovered that implant stiffness is a major cause of this so-called foreign body reaction.
This is the first time that stiffness of implant materials has been shown to be involved in foreign body reactions. The findings – published in the journal Biomaterials – could lead to major improvements in surgical implants and the quality of life of patients whose lives depend on them.
Foreign ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Depressed girls suffer the mostAdolescents with psychiatric problems are also likely to suffer chronic pain