(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO (Aug. 14, 2014) — Cardiovascular disease is the greatest killer of humans the world over, presenting huge financial and quality-of-life issues. It is well known that the heart becomes less efficient with age in all mammals studied to date, even in the absence of overt cardiac disease. However, scientists still don't have a good understanding of how to prevent these functional declines that ultimately may lead to debilitating cardiovascular disease.
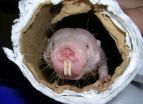
The longest-lived rodent, the naked mole rat, beats these odds and escapes cardiovascular aging, at least to ages equivalent to 92-year-old humans, according to researchers from the School of Medicine at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio.
Kelly Grimes, a graduate student in the lab of Rochelle Buffenstein, Ph.D., at the Health Science Center's Barshop Institute for Longevity and Aging Studies, conducted the first studies of naked mole rat cardiovascular function. Her findings support earlier studies that this species resists the common signs of aging.
Grimes found that, at rest, the heart of the naked mole rat beats very slowly (250 beats per minute). The rodent should have a heart rate twice as high for its body size. How much blood the heart pumps, how hard it contracts to pump the blood, and blood pressure in naked mole rats also are very low. "However, if they need to, for example during exercise, naked mole rats can ramp up their cardiac function with ease," Grimes said. "Their entire cardiovascular system seems to be optimized."
These data are from two papers recently published by Grimes and Dr. Buffenstein as part of a study supported by the American Heart Association. Dr. Buffenstein emphasized that the naked mole rat is unlike any other cardiovascular aging model studied.
"It looks like the naked mole rat maintains heart function at youthful levels at least till age 90," Dr. Buffenstein said. "Clearly these animals hold the secret to healthy hearts in aging humans."
Why do humans, rats, mice, monkeys, dogs and other animals show declines, but not the naked mole rat? Grimes is studying molecular mechanisms that might be protecting the naked mole rats' cardiovascular structure and function. The researchers think these protective mechanisms may be closely linked to the naked mole rats' natural habitat underground and exceptional stress resistance.
The two papers are in the American Journal of Physiology - Heart and Circulatory Physiology® published by the American Physiological Society.
INFORMATION:
For current news from the UT Health Science Center San Antonio, please visit our news release website, like us on Facebook or follow us on Twitter.
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, one of the country's leading health sciences universities, ranks in the top 3 percent of all institutions worldwide receiving National Institutes of Health funding. The university's schools of medicine, nursing, dentistry, health professions and graduate biomedical sciences have produced more than 29,000 graduates. The $765 million operating budget supports eight campuses in San Antonio, Laredo, Harlingen and Edinburg. For more information on the many ways "We make lives better®," visit http://www.uthscsa.edu.
Hope for healthy hearts revealed in naked mole rat studies
Rodents' 'entire cardiovascular system seems to be optimized'
2014-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Men fare worse than women in China regarding discrimination among obese workers
2014-08-19
New research that analyzes economic disparity among obese Chinese adults shows that there is no wage disparity for obese women in China, but there is pay inequality among obese men.
Women in China make less on average than men, but the study results showed no disparity in wages because of body weight. Results of the study for men showed increasing wage disparities by occupation when gaining weight.
The study, "The Obesity Pay Gap: Gender, Body Size, and Wage Inequalities: A Longitudinal Study of Chinese Adults, 1991-2009," which will be presented at the 109th Annual ...
Purdue ag economists: Shale oil 'dividend' could pay for smaller carbon footprint
2014-08-19
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Unanticipated economic benefits from the shale oil and gas boom could help offset the costs of substantially reducing the U.S.'s carbon footprint, Purdue agricultural economists say.
Wally Tyner and Farzad Taheripour estimate that shale technologies annually provide an extra $302 billion to the U.S. economy relative to 2007, a yearly "dividend" that could continue for at least the next two decades, Tyner said.
Using an economic model, they found that "spending" part of this dividend on slashing the nation's carbon emissions by about 27 percent ...
NASA's RXTE satellite decodes the rhythm of an unusual black hole
2014-08-19
Astronomers have uncovered rhythmic pulsations from a rare type of black hole 12 million light-years away by sifting through archival data from NASA's Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) satellite.
The signals have helped astronomers identify an unusual midsize black hole called M82 X-1, which is the brightest X-ray source in a galaxy known as Messier 82. Most black holes formed by dying stars are modestly-sized, measuring up to around 25 times the mass of our sun. And most large galaxies harbor monster, or supermassive, black holes that contain tens of thousands of times ...
Study of African dust transport to South America reveals air quality impacts
2014-08-19
MIAMI – A new study that analyzed concentrations of African dust transported to South America shows large seasonal peaks in winter and spring. These research findings offer new insight on the overall human health and air quality impacts of African dust, including the climate change-induced human health effects that are expected to occur from increased African dust emissions in the coming decades.
Researchers from the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science and colleagues analyzed the dust concentrations in aerosol samples from two locations, ...
Study at Deepwater Horizon spill site finds key to tracking pollutants
2014-08-19
MIAMI – A new study of the ocean circulation patterns at the site of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill reveals the significant role small-scale ocean currents play in the spread of pollutants. The findings provide new information to help predict the movements of oil and other pollutants in the ocean.
Nearly two years to the day after the Deepwater Horizon incident, scientists from the Consortium for Advanced Research on Transport of Hydrocarbon in the Environment (CARTHE), based at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, conducted ...
Graphene rubber bands could stretch limits of current healthcare, new research finds
2014-08-19
Although body motion sensors already exist in different forms, they have not been widely used due to their complexity and cost of production. Now researchers from the University of Surrey and Trinity College Dublin have for the first time treated common elastic bands with graphene, to create a flexible sensor that is sensitive enough for medical use and can be made cheaply.
Once treated, the rubber bands remain highly pliable. By fusing this material with graphene - which imparts an electromechanical response on movement – the team discovered that the material can be ...
Scaling up health innovation: Fertility awareness-based family planning goes national
2014-08-19
WASHINGTON, DC -- There is no guarantee that a successful pilot program introducing a health innovation can be expanded successfully to the national, regional, state or even metropolitan level because scaling up is typically complex and difficult.
A new study from Georgetown University's Institute for Reproductive Health reports on the results of the successful large-scale implementation, in a low resource environment, of the Standard Days Method®, a highly effective fertility awareness-based family planning method developed by Institute researchers. Lessons learned ...
Intimacy a strong motivator for PrEP HIV prevention
2014-08-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Men in steady same-sex relationships where both partners are HIV negative will often forgo condoms out of a desire to preserve intimacy, even if they also have sex outside the relationship. But the risk of HIV still lurks. In a new study of gay and bisexual men who reported at least one instance of condomless anal sex in the last 30 days, researchers found that the same desire for intimacy is also a strong predictor of whether men would be willing to take antiretroviral medications to prevent HIV, an emerging practice known as pre-exposure ...
Sequencing at sea
2014-08-19
SAN DIEGO, Calif. (August 19, 2014) — Daylight was breaking over the central Pacific and coffee brewing aboard the MY Hanse Explorer. Between sips, about a dozen scientists strategized for the day ahead. Some would don wetsuits and slip below the surface to collect water samples around the southern Line Islands' numerous coral reefs. Others would tinker with the whirring gizmos and delicate machinery strewn throughout the 158-foot research vessel. All shared a single goal: Be the first research group to bring a DNA sequencer out into the field to do remote sequencing in ...
Physically fit kids have beefier brain white matter than their less-fit peers
2014-08-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study of 9- and 10-year-olds finds that those who are more aerobically fit have more fibrous and compact white-matter tracts in the brain than their peers who are less fit. "White matter" describes the bundles of axons that carry nerve signals from one brain region to another. More compact white matter is associated with faster and more efficient nerve activity.
The team reports its findings in the open-access journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
"Previous studies suggest that children with higher levels of aerobic fitness show greater ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] Hope for healthy hearts revealed in naked mole rat studiesRodents' 'entire cardiovascular system seems to be optimized'