New quality improvement system significantly reduces CT misadministration
Best practices protocol facilitates analysis, accountability, change
2015-04-20
(Press-News.org) TORONTO, April 20, 2015--A protocol developed by radiologists at the Santa Clara Valley Medical Center reduced CT misadministration at the Santa Clara Valley Medical Center from 18 instances in 60,999 studies to zero in 36,608 in just 10 months. Misadministration includes, but is not limited to, imaging the wrong patient or body part without a physician's order or repeated imaging of a patient without a physician's order.
The best practices protocol includes several levels of assessment, including reverification checklists, workflow clarification, and individual accountability.
"CT misadministration is an important and actionable quality issue, particularly in light of growing public concern about radiation exposure," said Patrick Do, MD. "Our quality improvement analysis significantly reduced the rate of misadministration and potentially brings great benefits to patients, hospitals, and the public."
The study was featured in an electronic exhibit at the ARRS 2015 Annual Meeting in Toronto.
View the abstract
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-20
(Bethesda, MD, April 20, 2015) Researchers at the NFCR Center for Cancer System Informatics at MD Anderson Cancer Center have discovered a key factor that may explain drug resistance in glioblastoma (GBM), the most common and deadliest form of brain cancer.
GBM accounts for 17% of all brain tumors, and over 10,000 new cases of GBM are diagnosed in the US each year. Unfortunately - since there are no effective, long-term therapies available - survival is typically less than 17 months.
Approximately 50% of GBMs are known to have mutations in a gene called EGFR. However, ...
2015-04-20
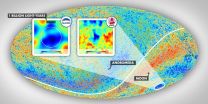
In 2004, astronomers examining a map of the radiation leftover from the Big Bang (the cosmic microwave background, or CMB) discovered the Cold Spot, a larger-than-expected unusually cold area of the sky. The physics surrounding the Big Bang theory predicts warmer and cooler spots of various sizes in the infant universe, but a spot this large and this cold was unexpected.
Now, a team of astronomers led by Dr. Istvan Szapudi of the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawaii at Manoa may have found an explanation for the existence of the Cold Spot, which Szapudi ...
2015-04-20
A badly dubbed foreign film makes a viewer yearn for subtitles; even subtle discrepancies between words spoken and facial motion are easy to detect. That's less likely with a method developed by Disney Research that analyzes an actor's speech motions to literally put new words in his mouth.
The researchers found that the facial movements an actor makes when saying "clean swatches," for instance, are the same as those for such phrases as "likes swats," "then swine," or "need no pots."
Sarah Taylor and her colleagues at Disney Research Pittsburgh and the University of ...
2015-04-20
Leading doctors today [Monday 20 April, 2015] warn that medical and public recognition of sepsis--thought to contribute to between a third and a half of all hospital deaths--must improve if the number of deaths from this common and potentially life-threatening condition are to fall.
In a new Commission, published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases, Professor Jonathan Cohen and colleagues outline the current state of research into this little-understood condition, and highlight priority areas for future investigation.
Sepsis--sometimes misleadingly called "blood poisoning"--is ...
2015-04-19
The college graduation rate for students who have lived in foster care is 3 percent, among the lowest of any demographic group in the country. And this rate is unlikely to improve unless community colleges institute formal programs to assist foster youth both financially and academically, concludes a new study by researchers at University of the Pacific.
The findings will be presented during the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association in Chicago on Sunday, April 19.
"Informal programs are less likely to work since foster youth lack guidance ...
2015-04-19
PHILADELPHIA-- Once again, researchers at Penn's Abramson Cancer Center have extended the reach of the immune system in the fight against metastatic melanoma, this time by combining the checkpoint inhibitor tremelimumab with an anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody drug. The first-of-its-kind study found the dual treatments to be safe and elicit a clinical response in patients, according to new results from a phase I trial to be presented at the AACR Annual Meeting 2015 on Sunday, April 19.
Researchers include first author David L. Bajor, MD, instructor of Medicine in the division ...
2015-04-19
PHILADELPHIA -- Women diagnosed with breast cancer are often told not to eat soyfoods or soy-based supplements because they can interfere with anti-estrogen treatment. But new research being presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2015 could eventually impact that advice, because in animals, a long history of eating soyfoods boosts the immune response against breast tumors, reducing cancer recurrence.
The study, conducted at Georgetown Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center, could offer good news to some women whose diet has long ...
2015-04-19
PHILADELPHIA, April 19, 2015 - Broccoli sprout extract protects against oral cancer in mice and proved tolerable in a small group of healthy human volunteers, the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI), partner with UPMC CancerCenter, announced today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting in Philadelphia.
The promising results will be further explored in a human clinical trial, which will recruit participants at high risk for head and neck cancer recurrence later this year. This research is funded through Pitt's Specialized Program ...
2015-04-19
PHILADEPHIA, April 19, 2015 - Identifying molecular changes that occur in tissue after chemotherapy could be crucial in advancing treatments for ovarian cancer, according to research from Magee-Womens Research Institute and Foundation (MWRIF) and the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute (UPCI), partner with UPMC CancerCenter, presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2015.
For years now, intraperitoneal chemotherapy, a treatment which involves filling the abdominal cavity with chemotherapy drugs after surgery, has been ...
2015-04-19
PHILADELPHIA -Genetically modified versions of patients' own immune cells successfully traveled to tumors they were designed to attack in an early-stage trial for mesothelioma and pancreatic and ovarian cancers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The data adds to a growing body of research showing the promise of CAR T cell technology. The interim results will be presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2015, April 18-22.
"The goal of this phase I trial was to study the safety and feasibility of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New quality improvement system significantly reduces CT misadministration
Best practices protocol facilitates analysis, accountability, change