INFORMATION:
New AI-based versatile software for tracking many cells in 3D microscope videos
Automatic tracking of cells in microscope videos will contribute to basic life science research and drug discovery by easily analyzing critical cellular activities
2021-03-30
(Press-News.org) In modern basic life science research as well as in drug discovery, recording and analyzing the images of cells over time using 3D microscopy has become extremely important. Once the images have been recorded, the same cell in different images at different time points has to be accurately identified ("cell tracking") because the living cells captured in the images are in motion. However, tracking many cells automatically in 3D microscope videos has been considerably difficult.
In the Kimura laboratory at the Nagoya City University, Dr. Chentao Wen and colleagues developed the 1st AI-based software called 3DeeCellTracker that can run on a desktop PC and automatically track cells in 3D microscope videos. Using the software, they were able to measure and analyze the activities of ~100 cells in the brain of a moving microscopic worm, in a naturally beating heart of a young small fish, and ~1000 cancer cells cultured in 3D under laboratory conditions, which were recorded with different types of cutting-edge microscope systems.
This versatile software can now be used across biology, medical research, and drug development to help monitor cell activities.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers reveal SARS-CoV-2 distribution and relation to tissue damage in patients
2021-03-30
Researchers have mapped the distribution of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, in deceased patients with the disease, and shed new light on how viral load relates to tissue damage.
Their study of 11 autopsy cases, published today in eLife, may contribute to our understanding of how COVID-19 develops in the body following infection.
More than 24 million SARS-CoV-2 infections have been reported to date, and the number of deaths attributed to COVID-19 has exceeded 828,000 worldwide. COVID-19 occurs with varying degrees of severity. While most patients have mild symptoms, some experience more severe symptoms and may need to be hospitalised. A minority of those in hospital may enter a critical condition, with respiratory failure, blood vessel complications, or multiple organ ...
Cardiorespiratory fitness improves grades at school
2021-03-30
Recent studies indicate a link between children's cardiorespiratory fitness and their school performance: the more athletic they are, the better their marks in the main subjects - French and mathematics. Similarly, cardiorespiratory fitness is known to benefit cognitive abilities, such as memory and attention. But what is the real influence of such fitness on school results? To answer this question, researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland tested pupils from eight Geneva schools. Their results, published in the journal Medicine & Science in Sport & Exercise, show that there is an indirect link with cardiorespiratory fitness influencing ...
Breaking records like baking bread
2021-03-30
Alloying, the process of mixing metals in different ratios, has been a known method for creating materials with enhanced properties for thousands of years, ever since copper and tin were combined to form the much harder bronze. Despite its age, this technology remains at the heart of modern electronics and optics industries. Semiconducting alloys, for instance, can be engineered to optimize a device's electrical, mechanical and optical properties.
Alloys of oxygen with group III elements, such as aluminum, gallium, and indium, are important semiconductor materials with vast applications ...
Beetle outbreak impacts vary across Colorado forests
2021-03-30
It's no secret. Colorado's forests have had a tough time in recent years. While natural disturbances such as insect outbreaks and wildfires occurred historically and maintained forest health over time, multiple, simultaneous insect disturbances in the greater region over the past two decades have led to rapid changes in the state's forests.
A bird's eye view can reveal much about these changes. Annual aerial surveys conducted by the Colorado State Forest Service and USDA Forest Service have provided yearly snapshots for the state. New collaborative research led by Colorado State University and the University of Wisconsin-Madison now supplements this understanding with even greater spatial detail.
The ...
Teens describe their gender and sexuality in diverse ways, but some are being left behind
2021-03-30
A growing number of young people are identifying as part of the LGBTQ+ community, and many are challenging binaries in gender and sexual identity to reflect a broader spectrum of experience beyond man or woman and gay or straight. But not everyone is participating equally in these diverse forms of expression, according to new research from the University of California, Santa Cruz.
Psychology Professor Phillip Hammack's latest paper, published in the Journal of Adolescent Research, is shedding light on the social factors that can either hinder or support expression of diversity in sexual and gender identity ...
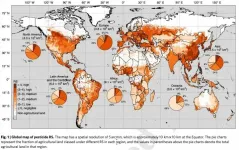
64% of global agricultural land at risk of pesticide pollution?
2021-03-30
The study, published in Nature Geoscience, produced a global model mapping pollution risk caused by 92 chemicals commonly used in agricultural pesticides in 168 countries.
The study examined risk to soil, the atmosphere, and surface and ground water.
The map also revealed Asia houses the largest land areas at high risk of pollution, with China, Japan, Malaysia, and the Philippines at highest risk. Some of these areas are considered "food bowl" nations, feeding a large portion of the world's population.
University of Sydney Research Associate and the study's lead author, Dr Fiona Tang, said the widespread use of pesticides in agriculture - while boosting productivity - could have potential implications for the environment, human and animal ...
Prime editing enables precise gene editing without collateral damage
2021-03-30
The latest gene editing technology, prime editing, expands the "genetic toolbox" for more precisely creating disease models and correcting genetic problems, scientists say.
In only the second published study of prime editing's use in a mouse model, Medical College of Georgia scientists report prime editing and traditional CRISPR both successfully shut down a gene involved in the differentiation of smooth muscle cells, which help give strength and movement to organs and blood vessels.
However, prime editing snips only a single strand of the double-stranded DNA. CRISPR makes double-strand cuts, which can be lethal to cells, and produces unintended edits at both the work site as well as randomly across the genome, ...
'Bottom-up' approach needed to study freshwater blooms
2021-03-30
HANOVER, N.H. - March 30, 2021 - Cyanobacteria living at the bottom of lakes may hold important, under-researched clues about the threat posed by these harmful organisms, according to a Dartmouth-led study.
The research, published in the Journal of Plankton Research, urges a more comprehensive approach to cyanobacteria studies in order to manage the dangerous blooms during a time of global climate change.
"Most studies of cyanobacteria focus on the times when they are visible in the water column," said Kathryn Cottingham, the Dartmouth Professor in the Arts and ...
How to talk to people about climate change
2021-03-30
As our planet warms, seas rise and catastrophic weather events become more frequent, action on climate change has never been more important. But how do you convince people who still don't believe that humans contribute to the warming climate?
New UBC research may offer some insight, examining biases towards climate information and offering tools to overcome these and communicate climate change more effectively.
Researchers examined 44 studies conducted over the past five years on the attentional and perceptual biases of climate change - the tendency to pay special attention to or perceive particular aspects of climate change. They identified a number of ...
New statistical method eases data reproducibility crisis
2021-03-30
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A reproducibility crisis is ongoing in scientific research, where many studies may be difficult or impossible to replicate and thereby validate, especially when the study involves a very large sample size. For example, to evaluate the validity of a high-throughput genetic study's findings scientists must be able to replicate the study and achieve the same results. Now researchers at Penn State and the University of Minnesota have developed a statistical tool that can accurately estimate the replicability of a study, thus eliminating the need to duplicate the work and effectively ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
[Press-News.org] New AI-based versatile software for tracking many cells in 3D microscope videosAutomatic tracking of cells in microscope videos will contribute to basic life science research and drug discovery by easily analyzing critical cellular activities