(Press-News.org) An England-wide study of over 58 million people has identified eight rare diseases that carry significantly increased risks for COVID-19-related mortality in fully vaccinated individuals. This important research calls for better inclusion of rare diseases in public health strategies, including future pandemic planning, vaccination policies, and NHS service provision.
Historically rare diseases have been difficult to study and neglected in research, in part due to a lack of large-scale data. This means that people living with rare conditions often struggle to get the treatment and support they need. Additionally, rare disease patients were overlooked in public health planning – for example during COVID-19 lockdown periods, the UK’s shielding list excluded most rare diseases, failing to protect highly vulnerable individuals.
Researchers at UCL (University College London) and the University of Glasgow, supported by the BHF Data Science Centre at Health Data Research UK (HDR UK), set out to harness the power of large-scale linked data, to uncover new insights into rare diseases. Using linked electronic health records (EHRs), they investigated the prevalence of rare diseases across the population, and the risks that COVID-19 may pose to people with these conditions.
They uncovered eight rare diseases linked with an increased risk of dying from COVID-19, and found that people with rare diseases were nearly five times more like to die from COVID-19 than the general population. The conditions carrying the highest risk were infertility disorders and kidney diseases.
The rarity of some diseases can contribute to a lack of comprehensive data due to lengthy waits for diagnosis. And as the study period spans two ‘waves’ of the pandemic, it’s difficult to untangle the effects of different COVID-19 variants, as well as overlapping symptoms in multiple illnesses.
However, this study takes advantage of one of our health system’s unique strengths, having population-wide granular data coverage in EHRs and diversity in representation, highlighting significant health inequalities faced by specific ethnic groups in which some rare diseases were disproportionately common. It’s also the first time an analysis has been performed on so many rare diseases, and the impact of COVID-19 on the people with such conditions, a landmark moment for rare disease research.
Living with a rare disease can be extremely challenging, from a difficult diagnosis to relentless appointments to manage health and wellbeing. But these findings fill a critical knowledge gap, emphasising the power of electronic health record data to bring to light the prevalence and outcomes of rare diseases.
Co-author Professor Honghan Wu, University of Glasgow and formerly UCL, said:
“Early detection means earlier intervention and better treatment and support. The ability to link data gives us deeper understanding, and allows us to spot individuals who would otherwise have slipped through the net. So research harnessing NHS data for impact through linking EHRs has enormous potential to inform care and public health decision-making, beyond the COVID-19 pandemic, especially for patient populations that are far too often neglected.”
This research was published in The Lancet Digital Health.
END
Researchers leverage large-scale data to uncover new insights into rare diseases and COVID-19
2025-01-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fresh embryo transfer may be better for women with low chance of IVF success
2025-01-30
Fresh embryo transfer may be a better option than use of frozen embryos for women with a low chance of having a healthy baby by vitro fertilisation (IVF), suggests a trial from China published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say their findings do not support the routine use of the freeze-all strategy in women with low prognosis of IVF treatment success, which can be due to older age, low quantity or quality of eggs, or certain underlying conditions.
IVF has revolutionised infertility treatment and a strategy of freezing all suitable embryos before transfer (freeze-all strategy) is now a routine part of the treatment to help prevent ...
First-of-its-kind research identifies beneficial prenatal vitamins to reduce risk of infant death
2025-01-30
Dongqing Wang, an assistant professor of Global and Community Health at George Mason’s College of Public Health, is pioneering research in prenatal nutritional interventions. His latest report identifies prenatal supplements that reduce health risks to small and vulnerable babies. This research was published in the prestigious The Lancet Global Health journal and funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
Wang found that compared to folic acid and iron alone, a multiple micronutrient supplement ...
Durham University scientists unveil breakthrough in predicting and engineering protein metalation
2025-01-30
-With images-
Researchers at Durham University have achieved a major advancement in understanding how proteins bind metals inside cells, a process crucial to life.
The study, published in Nature Communications, introduces a pioneering approach that allows scientists to accurately predict and engineer the metalation of proteins, a discovery with far-reaching implications for biotechnology and sustainable biomanufacturing.
The research builds upon years of work by the research team, dating back to key discoveries published in 2008.
In ...
The benefits of speaking multiple languages
2025-01-29
Encouraging bilingualism at home can have many cognitive benefits, which may be particularly helpful to kids with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), new research from the University of Miami College of Arts and Sciences indicates.
A team of researchers led by Celia Romero, a graduate student in clinical psychology, along with associate professor Lynn Perry, professor Michael Alessandri, and former University professor Lucina Uddin, explored the role of bilingualism in 112 children, including typically developing children and children with autism, between the ages of 7 to 12 years old. Overall, they found that children who spoke two or more languages often had stronger executive ...
Topical mupirocin lowers lupus inflammation
2025-01-29
Systemic lupus erythematosus, more commonly known as lupus, has a variety of symptoms and room for improvement when it comes to treatment.
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a common manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus.
The condition is characterized by rashes on various parts of the body including the face and scalp, hair loss and scarring of the skin.
The rashes are caused by inflammation from the immune system fighting the body.
The standard treatment for cutaneous lupus erythematosus is using immunosuppressants and biologic drugs to reduce inflammation.
While ...
New atom-based thermometer measures temperature more accurately
2025-01-29
Scientists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have created a new thermometer using atoms boosted to such high energy levels that they are a thousand times larger than normal. By monitoring how these giant “Rydberg” atoms interact with heat in their environment, researchers can measure temperature with remarkable accuracy. The thermometer’s sensitivity could improve temperature measurements in fields ranging from quantum research to industrial manufacturing.
Unlike traditional thermometers, a Rydberg thermometer doesn’t need to be first adjusted or calibrated at the ...
COVID lockdowns disrupted a crucial social skill among preschoolers, trailblazing study finds
2025-01-29
Lockdowns. Social distancing. Shuttered schools and businesses. The COVID-19 pandemic and its sweeping disruptions set off a stampede of “what it’s doing to us” research, focused largely on schoolchildren. How were students’ academics affected? Their mental health? Their social development?
Left unexamined was whether the pandemic impacted the social cognition of preschool children — kids younger than 6 — whose social norms were upended by day care closures and families sheltered at home.
That changed when a UC Merced ...
Otago scientists discover Antarctic fast ice secrets
2025-01-29
University of Otago – Ōtākou Whakaihu Waka scientists have successfully analysed more than 30 years of vital data on the thickness of landfast sea ice in Antarctica’s McMurdo Sound, which will prove useful to measure future impacts of climate change.
The study, published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, set out to discover what key influences determine the thickness of landfast sea-ice, known as fast ice, using data from 1986 to 2022.
Fast ice is frozen ocean water that is attached to shorelines and persists for at least 15 days. It provides vital habitats for penguins and seals, as well as fish, krill and algae underneath the ice.
Scientists ...
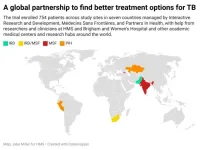
Study finds three new safe, effective ways to treat drug-resistant tuberculosis
2025-01-29
Tuberculosis remains one of the top infectious disease killers worldwide, a challenge amplified by drug-resistant forms of the disease. Now, in a major step forward, an international clinical trial has found three new safe and effective drug regimens for tuberculosis that is resistant to rifampin, the most effective of the first-line antibiotics used to treat TB.
The research, published Jan. 30 in the New England Journal of Medicine, was led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and other members of the endTB project, ...
A weekly injection could replace painful daily treatment for rare fat disorder
2025-01-29
Rutgers Health researchers have found that a weekly injection of diabetes medication could replace painful daily hormone shots for people with a rare genetic form of lipodystrophy that leaves patients with almost zero fat tissue, according to a study in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL), which affects only a few thousand people worldwide, results in severe metabolic disease, diabetes, insulin resistance and reduced life expectancy. With no fat tissue for proper storage, fat accumulates in organs ...