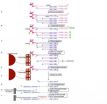
(Press-News.org) A new gene expression technique adapted for single molecule sequencing has enabled researchers at the RIKEN Omics Science Center (OSC) to accurately and quantitatively measure gene expression levels using only 100 nanograms of total RNA. The technique, which pairs RIKEN's Cap Analysis of Gene Expression (CAGE) protocol with the Helicos® Genetic Analysis System developed by Helicos BioSciences Corporation, opens the door to the detailed analysis of gene expression networks and rare cell populations.
In recent years, next-generation DNA sequencers have produced an increasingly detailed picture of how genes are expressed at the molecular level. The transcriptional output of these genes – the RNA copies produced from DNA – has revealed a richness of complexity in transcript structure and function, providing insights into the molecular-level properties of cancers and other diseases.
One of the most powerful methods for analyzing RNA transcripts is the Cap Analysis of Gene Expression (CAGE) protocol developed at the RIKEN OSC. A unique approach, CAGE enables not only high-throughput gene expression profiling, but also simultaneous identification of transcriptional start sites (TSS) specific to each tissue, cell or condition.
With HeliScopeCAGE, the OSC research team has adapted the existing CAGE protocol for use with the revolutionary HeliScopeTM Single Molecule Sequencer. Unlike earlier sequencers, the HeliScope Sequencer does not employ polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification to multiply a small number of DNA strands for analysis, a process which can introduce biases into data. Instead, the HeliScope Sequencer actually sequences the DNA strand itself, enabling direct, high-precision measurement.
In a paper published in Genome Research, RIKEN researchers confirm that this direct approach reduces biases and generates highly reproducible data from between 5 micrograms to as little as 100 nanograms of total RNA. A comparison using a leukemia cell line (THP-1) and a human cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) further shows that results from the technique are closely correlated to those from traditional microarray analysis. By making possible high-precision gene expression analysis from tiny samples, HeliScopeCAGE greatly expands the scope of research at the OSC, strengthening the institute's role in Japan as a hub for next-generation genome analysis.
INFORMATION:
About the RIKEN Omics Science Center
Omics is the comprehensive study of molecules in living organisms. The complete sequencing of genomes (the complete set of genes in an organism) has enabled rapid developments in the collection and analysis of various types of comprehensive molecular data such as transcriptomes (the complete set of gene expression data) and proteomes (the complete set of intracellular proteins). Fundamental omics research aims to link these omics data to molecular networks and pathways in order to advance the understanding of biological phenomena as systems at the molecular level.
Here at the RIKEN Omics Science Center, we are developing a versatile analysis system, called the "Life Science Accelerator (LSA)", with the objective of advancing omics research. LSA is a multi-purpose, large-scale analysis system that rapidly analyzes molecular networks. It collects various genome-wide data at high throughput from cells and other biological materials, comprehensively analyzes experimental data, and thereby aims to elucidate the molecular networks of the sample. The term "accelerator" was chosen to emphasize the strong supporting role that this system will play in supporting and accelerating life science research worldwide.
HeliScopeCAGE: A new gene expression analysis technique on a single molecule sequencer
2011-05-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breaking News! 2011 Urologist Report Reveals "Traction Beats Surgery for Permanent Lengthening of the Male Sex Organ"
2011-05-19
Penile enlargement is one of the most controversial topics today. Many physicians claim that there is no medical proof that the non-surgical methods for increasing the penile size actually work. In addition to that, there are many people online abusing this topic, which is one of the main reasons why everyone is so skeptic about it.
With the growing popularity of the penile extenders, one of the most reputable medical journals BJUI (British Journal of Urology International), which is issued as the official journal of the British Association of Urological Surgeons, have ...
Scottish data highlight dangerous practice in pediatric paracetamol prescribing
2011-05-19
Many of the prescriptions issued by GPs for paracetamol either give less than recommended doses to older children or exceed recommended doses in young children. Under-dosing may result in insufficient pain relief and over-dosing can damage a person's liver. "Getting the dose right can become even more complicated when parents also give their children additional paracetamol that they have bought over the counter," says James McLay, a senior member of the research team who studied this issue. The findings are published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.
Paracetamol ...
'Critical baby step' taken for spying life on a molecular scale
2011-05-19
The ability to image single biological molecules in a living cell is something that has long eluded researchers; however, a novel technique, using the structure of diamond, may well be able to do this and potentially provide a tool for diagnosing, and eventually developing a treatment for, hard-to-cure diseases such as cancer.
In a study published today, Thursday, 19 May, in the Institute of Physics and the German Physical Society's New Journal of Physics, researchers have developed a technique, exploiting a specific defect in the lattice structure of diamond, to externally ...
Break the Bank at City Bingo Rewards Loyal Players of Free Bingo
2011-05-19
Free bingo site City Bingo has gone yet further in order to reward customers at the site. With existing promotions sending members to locations such as New York City and Barcelona and daily games of free bingo no deposit required, the Break the Bank deal is specifically for those logging on to City Bingo on a daily basis.
As the site has been claiming on the website - "Regular Players Can Always Feel a Buzz in the City - and our Break the Bank Promotion is the Talk of the Town!" With the site quickly becoming one of the premier free bingo brands with its distinctive ...
Lizard fossil provides missing link in debate over snake origins
2011-05-19
Until a recent discovery, theories about the origins and evolutionary relationships of snakes barely had a leg to stand on.
Genetic studies suggest that snakes are related to monitor lizards and iguanas, while their anatomy points to amphisbaenians ("worm lizards"), a group of burrowing lizards with snake-like bodies. The debate has been unresolved--until now. The recent discovery by researchers from the University of Toronto Mississauga and the Museum für Naturkunde Berlin, Germany of a tiny, 47 million-year-old fossil of a lizard called Cryptolacerta hassiaca provides ...
National Jewish Health Conference highlights
2011-05-19
Genetic Variant Raises Risk of Fatal Pulmonary Fibrosis
Max Seibold, PhD, will extend findings recently reported in The New England Journal of Medicine, which identified a common genetic variant associated with a 7 to 22 fold increased risk for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and familial interstitial pneumonia. The discovery not only identifies a major risk factor for pulmonary fibrosis, but also points scientists in an entirely new direction for research into the causes and potential treatments for this difficult and deadly disease.
Muc5b is the Predominant Mucin Expressed ...
What's the Difference Between Juvederm, Restylane and Elevess?
2011-05-19
With time, your facial skin begins to lose its structure and volume. The result is unpleasant wrinkles that can make you feel old and unattractive. There are three injectable gel forms of hyaluronic acid, a natural complex sugar found in all living cells that can help mask the effects of aging: Juvederm, Restylane and Elevess.
The complex sugar in the hyaluronic acid gel is one of the major components of your skin. This gel makes wrinkle correction possible by retaining water much like a sponge. In fact, it can absorb more than 1,000 times its weight, helping to attract ...
End of life care for cancer patients differs in US and Canada
2011-05-19
In the United States, older patients with advanced lung cancer make much less use of hospital and emergency room services at the end of life than their counterparts in Ontario but use far more chemotherapy, according to a study published May 18th online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Government-financed health care covers elderly patients in both Canada and the U.S., but coverage at the end of life differs. In the U.S., Medicare covers hospice care for qualified patients. Ontario, the most populous Canadian province, has no hospice program comparable ...
Astronomer Bennett's team discovers new class of planets
2011-05-19
University of Notre Dame astronomer David Bennett is co-author of a new paper describing the discovery of a new class of planets — dark, isolated Jupiter-mass bodies floating alone in space, far from any host star. Bennett and the team of astronomers involved in the discovery believe that the planets were most likely ejected from developing planetary systems.
The study is described in a paper appearing in the May 19th issue of the journal Nature.
The discovery stems from an analysis of observations of the central bulge of the Milky Way galaxy taken in 2006 and 2007 by ...
Errors in protein structure sparked evolution of biological complexity
2011-05-19
Over four billion years of evolution, plants and animals grew far more complex than their single-celled ancestors. But a new comparison of proteins shared across species finds that complex organisms, including humans, have accumulated structural weaknesses that may have actually launched the long journey from microbe to man.
The study, published in Nature, suggests that the random introduction of errors into proteins, rather than traditional natural selection, may have boosted the evolution of biological complexity. Flaws in the "packing" of proteins that make them more ...