Scientists describe the deepest terrestrial arthropod ever found
2012-02-23
(Press-News.org) Scientists have recently described the deepest terrestrial animal ever found, together with 4 new species for science. These animals are springtails (Arthropoda, Insecta, Collembola), a minute primitive wingless insect with six-legs and without eyes that live in total darkness.
Described by Rafael Jordana and Enrique Baquero from University of Navarra (Spain), they are known for science as: Anurida stereoodorata, Deuteraphorura kruberaensis, Schaefferia profundissima and Plutomurus ortobalaganensis. The last one is the deepest arthropod ever found, at the remarkable depth of 1.980 meters (2,165 yards) below ground surface.
These animals were collected during the biospeleological works of Sofia Reboleira, from the University of Aveiro (Portugal) and Alberto Sendra, from the Valencian Museum of Natural History (Spain), both who were members of the Ibero-Russian CaveX Team Expedition to the World's deepest cave, during the summer of 2010.
The World's deepest cave, Krubera-Voronja, reaching nowadays the remarkable depth of -2.191 meters below ground level, is located in Abkhazia, a remote area near the Black Sea in the mountains of Western Caucasus, being the only cave in the World with more than 2 kilometres of depth.
The discovery of life in such deep systems launches new insights about the way we look at life on Earth. In total absence of light and extreme low food resources, cave-dwelling animals have unique adaptations to subterranean life. They lack body pigmentation, they have no eyes and have been developing morpho-physological strategies for survival at such depth, during millions of years. One of the species has, for example, a spectacular chemoreceptor, a highly specialised type of the habitual post-antennal organ of the springtails.
INFORMATION:
Journal article:
Reviews of the genera Schaefferia Absolon, 1900, Deuteraphorura Absolon, 1901, Plutomurus Yosii, 1956 and the Anurida Laboulbène, 1865 species group without eyes, with the description of four new species of cave springtails (Collembola) from Krubera-Voronya cave, Arabika Massif, Abkhazi
Source: Terrestrial Arthropod Reviews volume 5 (2012) pp. 1-51
The PDF of the article is available upon request with Michiel Thijssen, thijssen@brill.nl
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2012-02-23
WASHINGTON, DC, February 15, 2012 — Highly educated whites and minorities are no more likely to support workplace affirmative action programs than are their less educated peers, according to a new study in the March issue of Social Psychology Quarterly, which casts some doubt on the view that an advanced education is profoundly transformative when it comes to racial attitudes.
"I think this study is important because there's a common view that education is uniformly liberalizing, and this study shows—in a number of cases—that it's not," said study author Geoffrey T. Wodtke, ...
2012-02-23
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Based on a study of nearly 2,000 breast cancer patients, researchers at the Swedish Cancer Institute in Seattle say that, in women between the ages of 40 and 49, breast cancers detected by mammography have a better prognosis. The study appears in the March issue of Radiology.
"In our study, women aged 40 to 49 whose breast cancer was detected by mammography were easier to treat and had less recurring disease and mortality, because their cancer was found at an earlier stage," said Judith A. Malmgren, Ph.D., president of HealthStat Consulting, Inc.
Dr. ...
2012-02-23
A recent ruling from the Social Security Administration (SSA) clarifies the types of information that can be used to determine whether young adult applicants have a physical or mental disability. The SSA's policy interpretation ruling is now in effect for the processes that govern Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) applications.
The ruling applies specifically to people who are "young adults" for SSA purposes, meaning those from 18 to 25 years of age. Under current SSA procedures, the same definition of disability applies for both young adults and ...
2012-02-23
OAK BROOK, Ill. – In a new study published in the March issue of Radiology, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) shows that cognitive rehabilitation changes brain function and improves cognitive performance in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (MS).
"These results prompt the use of specific computer-based rehabilitation programs to treat deficits in selected neuropsychological domains in patients with relapsing-remitting MS," said the study's lead author, Massimo Filippi, M.D., professor of neurology at the San Raffaele Vita-Salute University ...
2012-02-23
If people see news coverage of alcohol's role in violent crime and fatal injuries, they may give more support to alcohol-control laws, according to a study in the March issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
It's estimated that drinking is involved in almost one third of deaths from accidents and violent crime. But the news reports on those deaths often make no mention of alcohol.
"People have some awareness of the social cost that alcohol can have," said the study's lead author, Michael D. Slater, Ph.D., of Ohio State University in Columbus. "But only ...
2012-02-23
A pioneering new study finds that a specific type of computerized cognitive training can lead to significant neural and behavioral improvements in individuals with schizophrenia. The research, published by Cell Press in the February 23 issue of the journal Neuron, reveals that 16 weeks of intensive cognitive training is also associated with improved social functioning several months later and may have far-reaching implications for improving the quality of life for patients suffering from neuropsychiatric illness.
Schizophrenia is a debilitating psychiatric illness that ...
2012-02-23
What: NIH-supported scientists will be presenting their latest research findings at the 2012 Midwinter Meeting of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (ARO).
When: February 25-29, 2012
Where: The Manchester Grand Hyatt Hotel, San Diego, California, USA
Additional Information: Research topics to be presented by NIDCD-funded scientists will include:
Bilateral ≠ Binaural: Can the Ability to Localize Sounds Be Regained After Bilateral Cochlear Implantation?
Ruth Litovsky, Ph.D., University of Wisconsin-Madison
Bilateral cochlear implants—one implant ...
2012-02-23
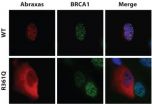
PHILADELPHIA - The infamous BRCA genes do not act alone in causing cancer; there is a molecular syndicate at work preventing the way cells normally repair breaks in DNA that is at the root of breast cancer. But finding all of the BRCA molecular collaborators has been elusive.
Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Oulu, Finland, published their discovery of a mutation in the Abraxas gene, which interacts with the well-known breast-cancer gene BRCA1, in Science Translational Medicine this week.
The mutation ...
2012-02-23
STANFORD, Calif. — When aortic walls buckle, the body's main blood pipe forms an ever-growing bulge. To thwart a deadly rupture, a team of Stanford University School of Medicine researchers has found two tiny molecules that may be able to orchestrate an aortic defense.
A team led by cardiovascular scientists Philip Tsao, PhD, and Joshua Spin, MD, PhD, identified two microRNAs — small molecules that usually block proteins from being made — that work to strengthen the aorta during bulge growth. By tweaking the activity of each molecule, they could reduce abdominal aortic ...
2012-02-23
Recently, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) called for every state in the nation and Washington, D.C., to ban all non-emergency cellphone use while driving a motor vehicle. This recommendation follows various studies that have concluded cellphone use while driving can be extremely distracting - often leading to severe or even deadly accidents.
One tragic trucking accident illustrating the NTSB's concerns was an accident in which a truck driver, while using his cellphone, crossed the median and hit a van, killing 11 people in the process. It remains to be ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists describe the deepest terrestrial arthropod ever found