(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA – September 23, 2012 – Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute have shown how to synthesize in the laboratory an important set of natural compounds known as terpenes. The largest class of chemicals made by living organisms, terpenes are made within cells by some of the most complex chemical reactions found in biology.
The new technique, described in an advance online edition of the journal Nature Chemistry on September 23, 2012, mimics a crucial but obscure biochemical phenomenon that allows cells to make terpenes. The discovery may one day result in cheaper, fully synthetic versions of the cancer drug Taxol, the antimalarial compound artemisinin and hundreds of other useful terpene products.
"It's exciting for us because we're now making molecules that have never been made in the laboratory before, and we've done this by first observing what nature does," said the senior investigator for the study Ryan A. Shenvi, a chemist at Scripps Research.
Powerful Biological Functions
Terpenes take their name from one of their best-known representatives, the paint thinner turpentine—a derivative of pine sap. Many terpenes, like those in turpentine, are small, plant-made molecules that turn into vapor at relatively low temperatures and waft easily through the air. These often serve as important chemical signals for plants, and are used by humans in fragrances and flavorings.
Some terpenes are more complex, and are synthesized by plants and other organisms as powerful cellular defense mechanisms. "Having such strong biological functions can make them very useful in medicine," said Shenvi. Paclitaxel (Taxol), a widely used cancer drug, is a terpene derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree. Artemisinin, the basis for a major class of antimalarial therapy, is a terpene made by the sweet wormwood herb. But the terpene family is highly diverse and also includes vitamin A, menthol, cholesterol and steroids.
Many terpenes, including Taxol and artemisinin, are made naturally in cells by processes that are so complicated, and so hard to understand, that chemists haven't been able to recreate them fully using organic chemistry techniques. The commercial production of these two medicines still depends on the relatively expensive harvesting of starting compounds from plants.
Taking Up the Challenge
In the new study, Shenvi and a postdoctoral researcher in his laboratory, Sergey V. Pronin, set out to recreate one of the two major terpene synthesis processes in nature. Known as tail-to-head polycyclization, this process is used by cells to make numerous complex terpenes. (The other major terpene synthesis process, head-to-tail polycyclization, is already partially reproducible with organic chemistry, and results in terpenes that include steroids.)
The tail-to-head polycyclization process begins with a relatively simple chain of carbon atoms, each of which is decorated with other, mostly hydrogen atoms. The goal of the process is to bend this linear hydrocarbon structure in a way that yields one ringlike structure, then another, and so on in a "polycyclic" chain.
A crucial feature of this process is the effective displacement of positive charge from one carbon atom on the structure to another, in just the right sequence. What makes this feat so challenging for chemists to reproduce, and even to analyze, is that this positively charged state in principle can slide along numerous alternative pathways on the emerging structure. Moreover, because it powerfully attracts negatively charged ions, this carbon-based positive charge, which chemists refer to as a carbocation ["carbo-cat-eye-on"], is inclined to snuff itself out almost immediately.
"Carbocations are notoriously tricky to include in synthetic procedures in the laboratory, because their lifetimes are so short," said Shenvi. "And yet nature has evolved tools to handle them."
Chief among these tools are cyclase enzymes, which hold terpene molecules that are under construction and use their own charged structures to protect carbocations from being quenched—at least long enough to let them do their work. Chemists who have sought to synthesize terpenes in the laboratory generally have done so without trying to mimic these enzymes' charge sequestration mechanism.
"The natural synthetic pathways were assumed to be much too difficult and maybe impossible," Shenvi said. "But we decided that we would have to recreate it somehow if we wanted to develop a broadly useful technique for making this group of terpenes."
Following Nature's Lead
Pronin and Shenvi eventually found that a type of vinyl epoxide seems to serve as a partial substitute for cyclase enzymes. "We think that it effectively holds the negatively charged counteranion, which would otherwise follow and quench the carbocation before the reaction is complete," said Pronin.
As a demonstration of the power of their new technique, the chemists used it to make two different types of terpene, known as funebrene and cumacrene, starting from relatively simple organic chemistry ingredients. These terpene compounds had never before been fully synthesized outside of living cells.
Shenvi emphasizes that this report represents merely an initial, foundational description of this new strategy, and that technical obstacles still prevent its widespread use. "But once we can get past these obstacles, we should be able to use this new approach to fully synthesize many other valuable compounds," he said. "Basically the entire realm of terpenes will be reproducible with organic chemistry."
INFORMATION:
Funding for the study, "Synthesis of highly strained terpenes by non-stop tail-to-head polycyclization," was provided by a start-up grant from the Scripps Research Institute and a grant from Eli Lilly & Co.
About The Scripps Research Institute
The Scripps Research Institute is one of the world's largest independent, not-for-profit organizations focusing on research in the biomedical sciences. Over the past decades, Scripps Research has developed a lengthy track record of major contributions to science and health, including laying the foundation for new treatments for cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, hemophilia, and other diseases. The institute employs about 3,000 people on its campuses in La Jolla, CA, and Jupiter, FL, where its renowned scientists—including three Nobel laureates—work toward their next discoveries. The institute's graduate program, which awards Ph.D. degrees in biology and chemistry, ranks among the top ten of its kind in the nation. For more information, see www.scripps.edu.
New chemistry technique from the Scripps Research Institute reproduces nature's elusive complexity
2012-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Understanding the brain by controlling behavior
2012-09-24
In the quest to understand how the brain turns sensory input into behavior, Harvard scientists have crossed a major threshold. Using precisely-targeted lasers, researchers have been able to take over an animal's brain, instruct it to turn in any direction they choose, and even to implant false sensory information, fooling the animal into thinking food was nearby.
As described in a September 23 paper published in Nature, a team made up of Sharad Ramanathan, an Assistant Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology, and of Applied Physics, Askin Kocabas, a Post-Doctoral ...
Scientists predict major shifts in Pacific ecosystems by 2100
2012-09-24
What if you woke up every day to find that the closest grocery store had moved several miles farther away from your home? Over time, you would have to travel hundreds of extra miles to find essential food for yourself and your family. This is potentially a scenario faced by thousands of marine animals affected by climate change.
A new study published in Nature Climate Change examines the distribution of various open ocean animals in the North Pacific and explores how that could change over the next century as global ocean temperatures increase and productivity levels ...
Preterm birth of mother increases risk of pregnancy complications
2012-09-24
Women who were born preterm are at increased risk of complications during pregnancy compared to those born at term, and the risk almost doubles for mothers born before 32 weeks, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Pregnancy complications include gestational diabetes, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia or eclampsia.
The findings are based on a study of 7405 women born preterm and 16 714 women born at term between 1976 and 1995 in the province of Quebec. Of the preterm women, 554 were less than 32 weeks at birth and 6851 were at ...
What does the feminization of family medicine mean?
2012-09-24
With more women in family medicine in Canada, what does this mean for the specialty and the profession, for patients and for society, asks a Salon opinion piece in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Female family physicians (FPs) now outnumber males, with 50.6% of the profession now female; this trend will continue as older, mainly male, physicians retire. These changing demographics will have implications for the way medicine is practised and for patients. Female FPs practise differently than men, working fewer hours (47 v. 52), seeing fewer patients but with ...
Eunuchs outlive other men
2012-09-24
Castrated men living in Korea centuries ago outlived other men by a significant margin. The findings, reported in the September 25 issue of Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, suggest that male sex hormones are responsible for shortening the lives of men, the researchers say.
The evidence comes after careful study of genealogy records of noble members of the Imperial court of the Korean Chosun dynasty (AD 1392-1910).
"This discovery adds an important clue for understanding why there is a difference in the expected life span between men and women," said Kyung-Jin ...
JCI early table of contents for September 24, 2012
2012-09-24
Small proteins in the cornea protect against bacterial infection
Exposed tissue surfaces, including skin and mucous membranes, are under constant threat of attack by microorganisms in the environment. The layer of cells that line these areas, known as epithelial cells, are the first line of defense against these pathogens, but the underlying molecular mechanisms that allow them to repel microbes are unknown. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, report that epithelial cells in the cornea, which ...
Small proteins in the cornea protect against bacterial infection
2012-09-24
Exposed tissue surfaces, including skin and mucous membranes, are under constant threat of attack by microorganisms in the environment. The layer of cells that line these areas, known as epithelial cells, are the first line of defense against these pathogens, but the underlying molecular mechanisms that allow them to repel microbes are unknown. In this issue of the Journal of Clinical Investigation, researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, report that epithelial cells in the cornea, which is highly resistant to bacterial infection, express small antimicrobial ...
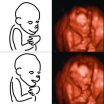
Human brains outpace chimp brains in the womb
2012-09-24
VIDEO:
This movie shows a pregnant chimpanzee undergoing an ultrasound imaging procedure to explore brain growth in her fetus.
Click here for more information.
Humans' superior brain size in comparison to their chimpanzee cousins traces all the way back to the womb. That's according to a study reported in the September 25 issue of Current Biology, a Cell Press publication, that is the first to track and compare brain growth in chimpanzee and human fetuses.
"Nobody knew ...
Pregnancy complications up to twice higher in women born preterm
2012-09-24
This press release is available in French. Women who were born premature are more likely to have pregnancy complications than women who weren't, according to data analyzed by a team lead by Dr. Anne Monique Nuyt, a neonatal specialist and researcher at the Sainte-Justine Mother and Child University Hospital Center and University of Montreal. This is the first study to clearly show the impact of preterm birth (i.e. before 37 weeks of gestation) itself on pregnancy risks. "We knew that to be born with a low birth weight could be associated with increased risk of pregnancy ...
Research shows ants share decision-making, lessen vulnerability to 'information overload'
2012-09-24
TEMPE, Ariz. – Scientists at Arizona State University have discovered that ants utilize a strategy to handle "information overload." Temnothorax rugatulus ants, commonly found living in rock crevices in the Southwest, place the burden of making complicated decisions on the backs of the entire colony, rather than on an individual ant.
In a study published in the early, online version of scientific journal Current Biology, Stephen Pratt, an associate professor in ASU's School of Life Sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, and Takao Sasaki, a graduate student ...