Seismic detectors measure soil moisture using traffic noise
2024-08-05
Caltech researchers have developed a new method to measure soil moisture in the shallow subterranean region between the surface and underground aquifers. This region, called the vadose zone, is crucial for plants and crops to obtain water through their roots. However, measuring how this underground moisture fluctuates over time and between geographical regions has traditionally relied on satellite imaging, which only gives low-resolution averages and cannot penetrate below the surface. Additionally, moisture within the vadose zone changes rapidly—a thunderstorm can saturate a region that dries ...
State-level, out-of-pocket insulin caps do not substantially increase utilization, study finds
2024-08-05
AURORA, Colo. (August 5, 2024) – In a first-of-its-kind study, a cohort of researchers, led by the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, evaluated the effects of state-level insulin out-of-pocket costs across states and payers and over time. The team found that state-level caps on insulin out-of-pocket costs do not significantly increase insulin claims for patients with Type 1 or patients using insulin to manage Type 2 diabetes. Study results could help inform policies aimed at better delivering cost-capped insulin to patients struggling with insulin affordability.
Approximately ...
Preventing Parkinson’s disease may lie in seaweed antioxidants
2024-08-05
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by the loss of neurons that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in motor control and cognitive function. As the global population ages, the number of Parkinson's disease patients is rapidly increasing. Parkinson's disease is induced by neuronal damage due to excessive production of reactive oxygen species.
Suppression of reactive oxygen species generation is essential because it is fatal to dopaminergic neurons that manage dopamine neurotransmitters. ...
Streetlights running all night makes leaves so tough that insects can’t eat them, threatening the food chain
2024-08-05
Light pollution disrupts circadian rhythms and ecosystems worldwide – but for plants, dependent on light for photosynthesis, its effects could be profound. Now scientists writing in Frontiers in Plant Science have found that exposure to high levels of artificial light at night makes tree leaves grow tougher and harder for insects to eat, threatening urban food chains.
“We noticed that, compared to natural ecosystems, tree leaves in most urban ecosystems generally show little sign of insect damage. We were curious as to why,” said corresponding author Dr Shuang Zhang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. “Here we show that in ...
Upfront mental health supports for men with prostate cancer
2024-08-04
Mental health screenings must be incorporated in routine prostate cancer diagnoses say University of South Australia researchers. The call follows new research that shows men need more supports both during and immediately after a diagnosis of prostate cancer.
Funded by Movember, the UniSA study tracked the scale and timing of mental health issues among 13,693 South Australian men with prostate cancer, finding that 15% of prostate cancer patients began mental health medications directly after a prostate cancer diagnosis, with 6% seeking help from mental health ...
Strengthening global regulatory capacity for equitable access to vaccines in public health emergencies
2024-08-03
WASHINGTON – Three high-impact steps could be taken by global health leaders to reshape the global regulatory framework and help address the pressing need for equitable access to diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccines during public health emergencies, say a Georgetown global health law expert and a medical student.
In their “Perspective” published today in the New England Journal of Medicine, Georgetown School of Health professor Sam Halabi, JD, and George O’Hara, a Georgetown medical student and David E. Rogers Student ...
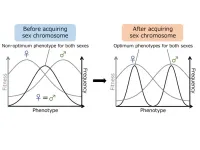
Sex chromosomes may reduce “sexual conflict” during evolution
2024-08-03
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have taken a big step in solving the mystery around why animals evolve sex chromosomes. It had long been proposed that sex chromosomes evolve to reduce “sexual conflict,” the evolution of features which are sub-optimal for either sex. By using fruit flies, the team showed that genes on newly formed neo-sex chromosomes in fruit flies tend to evolve “sex-biased genes” which give sex-specific phenotypes.
Chromosomes are neatly packaged bundles of DNA that carry all the genetic material of an organism. While prokaryotes ...
A blueprint for building the future: Eco-friendly 3D concrete printing
2024-08-02
A research team led by engineers at the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science is the first to explore how an emerging plant-based material, cellulose nanofibrils, could amplify the benefits of 3D-printed concrete technology.
“The improvements we saw on both printability and mechanical measures suggest that incorporating cellulose nanofibrils in commercial printable materials could lead to more resilient and eco-friendly construction practices sooner rather than later,” said Osman E. Ozbulut, a professor in the Department of Civil and Environmental ...
A Bronze Age technology could aid the switch to clean energy
2024-08-02
Technology with roots going back to the Bronze Age may offer a fast and inexpensive solution to help achieve the United Nations climate goal of net zero emissions by 2050, according to recent Stanford-led research in PNAS Nexus.
The technology involves assembling heat-absorbing bricks in an insulated container, where they can store heat generated by solar or wind power for later use at the temperatures required for industrial processes. The heat can then be released when needed by passing air through channels in the stacks of “firebricks,” thus allowing cement, steel, glass, and paper factories to run on renewable energy even when wind and sunshine ...
What researchers know about the genetic complexity of schizophrenia, to date
2024-08-02
Patrick Sullivan, MD, FRANZCP, the Yeargan Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry and Genetics at the UNC School of Medicine, and researchers at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, have developed a comprehensive outline of the genetics of schizophrenia. The review was published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience.
Schizophrenia is a neuropsychiatric disorder featuring recurrent episodes of psychosis – such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking – with many patients developing apathy, social withdrawal, ...
New study highlights scale and impact of long COVID
2024-08-02
In a new review paper, researchers from the Universities of Arizona, Oxford and Leeds analyzed dozens of previous studies into long COVID to examine the number and range of people affected, the underlying mechanisms of disease, the many symptoms that patients develop, and current and future treatments.
Long COVID, also known as Post-COVID-19 condition, is generally defined as symptoms persisting for three months or more after acute COVID-19. The condition can affect and damage many organ systems, leading to severe ...
How the rising earth in Antarctica will impact future sea level rise
2024-08-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The rising earth beneath the Antarctic Ice Sheet will likely become a major factor in future sea level rise, a new study suggests.
Despite feeling like a stationary mass, most solid ground is undergoing a process of deformation, sinking and rising in response to many environmental factors. In Antarctica, melting glacial ice means less weight on the bedrock below, allowing it to rise. How the rising earth interacts with the overlying ice sheet to affect sea level rise is not well-studied, said Terry Wilson, co-author of the study and a senior research scientist at the Byrd Polar and Climate Research Center ...
Research spotlight: Uncovering the links between sleep struggles, substance abuse and suicidal thoughts in teens with depression
2024-08-02
Rebecca Robbins, PhD, of the Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, is the senior author of a paper published in Psychiatry Research, “Exploring sleep difficulties, alcohol, illicit drugs, and suicidal ideation among adolescents with a history of depression.”
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Suicide is one of the leading causes of death for adolescents in the U.S. We know, due to previous research, that difficulty falling asleep or waking up too early as well as abuse of prescription ...
Boosting children’s voices could help to relieve significant backlogs in the family court, study says
2024-08-02
Giving children a right to be heard and taken seriously when parents separate could help couples reach sustainable child arrangements and relieve significant backlogs in the family court, avoiding unnecessary financial and emotional costs, a new study says.
Mediation, court and legal processes should provide a forum for young people’s views on post-separation arrangements being considered for them to be aired independently and factored in wherever appropriate. Giving them more agency about decisions which affect their lives and futures will help families make more effective ...
Study yields new insights into the link between global warming and rising sea levels
2024-08-02
A McGill-led study suggests that Earth's natural forces could substantially reduce Antarctica’s impact on rising sea levels, but only if carbon emissions are swiftly reduced in the coming decades. By the same token, if emissions continue on the current trajectory, Antarctic ice loss could lead to more future sea level rise than previously thought.
The finding is significant because the Antarctic Ice Sheet is the largest ice mass on Earth, and the biggest uncertainty in predicting future sea levels is how this ice will respond to climate change.
“With nearly 700 million people living in coastal areas and the potential ...
Controlling thickness in fruit fly hearts reveals new pathway for heart disease
2024-08-02
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys and Salk Institute for Biological Studies have uncovered a new role for a protein known for its role in the brain helping control feelings of hunger or satiety, as well as in the liver to aid the body in maintaining a balance of energy during fasting. The new study shows that this protein also supports the maintenance of heart structure and function, but when it is overactive it causes thickening of the heart muscle, which is associated with heart disease.
Excessive thickening of the heart muscle—known as cardiac hypertrophy—is often ...
Improving cat food flavors with the help of feline taste-testers
2024-08-02
Cats are notoriously picky eaters. But what if we could design their foods around flavors that they’re scientifically proven to enjoy? Researchers publishing in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry used a panel of feline taste-testers to identify favored flavor compounds in a series of chicken-liver-based sprays. The cats particularly enjoyed the sprays that contained more free amino acids, which gave their kibble more savory and fatty flavors.
Cats have a more acute sense of smell than humans, and the aroma of their food plays a big role in whether they’ll eat or snub what their owner serves for dinner. Feline palates are also more sensitive to umami ...
Subclinical hypothyroidism in early pregnancy associated with more than quadrupled risk of reduced thyroid function within 5 years of delivery
2024-08-02
A new study has shown that subclinical hypothyroidism diagnosed before 21 weeks of pregnancy is associated with more than fourfold higher rates of overt hypothyroidism or thyroid replacement therapy within 5 years of delivery. The study is published in the peer-reviewed journal Thyroid®, the official journal of the American Thyroid Association® (ATA®).
Subclinical hypothyroidism, or a change in the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) that isn’t severe enough to cause symptoms, ...
BNP-Track algorithm offers a clearer picture of biomolecules in motion
2024-08-02
It’s about to get easier to catch and analyze a high-quality image of fast-moving molecules. Assistant Professor Ioannis Sgouralis, Department of Mathematics, and colleagues have developed an algorithm that adds a new level to microscopy: super-resolution in motion.
The cutting-edge advancement of super-resolution microscopy was recognized with the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for its groundbreaking innovation. It improves optical microscopy with a suite of techniques that overcome the inherent limitations set by the physics of light. The high-frequency oscillations of light waves escape detection ...
Not the day after tomorrow: Why we can't predict the timing of climate tipping points
2024-08-02
A new study published in Science Advances reveals that uncertainties are currently too large to accurately predict exact tipping times for critical Earth system components like the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), polar ice sheets, or tropical rainforests. These tipping events, which might unfold in response to human-caused global warming, are characterized by rapid, irreversible climate changes with potentially catastrophic consequences. However, as the new study shows, predicting when these events will occur is more difficult than previously thought.
Climate scientists from the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and ...
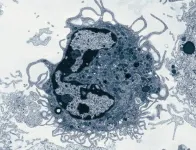
Discovery of a new population of macrophages promoting lung repair after viral infections
2024-08-02
Researchers at the University of Liège (Belgium) have discovered a new population of macrophages, important innate immune cells that populate the lungs after injury caused by respiratory viruses. These macrophages are instrumental in repairing the pulmonary alveoli. This groundbreaking discovery promises to revolutionize our understanding of the post-infectious immune response and opens the door to new regenerative therapies.
Respiratory viruses, typically causing mild illness, can have more serious consequences, as shown during the Covid-19 pandemic, including severe cases requiring hospitalization and the chronic sequelae of "long Covid." These conditions ...
Scientists pin down the origins of the moon’s tenuous atmosphere
2024-08-02
While the moon lacks any breathable air, it does host a barely-there atmosphere. Since the 1980s, astronomers have observed a very thin layer of atoms bouncing over the moon’s surface. This delicate atmosphere — technically known as an “exosphere” — is likely a product of some kind of space weathering. But exactly what those processes might be has been difficult to pin down with any certainty.
Now, scientists at MIT and the University of Chicago say they have identified the main process that formed the moon’s atmosphere and continues to sustain ...
More than 1 in 5 Californians who are impacted by climate events report negative effects on their mental health
2024-08-02
More than 1 in 5 Californians who are impacted by climate events report negative effects on their mental health, with young, white women and those who’ve experienced property damage being especially affected.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000387
Article Title: Exposure to climate events and mental health: Risk and protective factors from the California Health Interview Survey
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
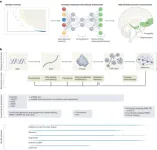
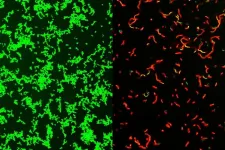
New compound effective against flesh-eating bacteria
2024-08-02
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a novel compound that effectively clears bacterial infections in mice, including those that can result in rare but potentially fatal “flesh-eating” illnesses. The compound could be the first of an entirely new class of antibiotics, and a gift to clinicians seeking more effective treatments against bacteria that can’t be tamed easily with current antibiotics.
The research is published Aug. 2 in Science Advances.
The compound targets gram-positive bacteria, which can cause drug-resistant staph infections, toxic shock syndrome and ...
We should think twice before calling 911 for people experiencing a mental health crisis, advocated Harvard-trained psychiatrist Dr. Rupinder Legha
2024-08-02
We should think twice before calling 911 for people experiencing a mental health crisis, advocated Harvard-trained psychiatrist Dr. Rupinder Legha, who describes the potential risks of relying on emergency services in the US for mental health crisis management.
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000084
Article Title: Reconsidering calling 911: Is it time to set a new standard for mental health crisis response?
Author Countries: United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
[1] ... [1022]
[1023]
[1024]
[1025]
[1026]
[1027]
[1028]
[1029]
1030
[1031]
[1032]
[1033]
[1034]
[1035]
[1036]
[1037]
[1038]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.