Study tracks exposure to air pollution through the day
2024-07-29
There are significant differences in how much people are exposed to air pollution, according to a new study co-authored by MIT scholars that takes daily mobility into account.
The study, based in the Bronx, New York, does not just estimate air pollution exposure based on where people live or work, but uses mobile data to examine where people go during a typical day, building a more thorough assessment of the environment’s impact on them.
The research finds exposure to particulate matter 2.5 microns or bigger rises by about 2.4 percent when daily travel patterns are taken into account.
“One of the main strengths of the study is that we ...
UC San Diego researchers use non-invasive technique to record involuntary nervous system
2024-07-29
A research team led by UC San Diego has, for the first time, shown that a wearable, non-invasive device can measure activity in human cervical nerves in clinical settings.
The device records what the team calls Autonomic Neurography (ANG), neural activity from the human vagus and carotid sinus nerves as well as other autonomic nerves found in the skin and muscle of the neck. The vagus nerve is a “superhighway” of the involuntary nervous system, with tendrils extending from the base of the skull through the torso and abdomen to influence digestion, heart rate and the immune system. The vagus nerve ...
Most US voters agree on basic human values – so is polarization exaggerated?
2024-07-29
The vast majority of American voters think alike on what they find important in life, but both Republicans and Democrats fail to recognise their shared views and values, according to new research from the Universities of Bath and Essex.
This finding is revealed today in the academic journal Social Psychological and Personality Science less than a month after the US Republican presidential nominee Donald Trump survived an assassination attempt when a gunman shot at him during a campaign rally.
“There’s a general perception ...
Optical fibers fit for the age of quantum computing
2024-07-29
A new generation of specialty optical fibres has been developed by physicists at the University of Bath in the UK to cope with the challenges of data transfer expected to arise in the future age of quantum computing.
Quantum technologies promise to provide unparalleled computational power, allowing us to solve complex logical problems, develop new medicines and provide unbreakable cryptographic techniques for secure communications. However, the cable networks used today to transmit information across the globe are likely to be sub-optimal for quantum communications, due to the solid cores of their optical fibres.
Unlike regular optical ...
Do non-statin cholesterol-lowering drugs affect liver cancer risk?
2024-07-29
Past studies have suggested that taking cholesterol-lowering statin drugs may lower individuals’ risk of developing liver cancer. In a new study of non-statin cholesterol-lowering medications, one type was linked to lower risks of liver cancer. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors, bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, niacin, and omega-3 fatty acids are types of non-statin cholesterol-lowering medications prescribed to manage cholesterol and lipid levels. The different classes ...
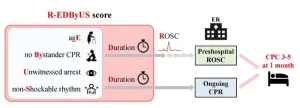
Every minute counts: rapid and accurate prediction model for cardiac arrest treatment
2024-07-29
When it comes to treating cardiac arrest, acting quickly can mean the difference between life and death.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have developed a new scoring model, using only prehospital resuscitation data, that accurately predicts neurological outcomes of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). This model potentially allows healthcare providers to make quick and accurate decisions upon the patient’s arrival at the hospital, ultimately improving patient care and resource allocation.
Their findings were published in Resuscitation on May 31.
Cardiac arrest can lead to death within minutes. OHCA is not uncommon and often results ...
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy increasing in Canada
2024-07-29
In Canada, rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) have increased, but the good news is there has been a decline in some related health conditions, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231547.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy include chronic hypertension (high blood pressure), gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia or eclampsia. These disorders affect 5%–10% of pregnancies worldwide, and cause more than 50 000 maternal deaths and 500 000 deaths in fetuses and infants ...
Is free genetic testing really free?
2024-07-29
Free genetic testing, offered partially or fully subsidized by industry, may have trade-offs, and health systems in Canada must carefully weigh potential clinical, ethical, and legal considerations to protect patient data, authors argue in a CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) commentary https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231588.
“Near- and long-term expansion in no-cost testing and industry partnership in genetics, with patient data as the commodity, is likely,” writes Kirsten ...
Health: Short-term vegan diet associated with reductions in biological age estimates
2024-07-29
Eating a vegan diet for eight weeks is associated with reductions in biological age estimations based on levels of DNA methylation — a type of chemical modification of DNA (known as an epigenetic modification) that alters gene expression but not DNA itself. Previous research has reported that increased DNA methylation levels are associated with ageing. The findings, which are based on a small randomised controlled trial of 21 pairs of adult identical twins, are published in BMC Medicine.
Varun Dwaraka, Christopher ...
Evidence-based information combats misleading and false claims on the internet and social media about the anti-Mullerian hormone test
2024-07-29
Researchers in Australia have found that when women are given accurate information about a test that indicates the number of eggs in their ovaries, they have less interest in taking the test compared to women who viewed information available online.
The researchers initiated the study, which is published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, because of the large amount of misleading and incorrect information promoted to women about the anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) test on websites, including fertility clinic websites, and via social media.
AMH ...
Steel industry’s net zero drive could make lower-grade iron ore viable
2024-07-29
A decarbonised steel industry that includes carbon dioxide removal techniques in its net zero arsenal could use lower-grade iron ore, according to a new study.
Steel accounts for 5-8% of carbon dioxide emissions globally. Its total emissions have risen over the past decade, largely due to increased demand.
The International Energy Agency has stated that, without innovation, the scope to limit emissions is ‘limited’. Therefore, the commercialisation of new zero-emission production processes is critical.
Innovative ...
Plasma phosphorylated tau 217 and Aβ42/40 to predict early brain Aβ accumulation in people without cognitive impairment
2024-07-28
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that combining plasma p-tau217 and Aβ42/40 levels could be useful for predicting development of Aβ pathology in people with early stages of subthreshold Aβ accumulation. These biomarkers might thus facilitate screening of participants for future primary prevention trials.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Oskar Hansson, M.D, Ph.D. (Oskar.Hansson@med.lu.se) and Shorena Janelidze, Ph.D. (shorena.janelidze@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2619)
Editor’s ...
MRI signature of α-synuclein pathology in asymptomatic stages and a memory clinic population
2024-07-28
About The Study: In this cohort study, seed amplification assays (SAA) α-syn+ was consistently associated with nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM) atrophy already during asymptomatic stages. Further, in memory clinic cognitively impaired populations, SAA α-syn+ was associated with NBM atrophy, which partially mediated α-syn–induced attention/executive impairment.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Laura E.M. Wisse, Ph.D. (laura.wisse@med.lu.se) and Oskar Hansson, M.D., Ph.D. (oskar.hansson@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.2713)
Editor’s ...
Blood biomarkers to detect Alzheimer disease in primary care and secondary care
2024-07-28
About The Study: The amyloid probability score 2 (APS2) blood test and percentage of p-tau217 alone had high diagnostic accuracy for identifying Alzheimer disease among individuals with cognitive symptoms in primary and secondary care using predefined cutoff values. Future studies should evaluate how the use of blood tests for these biomarkers influences clinical care.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Sebastian Palmqvist, M.D., Ph.D. (sebastian.palmqvist@med.lu.se) and Oskar Hansson, M.D., Ph.D. (oskar.hansson@med.lu.se).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.13855)
Editor’s ...
Changes in Alzheimer disease blood biomarkers and associations with incident all-cause dementia
2024-07-28
About The Study: Plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer disease (AD) neuropathology, neuronal injury, and astrogliosis increase with age and are associated with known dementia risk factors. AD-specific biomarkers’ association with dementia starts in midlife whereas late-life measures of AD, neuronal injury, and astrogliosis biomarkers are all associated with dementia.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Priya Palta, Ph.D., M.H.S., email priya_palta@med.unc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.6619)
Editor’s ...
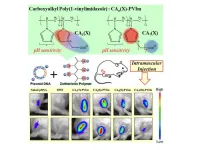
New and improved drug delivery molecules for skeletal muscle
2024-07-27
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new drug delivering molecule, a zwitterionic polymer complex that can help get plasmid DNA inside cells when injected into skeletal muscle, a crucial step in the expression of therapeutic RNA and proteins. The new compound effectively bound to plasmid DNA without affecting its structure. Injected into mouse muscles, the team observed widespread gene expression, promising applications to treatments of serious muscle diseases.
Drug delivery systems underpin many of the clinical breakthroughs of our age. For example, ...
UC San Diego Health ends negotiations with Tri-City Medical Center Healthcare District
2024-07-27
UC San Diego Health has ended more than nine months of negotiations for a potential partnership with the Tri-City Medical Center (TCMC) Healthcare District.
A final revised offer was presented to the TCMC Healthcare District on July 24 and no agreement was reached.
Highlights of the final proposal for TCMC included a financial recovery and growth plan that included:
$100 million infusion of cash within the first two years plus other financial supports, including a line of credit designed to protect the financial stability of TCMC during the first five years.
All assets and liabilities would transfer to UC San Diego Health, including employment ...
MLB add lifesavers to the chain of survival in New York City
2024-07-27
NEW YORK CITY, July 26, 2024 — The American Heart Association and Major League Baseball (MLB) brought cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and automated external defibrillator (AED) training to MLB staff at the New York headquarters office located on Avenue of the Americas on Monday, July 22. Nearly 100 employees attended to learn the lifesaving skills building confidence and capabilities to respond in the event of a cardiac emergency. According to American Heart Association data, nine out of every ten people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part because they do not receive immediate CPR more than half of the time. CPR, especially if performed ...
ISU studies explore win-win potential of grass-powered energy production
2024-07-27
AMES, Iowa – Strategically planting perennial grass throughout corn and soybean fields helps address the unintended environmental consequences of growing the dominant row crops, including soil erosion, fertilizer runoff and greenhouse gas emissions.
But converting portions of farmland back to prairie has to make financial sense for farmers, which is why a research team led by Iowa State University landscape ecologist Lisa Schulte Moore has spent the past six years studying how to efficiently turn harvested ...
Study identifies biomarker that could predict whether colon cancer patients benefit from chemotherapy
2024-07-27
MIAMI, FLORIDA (July 25, 2024) – Many people with stage II or III colon cancer receive additional, or adjuvant, chemotherapy following surgery. However, clinical trials have shown that this treatment doesn’t improve the chances of survival for every patient. A study published July 25 in Cell Reports Medicine identifies and validates a 10-gene biomarker that potentially predicts whether a stage II or III colon cancer patient will benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy.
A secondary finding from the study could also lead to further research and application. Researchers found that the gene signature could potentially also predict ...
Children are less likely to have type 1 diabetes if their mother has the condition than if their father is affected
2024-07-27
New research to be presented at this year’s Annual Meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (Madrid, 9-13 September) shows that a child is almost twice as likely to develop type 1 diabetes (T1D) if their father has the condition, than if their mother has the condition.
The study, the largest of its kind, suggests that exposure to T1D in the womb confers long-term protection against the condition in children with affected mothers relative to those with affected fathers.
Understanding what is responsible for this relative protection could lead to opportunities ...
Two shark species documented in Puget Sound for first time by Oregon State researchers
2024-07-26
CORVALLIS, Oregon – Oregon State University researchers have made the first scientific confirmation in Puget Sound of two distinct shark species, one of them critically endangered.
The presence of the broadnose sevengill shark and endangered soupfin shark in the sound, the southern portion of the Salish Sea, may indicate changes in what biologists in OSU’s Big Fish Lab describe as an economically, culturally and ecologically valuable inland waterway.
The Salish Sea separates northwest Washington from British Columbia’s Vancouver Island. The ...
AI method radically speeds predictions of materials’ thermal properties
2024-07-26
CAMBRIDGE, MA — It is estimated that about 70 percent of the energy generated worldwide ends up as waste heat.
If scientists could better predict how heat moves through semiconductors and insulators, they could design more efficient power generation systems. However, the thermal properties of materials can be exceedingly difficult to model.
The trouble comes from phonons, which are subatomic particles that carry heat. Some of a material’s thermal properties depend on a measurement called the phonon ...
Study: When allocating scarce resources with AI, randomization can improve fairness
2024-07-26
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Organizations are increasingly utilizing machine-learning models to allocate scarce resources or opportunities. For instance, such models can help companies screen resumes to choose job interview candidates or aid hospitals in ranking kidney transplant patients based on their likelihood of survival.
When deploying a model, users typically strive to ensure its predictions are fair by reducing bias. This often involves techniques like adjusting the features a model uses to make decisions or calibrating the scores it generates.
However, researchers from MIT and Northeastern University argue that these fairness ...
Wencai Liu earns 2024 IUPAP Early Career Scientist Prize in Mathematical Physics
2024-07-26
Dr. Wencai Liu, an associate professor of mathematics at Texas A&M University, has been selected to receive the 2024 International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) Early Career Scientist Prize in Mathematical Physics in recognition of his exceptional achievements and future potential in mathematical physics.
Liu is one of three scientists worldwide honored with the prize, one of 19 celebrating the contributions of early career physicists within the subfields of each commission comprising the IUPAP, which was founded in 1976 to promote research in mathematical physics. Each prize consists of a certificate, medal and a monetary award.
Liu ...
[1] ... [1023]
[1024]
[1025]
[1026]
[1027]
[1028]
[1029]
[1030]
1031
[1032]
[1033]
[1034]
[1035]
[1036]
[1037]
[1038]
[1039]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.