MicroRNA study sets stage for crop improvements
2024-07-29
MEDIA INQUIRES
WRITTEN BY
Laura Muntean
Ashley Vargo
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR ...
Semaglutide may show promise for smoking cessation
2024-07-29
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 29 July 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
Self-powered ’bugs’ can skim across water to detect environmental data
2024-07-29
INGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York have developed a self-powered “bug” that can skim across the water, and they hope it will revolutionize aquatic robotics.
Futurists predict that more than one trillion autonomous nodes will be integrated into all human activities by 2035 as part of the “internet of things.” Soon, pretty much any object — big or small — will feed information to a central database without the need for human involvement.
Making this idea tricky is that 71% of the Earth’s ...
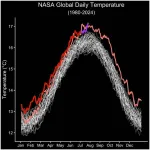
NASA data shows July 22 was Earth’s hottest day on record
2024-07-29
July 22, 2024, was the hottest day on record, according to a NASA analysis of global daily temperature data. July 21 and 23 of this year also exceeded the previous daily record, set in July 2023. These record-breaking temperatures are part of a long-term warming trend driven by human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases. As part of its mission to expand our understanding of Earth, NASA collects critical long-term observations of our changing planet.
“In a year that has been the hottest on record to date, these past two weeks have ...
Prestigious NIH award will advance brain research at UCR
2024-07-29
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A National Institutes of Health grant received by Vijayalakshmi (Viji) Santhakumar, a professor of molecular, cell and systems biology at the University of California, Riverside, has been selected for the prestigious Javits Neuroscience Investigator Award, the first time for the campus.
The five-year, $3.5 million grant from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, or NINDS, of the National Institutes of Health is a collaborative study with Edward Zagha, an associate professor of psychology at UCR. The award will support research into how brain circuits contribute to episodic memory formation and how ...
Purdue researchers trap atoms, forcing them to serve as photonic transistors
2024-07-29
Researchers at Purdue University have trapped alkali atoms (cesium) on an integrated photonic circuit, which behaves like a transistor for photons (the smallest energy unit of light) similar to electronic transistors. These trapped atoms demonstrate the potential to build a quantum network based on cold-atom integrated nanophotonic circuits. The team, led by Chen-Lung Hung, associate professor of physics and astronomy at the Purdue University College of Science, published their discovery in the American Physical Society’s Physical Review X.
“We developed a technique to use lasers ...
Analogies for modeling belief dynamics
2024-07-29
Researchers who study belief dynamics often use analogies to understand and model the complex cognitive–social systems that underly why we believe the things we do and how those beliefs can change over time. Ideas can be transmitted like a virus, for instance, “infecting” a population as they spread from person to person. We might be drawn — like magnets — to others with a similar worldview. A society’s beliefs can shift slowly before reaching a tipping point that thrusts society into a new phase.
In a new paper in Trends in Cognitive Sciences, SFI Professor Mirta Galesic and ...
Many juvenile ‘lifers’ freed
2024-07-29
In 1953, 15-year-old Joe Ligon and four other Pennsylvania teens went on an alcohol-fueled tear that resulted in the stabbing deaths of two people and injuries to six more.
The teens were tried as a group, and all received life without parole.
After a series of U.S. Supreme Court decisions in 2012 and 2016 found that mandatory life sentences for juveniles was unconstitutional, Ligon’s case went to federal court. After 67 long years in prison, the case was decided in his favor in 2020.
Ligon was granted his freedom in 2021 — at 83 years of age and after ...
UW model shows cortical implants like Elon Musk’s Blindsight unlikely to ‘exceed normal human vision’
2024-07-29
Elon Musk recently declared on X that Blindsight, a cortical implant to restore vision, would have low resolution at first “but may ultimately exceed normal human vision.”
That pronouncement is unrealistic at best, according to new research from the University of Washington.
Ione Fine, lead author and UW professor of psychology, said Musk’s projection for the latest Neuralink project rests on the flawed premise that implanting millions of tiny electrodes into the visual cortex, the region of the brain that processes information received from the eye, will result in high-resolution vision.
For the study, ...
UVA's Data Justice Academy receives new funding from NSF
2024-07-29
The National Science Foundation will provide funding to the University of Virginia’s Data Justice Academy, the agency recently announced, support that will help the summer program continue to serve undergraduate students from groups that are historically underrepresented in data science.
Established in 2021, the Data Justice Academy provides a 10-week residential experience to participants in which they perform mentored research while learning technical skills.
The overriding goal of the Data Justice Academy, which is jointly managed by UVA’s School of Data Science and Equity Center, ...
Orthopedic surgeon-scientist Dr. Frank Henn named Chair of the Department of Orthopaedics
2024-07-29
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean Mark T. Gladwin, MD, announced today that R. Frank Henn, III, MD, Professor of Orthopaedics, who has served as Interim Chair of the Department since 2022, has been appointed to serve as the new Chair of UMSOM’s Department of Orthopaedics, effective immediately.
Dr. Henn, who joined the Department in 2010, is an academic leader and highly regarded, board-certified orthopaedic surgeon; he has published significant scientific research, and is a leading clinician focusing on the care of the shoulder and knee, with an emphasis in cartilage ...
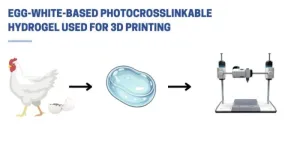
Nature inspires a breakthrough: scientists develop revolutionary egg white-based bioink for advanced tissue engineering
2024-07-29
Los Angeles, California – July 29, 2024 - Terasaki Institute scientists have created a cutting-edge technology inspired by nature by developing a novel bioink derived from egg whites or Egg White methacryloyl (EWMA). Bioinks are mainly used in 3D bioprinting to create artificial tissues. These natural or synthetic materials support living cells, aiding their adhesion, growth, and differentiation. They are essential for developing complex tissue structures for medical research, drug testing, and organ transplantation. This novel EWMA bioink represents a promising addition to this field, offering a unique combination of properties that address many challenges faced in tissue engineering.
The ...
California a botanical and climate change hot spot
2024-07-29
From coastal redwoods and Joshua trees to golden poppies and sagebrush, California is a global botanical hotspot. It’s also a place confronted with extreme heat, wildfires and crumbling coastlines. The state’s natural beauty and history of pioneering conservation efforts make it a test bed for protecting biodiversity in the face of current and future climate change, argues a study led by the University of California, Davis.
Published July 29 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study, “Climate Change and California’s Terrestrial Biodiversity,” is part of a special ...
Young scientists face career hurdles in interdisciplinary research
2024-07-29
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists agree that solving some of society’s greatest challenges in biomedicine such as food sustainability, aging and disease treatment will need researchers from a variety of scientific fields working together.
But a new study finds that the young scientists who most embrace interdisciplinary research face “career impediments” not seen in their peers who focus their work only within their own disciplines.
The results are troublesome and pose a “grave challenge” to efforts to increase interdisciplinary ...
New progress in research into malignant catarrhal fever in cattle
2024-07-29
A research team led by University of Liège scientists has published a groundbreaking study on malignant catarrhal fever (MCF). This disease is caused by the alcelaphine gammaherpesvirus 1 (AlHV-1), which infects its natural host, the wildebeest. This study sheds light on the mechanisms by which this virus, which is asymptomatic and latent in the wildebeest, causes an oligoclonal expansion of CD8+ T lymphocytes in cattle, leading to the development of MCF.
In 2013, the research team had already demonstrated (1) that malignant catarrhal fever (MCF), which is fatal in cattle, only develops if the AlHV-1 virus can maintain a ...
Words like ‘this’ and ‘that’ act as attention tools across languages
2024-07-29
All languages have words like ‘this’ and ‘that’ to distinguish between referents that are ‘near’ and ‘far’. Languages like English or Hebrew have two of these ‘demonstratives’. Languages like Spanish or Japanese use a three-word system. For instance, in Spanish, ‘este’ signals something close to the speaker, ‘ese’ signals something far from the speaker but close to the listener, and ‘aquel’ signals something far from both.
“The reason why we were interested in demonstratives is because of their ...
Local food production saves costs and carbon
2024-07-29
Local foods are critical to the food security and health of Indigenous peoples around the world, but local "informal" economies are often invisible in official economic statistics. Consequently, these economies may be overlooked in the policies designed to combat climate change. For instance, Indigenous communities in the North American Arctic are characterized by mixed economies featuring hunting, fishing, gathering and trapping activities, alongside the formal wage economy. The region is also undergoing a rapid transformation due to social, economic and climatic changes. In Canada, the introduction ...
Bold moves needed for California agriculture to adapt to climate change
2024-07-29
California should take urgent and bold measures to adapt its $59 billion agriculture sector to climate change as the amount of water available for crops declines, according to a collaborative report by University of California faculty from four campuses.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the report provides a roadmap for more water capture, storage, and distribution systems that are in harmony with climate projections and ecosystems. It further considers how runoff and groundwater can be used repeatedly ...
To get drivers to put down their phones, make it a game
2024-07-29
If you’re trying to keep drivers from picking up their phones, make it a game, according to a new Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) study led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. When drivers could earn points for making reductions in handheld phone use and had the chance to compete in a weekly leaderboard of others like them, researchers saw as much as a 28 percent reduction in handheld phone use while driving, a habit that stuck once the intervention—and the games—ended.
“Distracted driving ...
Study identifies protein that affects health of gut microbiota and response to bacterial infection
2024-07-29
A study reported in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) shows how the presence of a specific protein called IL-22BP affects the composition of the gut microbiota and the body’s response to bacterial infection.
“We discovered that mice that don’t produce this protein are more protected against intestinal infections by bacteria like Clostridioides difficile and Citrobacter rodentium,” Marco Aurélio Ramirez Vinolo, a co-author of the article, told. He is a professor at the State University of Campinas’s Institute of Biology (IB-UNICAMP) in Brazil and head of its Immunoinflammation Laboratory.
IL-22BP ...
Fetal brain impacted when mom fights severe flu: New mouse study explains how
2024-07-29
URBANA, Ill. -- A bad case of the flu during pregnancy can increase the risk for fetal neurodevelopmental disorders such as schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorder. But it’s not the virus itself doing the damage; it’s the mother’s immune response.
New University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign research using live mouse-adapted influenza virus improves upon previous mouse experiments to explain the process on a cellular and molecular level. It also indicates fetal brain changes are more likely once the severity of the mother’s infection meets a specific threshold.
“Our data provide really compelling evidence for an infection severity ...
A camera trap for the invisible
2024-07-29
DURHAM, N.C. -- It sounds fantastical, but it’s a reality for the scientists who work at the world’s largest particle collider:
In an underground tunnel some 350 feet beneath the France–Switzerland border, a huge device called the Large Hadron Collider sends beams of protons smashing into each other at nearly the speed of light, creating tiny eruptions that mimic the conditions that existed immediately after the Big Bang.
Scientists like Duke physicist Ashutosh Kotwal think the subatomic debris of these collisions could contain hints ...
Neurodivergent children are twice as likely to experience chronic disabling fatigue in adolescence
2024-07-29
The research, led by Dr Lisa Quadt, Research Fellow in Psychiatry at BSMS and Dr Jessica Eccles, Reader in Brain-Body Medicine at BSMS, highlights a significant link between neurodivergence and chronic fatigue. The study found that increased inflammation in childhood, often resulting from heightened stress levels, may be a contributing factor. This supports previous findings that suggest chronic fatigue can be rooted in inflammatory processes.
“These results show the importance of trans-diagnostic screening for children and the need for better support for neurodivergent children” says Dr Quadt. “Children with neurodivergent ...
Engineers use data to manage grid transformers, boosting reliability to homes, farms
2024-07-29
AMES, Iowa – Pay attention the next time you drive near your home, farm or business. You’ll notice small, green utility boxes all over the place. They’re distribution transformers. If they’re not working properly, electricity won’t flow to your lights and appliances.
Those boxes take kilovolts of electricity (that’s high voltage, measured in 1,000s of volts) from transmission lines and step it down to the safer, practical 120 or 240 volts that power our daily lives.
“Utilities have plenty of them,” said Zhaoyu Wang, an Iowa State University professor of electrical and computer engineering. “Most of them only ...
PSU awarded $1.9M NOAA grant to address microplastic pollution in coastal communities
2024-07-29
Portland State University (PSU) has been awarded $1,976,806 from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) National Sea Grant Marine Debris Challenge Award Program to lead an innovative and collaborative three-year project to address microplastic pollution on the Oregon coast.
This grant is part of a $27 million project between the U.S. Department of Commerce and NOAA. Portland State will host one of 11 projects that received a total of $25 million in funding across Alabama, California, Florida, Illinois, Massachusetts, New York, North Carolina, Oregon, Texas and Wisconsin. These projects ...
[1] ... [1021]
[1022]
[1023]
[1024]
[1025]
[1026]
[1027]
[1028]
1029
[1030]
[1031]
[1032]
[1033]
[1034]
[1035]
[1036]
[1037]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.