Persons diagnosed with PCOS face 8-fold increase in suicide risk
2024-02-05
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 5 February 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also ...
Mental health care during the COVID-19 era remains inaccessible to many distressed US adults
2024-02-05
U.S. adults experienced considerable psychological distress and adverse mental health effects as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic according to a study at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health and Columbia University Irving Medical Center. Based on insurance claims, mental health care provider surveys, and electronic health records the research further revealed a decline in in-person outpatient mental health visits during the acute phase of the pandemic. Findings are reported ...
Magnesium protects tantalum, a promising material for making qubits
2024-02-05
UPTON, NY—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered that adding a layer of magnesium improves the properties of tantalum, a superconducting material that shows great promise for building qubits, the basis of quantum computers. As described in a paper just published in the journal Advanced Materials, a thin layer of magnesium keeps tantalum from oxidizing, improves its purity, and raises the temperature at which it operates as a superconductor. All three may increase tantalum’s ability ...
From Colombia to Laos: protecting crops through nanotechnology
2024-02-05
In a recent breakthrough, DNA sequencing technology has uncovered the culprit behind cassava witches’ broom disease: the fungus genus Ceratobasidium.
The cutting-edge nanopore technology used for this discovery was first developed to track the COVID-19 virus in Colombia, but is equally suited to identifying and reducing the spread of plant viruses. The findings, published in Scientific Reports, will help plant pathologists in Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand protect farmers’ valued cassava harvest.
“In Southeast ...
New guideline details acute pain management strategies for adolescent, adult dental patients
2024-02-05
CHICAGO, Feb. 5, 2024 – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) taken alone or along with acetaminophen are recommended as first-line treatments for managing short-term dental pain in adults and adolescents aged 12 or older, according to a new clinical practice guideline developed by the American Dental Association (ADA), the University of Pittsburgh School of Dental Medicine and the Center for Integrative Global Oral Health at the University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine. The guideline has been endorsed by the ADA and is now available in the February issue of The Journal ...
How ‘deaths of despair’ differ by race and ethnicity
2024-02-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – White Americans are more likely than Black and Hispanic people in the United States to experience “deaths of despair” even though they are less likely to suffer from severe psychological distress, a new study finds.
The results suggest that, for some reason, whites are more vulnerable to the damaging effects of psychological distress than Blacks or Hispanics, said Hui Zheng, lead author of the study and professor of sociology at The Ohio State University. Zheng is currently on leave at the University of Hong Kong.
“The white population has an increasing trend of despair-related mortality after 2000,” Zheng said. ...
Understanding how soil traps carbon
2024-02-05
EVANSTON, Ill. — When carbon molecules from plants enter the soil, they hit a definitive fork in the road.
Either the carbon gets trapped in the soil for days or even years, where it is effectively sequestered from immediately entering the atmosphere. Or it feeds microbes, which then respire carbon dioxide (CO2) into the ever-warming environment.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers determined the factors that could tip plant-based organic matter in one direction or the other.
By combining laboratory experiments and molecular modeling, researchers ...
USC researchers uncover biological circuit that protects plants from extreme conditions
2024-02-05
Climate change is already harming agricultural yields and may one day pose a significant threat to the world’s food supply. Engineering more resilient crops, including those able to thrive in the face of drought or high soil salinity levels, is an increasingly urgent need.
A new study from the Keck School of Medicine of USC, funded in part by the National Institutes of Health, reveals details about how plants regulate their responses to stress that may prove crucial to those efforts. Researchers found that plants use their circadian clocks to respond to changes in external water and salt levels throughout the day. That same circuitry—an ...
Study reveals significant discrepancies in common poverty measurement approaches
2024-02-05
Methods commonly used to measure poverty can lead to vastly different conclusions about who actually lives in poverty, according to a new Stanford University-led study. Based on household surveys in sub-Saharan Africa, the first-of-its-kind analysis, published Feb. 5 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, underscores the importance of accurately defining and measuring poverty. Its findings could help inform how governments, nonprofit organizations, and international development agencies allocate resources and evaluate the effectiveness of poverty-alleviation policies around the world.
“They say you can’t manage what ...
Mystery of moths’ warning sound production explained in new study
2024-02-05
The workings of the ultrasonic warning sounds produced by the wings of a species of moth have been revealed by researchers at the University of Bristol.
Scientists recently discovered that moths of the genus Yponomeuta (so-called ermine moths) have evolved a very special acoustic defence mechanism against their echolocating predators—bats.
Ermine moths produce ultrasonic clicking sounds twice per wingbeat cycle using a minute corrugated membrane in their hindwing. Strikingly, these moths lack hearing organs and are therefore not aware of their unique defence mechanism, nor do they have the capability to control it using muscular ...
MIT researchers map the energy transition’s effects on jobs
2024-02-05
A new analysis by MIT researchers shows the places in the U.S. where jobs are most linked to fossil fuels. The research could help policymakers better identify and support areas affected over time by a switch to renewable energy.
While many of the places most potentially affected have intensive drilling and mining operations, the study also measures how areas reliant on other industries, such as heavy manufacturing, could experience changes. The research examines the entire U.S. on a county-by-county level.
“Our result ...
It’s true, happiness doesn’t cost much
2024-02-05
THIS PRESS RELEASE IS EMBARGOED UNTIL FEBRUARY 5, 2024 at 3:00 PM U.S. EASTERN TIME
Many Indigenous peoples and local communities around the world are leading very satisfying lives despite having very little money. This is the conclusion of a study by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB), which shows that many societies with very low monetary income have remarkably high levels of life satisfaction, comparable to those in wealthy countries.
Economic growth is often prescribed as a sure way of increasing the well-being of people in low-income countries, and ...
Lighting up Alzheimer’s-related proteins to allow for earlier disease detection
2024-02-05
Many neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are difficult to diagnose before symptoms begin to appear. However, disease-related biomarkers such as aggregated proteins called amyloids could provide important insight much earlier, if they can be readily detected. Researchers publishing in ACS Sensors have developed one such method using an array of sensor molecules that can light up amyloids. The tool could help monitor disease progression or distinguish between different ...
HHMI Janelia scientists Eric Betzig and Harald Hess to be inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame
2024-02-05
Janelia scientists and longtime collaborators Eric Betzig and Harald Hess will be inducted into the 2024 class of the National Inventors Hall of Fame for their invention of photoactivated localization microscopy (PALM), a pioneering imaging technology that enables scientists to image live cells in super-resolution to study biological structures and processes in unprecedented detail.
Betzig, a senior fellow at Janelia and an HHMI Investigator at the University of California, Berkeley, and Hess, a senior ...
Violence is contagious among members of Italian mafia groups, study shows
2024-02-05
Violence spreads in a contagious way like a disease among members of the Italian mafia, a new study shows.
Researchers have found committing violent acts with others increases the likelihood people in these groups will go on to carry out more violent offences in the future.
The analysis of the criminal careers of organised crime offenders shows previous violence has a “persistent and long-lasting” impact on their behaviour.
Prior violent co-offending has a greater impact than prior violent solo offending on the probability of future violence. Prior violent co-offending increases the probability ...
Petrina Kamya, Ph.D., Head of AI Platforms at Insilico Medicine, presents at BIO CEO & Investor Conference
2024-02-05
Petrina Kamya, PhD, Head of AI Platforms and President of Insilico Medicine Canada, will present at the BIO CEO & Investor Conference happening Feb. 26-27 at the New York Marriott Marquis in New York City. Dr. Kamya will speak as part of the panel “AI within Biopharma: Separating Value from Hype,” on Feb. 27, 1pm ET along with Michael Nally, CEO of Generate: Biomedicines and Liz Schwarzbach, PhD, CBO of BigHat Biosciences.
The session will look at how the latest artificial intelligence (AI) tools – including generative AI and large language models – ...
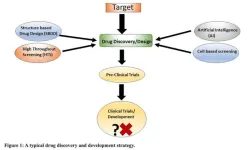
The fate of drug discovery in academia; dumping in the publication landfill?
2024-02-05
“[...] fruitful efforts to bring more drugs from bench to bedside could only be possible if we do not leave them ‘midway’!”
BUFFALO, NY- February 5, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on January 24, 2024, entitled, “The fate of drug discovery in academia; dumping in the publication landfill?”
In this new editorial, researchers Uzma Saqib, Isaac S. Demaree, Alexander G. Obukhov, Mirza S. Baig, Amiram Ariel, and Krishnan Hajela, from Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore, discuss drug discovery—a tedious process that is time consuming in both divulging whether a molecule is efficacious and specific in hitting ...
Currently stable parts of East Antarctica may be closer to melting than anyone realized
2024-02-05
In a warming climate, meltwater from Antarctica is expected to contribute significantly to rising seas. For the most part, though, research has been focused on West Antarctica, in places like the Thwaites Glacier, which has seen significant melt in recent decades.
In a paper published Jan. 19 in Geophysical Research Letters, researchers at Stanford have shown that the Wilkes Subglacial Basin in East Antarctica, which holds enough ice to raise global sea levels by more than 10 feet, could be closer to runaway melting than anyone realized.
“There hasn’t been much analysis in this region – there’s huge ...
System for early diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers
2024-02-05
Gastrointestinal cancers (GCs) are among the most common forms of cancer and account for as much as one-third of all cancer deaths worldwide. Early diagnosis is an effective way of reducing the mortality associated with GCs, and endoscopic screening has proved to be an excellent approach for detecting potentially malignant tumors.
To extend the benefits of screening programs to as many people as possible, the imaging systems used should be inexpensive to manufacture and operate, yet accurate enough ...
Study: weight loss surgery most effective for long-term blood pressure control
2024-02-05
Bariatric surgery is more effective in controlling hypertension rates, or high blood pressure, in people with obesity and uncontrolled high blood pressure compared to blood pressure medication alone, according to a study published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. People who underwent bariatric surgery had lower BMI and were on fewer medications after five years while maintaining normal blood pressure levels than those who only used antihypertensive medications.
According to the CDC, the U.S. obesity and hypertension rates in adults are 41.9% and 45.4%, respectively. Obesity is a known ...
Study confirms fears that COVID pandemic reduced kindergarten readiness
2024-02-05
Numerous studies have raised alarms about how the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted learning, development and mental health among school-aged children. But few have focused on the effects felt by the 22 million children under age 6 who were not yet in school.
Now a study published Feb. 5, 2024, in JAMA Pediatrics, led by researchers at Cincinnati Children’s in collaboration with the Cincinnati Public Schools, documents the pandemic’s harmful effects on kindergarten readiness. The findings are based on data from about 8,000 kindergartners who took ...
MSU making voice-activated artificial intelligence more accessible
2024-02-05
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – As artificial intelligence technology advances, one area lags behind: voice-activated AI. For the more than 80 million people who stutter, voice AI technologies, which are increasingly being used in job hiring practices, can still be impossible to navigate.
HeardAI, a multidisciplinary project from Michigan State University, Western Michigan University, and the nonprofit Friends: The National Association of Young People Who Stutter, has advanced to Phase 2 of the National Science Foundation’s Convergence Accelerator program to ...
Lowder & Foudray receive funding for Fairfax county peer recovery services evaluability assessment
2024-02-05
Lowder & Foudray Receive Funding For Fairfax County Peer Recovery Services Evaluability Assessment
Evan Marie Lowder, Assistant Professor, Criminology, Law and Society, and Chelsea Foudray, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Criminology, Law and Society, received funding from County of Fairfax for: "Fairfax County Peer Recovery Services Evaluability Assessment."
Lowder and Foudray are laying the groundwork for a formal evaluation of Fairfax County Peer Recovery Services (PRS) programming.
For ...
Watching the enzymes that convert plant fiber into simple sugars
2024-02-05
This work was adapted from articles by Elizabeth Boatman and Emily C. Dooley.
Research from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), and UC Davis sheds new light on how to access the sugars locked up in plants to produce petroleum-free fuels, chemicals, and medicines.
Using microbes to convert grasses, weeds, wood, and other plant residues into sustainable products will be key to achieving carbon neutrality and could even help eliminate drug shortages. But cellulose, the tough tissue that makes up a large proportion of herbaceous and woody plant ...
Argonne’s Lin X. Chen receives the Mildred Dresselhaus Guest Professorship Award from the University of Hamburg
2024-02-05
Lin X. Chen, a chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, has received the Senior Prize as part of the two 2023 Mildred Dresselhaus Guest Professorship Awards from the University of Hamburg, Germany. The award recognizes outstanding international women scientists and offers an opportunity for awardees to conduct research at the Hamburg Centre for Ultrafast Imaging Cluster of Excellence. Chen has held a joint appointment as professor of chemistry at Northwestern University since 2007.
“I am very honored ...
[1] ... [1388]
[1389]
[1390]
[1391]
[1392]
[1393]
[1394]
[1395]
1396
[1397]
[1398]
[1399]
[1400]
[1401]
[1402]
[1403]
[1404]
... [8820]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.