New ‘pangenome’ offers more inclusive view of human genome
2023-05-10
New Haven, Conn. — When it was launched in April 2003, the Human Genome Project helped revolutionize biomedical research by providing scientists a reference map that allowed them to analyze DNA sequences for genetic clues to the origins of a host of diseases.
Twenty years later, a team of researchers that includes Yale scientists has created a new “pangenome” that fills in missing sequencing gaps from the original genome project and greatly expands the diversity of genomes represented.
The achievement is described in ...
Study: palliative care provided at point of oncology surgery does not improve patient outcomes
2023-05-10
One of the most important advances in palliative care in oncology over the past 15 years has been the recognition that palliative care specialists can improve cancer patients’ outcomes well before their end of life.
Palliative care is specialized care provided to individuals with a serious illness that focuses on decision-making support, pain and symptom management, as well as psychosocial interventions to improve quality of life.
Several past randomized clinical trials have shown palliative care specialists can improve the quality of life and lengthen the ...
Investigating social media to evaluate emergency medicine physicians’ emotional well-being during COVID-19
2023-05-10
About The Study: In this study, key thematic shifts and increases in language related to anxiety, anger, depression, and loneliness were identified in the content posted on social media by academic emergency medicine physicians and resident physicians during the pandemic. Social media may provide a real-time and evolving landscape to evaluate thematic content and linguistics related to emotions and sentiment for health care workers.
Authors: Anish K. Agarwal, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of the ...
Analysis of BMI in early and middle adulthood and estimated risk of gastrointestinal cancer
2023-05-10
About The Study: In this secondary analysis of the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial, overweight and obese body mass index (BMI) in early and middle adulthood was associated with an elevated risk of colorectal cancer and non-colorectal gastrointestinal cancers. The results of the current study prompt further exploration into the mechanistic role of obese BMI in carcinogenesis.
Authors: Holli A. Loomans-Kropp, Ph.D., M.P.H., of Ohio State University in Columbus, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.10002)
Editor’s ...
UW Medicine scientists among leads of NIH pangenome studies
2023-05-10
UW Medicine genome experts made significant scientific contributions to a National Institutes of Health Human Genome Research Institute reference collection that better represents the genetic diversity of the world’s populations.
Called the Human Pangenome Reference Consortium, the multi-institutional effort expands and updates earlier work that started as the Human Genome Project. That original project, with drafts reported in 2001 and 2003, was based on a more limited sampling of human DNA. The goal then was to create an entire sequence of a human genome to use as a reference. ...
The clearest snapshot of human genomic diversity ever taken
2023-05-10
For more than 20 years, scientists have relied on the human reference genome, a consensus genetic sequence, as a standard against which to compare other genetic data. Used in countless studies, the reference genome has made it possible to identify genes implicated in specific diseases and trace the evolution of human traits, among other things.
But it has always been a flawed tool. One of its biggest problems is that about 70 percent of its data came from a single man of predominantly African-European background whose DNA was sequenced during ...
Researchers measure the light emitted by a sub-Neptune planet’s atmosphere for the first time
2023-05-10
For more than a decade, astronomers have been trying to get a closer look at GJ 1214b, an exoplanet 40 light-years away from Earth. Their biggest obstacle is a thick layer of haze that blankets the planet, shielding it from the probing eyes of space telescopes and stymying efforts to study its atmosphere.
NASA’s new James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) solved that issue. The telescope’s infrared technology allows it to see planetary objects and features that were previously obscured ...
Paper refutes assertion that effects of bottom trawling on blue carbon can be compared to that of global air travel
2023-05-10
A ‘Matter Arising’ paper published in Nature today refutes the findings of a paper by Sala et al on the amount of CO2 released from the seabed by bottom trawling. The paper made significant headlines around the world on release in 2021, as it equated the carbon released by bottom trawling to be of a similar magnitude to the CO2 created by the global airline industry.
In their paper quantifying the carbon benefits of ending bottom trawling, Prof Jan Hiddink of Bangor University’s world-renowned School of Ocean Science and others, explain that the methodology ...
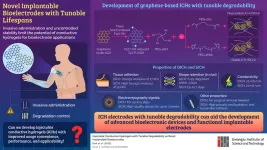
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology researchers develop injectable bioelectrodes with tunable lifetimes
2023-05-10
Implantable bioelectrodes are electronic devices that can monitor or stimulate biological activity by transmitting signals to and from living biological systems. Such devices can be fabricated using various materials and techniques. But, because of their intimate contact and interactions with living tissues, selection of the right material for performance and biocompatibility is crucial. In recent times, conductible hydrogels have attracted great attention as bioelectrode materials owing to their flexibility, compatibility, and excellent interaction ability. However, the absence ...
Study of cancer metastasis, most common cause of cancer death, gets $35 million boost at Johns Hopkins Medicine
2023-05-10
FOR IMMMEDIATE RELEASE
With a $35 million gift from researcher, philanthropist and race car driver Theodore Giovanis, scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine will study the biological roots of the most fatal aspect of cancer: how it metastasizes, or spreads, through the body.
The contribution, a 15-year commitment, will establish the Giovanis Institute for Translational Cell Biology, dedicated to studying metastasis. The institute’s researchers aim to make discoveries that reveal common features of metastasis across cancer types, ...
Pandemic stress reshapes the placentas of expectant moms
2023-05-10
WASHINGTON (May 10, 2023) – Elevated maternal stress during the COVID-19 pandemic changed the structure, texture and other qualities of the placenta in pregnant mothers – a critical connection between mothers and their unborn babies – according to new research from the Developing Brain Institute at Children’s National Hospital.
Published in Scientific Reports, the findings spotlight the underappreciated link between the mental health of pregnant mothers and the health of the placenta – a critical organ ...
Local Phoenix medical students invited to upcoming medical conference to learn about opportunities in interventional cardiology
2023-05-10
A newly piloted program from the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI), the leading society representing interventional cardiology, hopes to increase access and encourage interest in interventional cardiology early in students' medical careers.
SCAI's Ready to Launch - Careers in Cardiology program is designed to introduce future physicians to the field of interventional cardiology through a half-day program where attendees will get the opportunity to have impactful conversations with nationally recognized interventional cardiologists, learning about training paths, barriers to care and solutions for the future, the importance of health ...
A jumping conclusion: Fossil insect ID’d as new genus, species of prodigious leaper, the froghopper
2023-05-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. – A fossil arthropod entombed in 100-million-year-old Burmese amber has been identified as a new genus and species of froghopper, known today as an insect with prodigious leaping ability in adulthood following a nymphal stage spent covered in a frothy fluid.
Oregon State University researcher George Poinar Jr., an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn about the biology and ecology of the distant past, and his co-author, Alex E. Brown, published ...
Allison Institute announces appointment of inaugural members
2023-05-10
HOUSTON ― The James P. Allison Institute at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced the appointment of its first members, James P. Allison, Ph.D., Padmanee Sharma, M.D., Ph.D., Jennifer Wargo, M.D., Sangeeta Goswami, M.D., Ph.D., and Kenneth Hu, Ph.D. In addition, Garry Nolan, Ph.D., will join the Allison Institute as an adjunct member.
These members include pioneering researchers who have made notable contributions to science as well as rising stars on the path toward important breakthroughs. This group ...
St. Jude scientist M. Madan Babu elected to the Royal Society of London
2023-05-10
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientist Madan Babu Mohan, Ph.D., Center of Excellence in Data-Driven Discovery director and member of the Department of Structural Biology, has been elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of London. The Royal Society is the oldest scientific academy in continuous existence.
Babu was selected to join the Royal Society for his pioneering data science-based strategies to reveal fundamental principles in biological systems. His scientific accomplishments include determining the molecular mechanisms governing G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling, uncovering the roles of disordered protein regions in biology and disease, ...
Sleep-tracker study finds fatigued officers struggle with investigations
2023-05-10
AMES, IA — Like many first responders, law-enforcement investigators and detectives often struggle with sleep. Late-night shifts, stress, and the 24-hour nature of crime can throw off biological clocks and cut sleep cycles short. Along with the negative health implications, new research indicates officers who are fatigued have a harder time collecting information that could bring justice to victims.
Zlatan Križan, a sleep scientist and psychology professor at Iowa State University, led the study. He ...
Cheese experiments show fungal antibiotics can influence microbiome development
2023-05-10
Washington, DC – Fungi produce metabolites that humans have used to improve health. For example, they secrete penicillin, which is then purified and used as an antibiotic for humans, leading to the development of many other antibiotics. However, the ecology of fungal metabolites in microbial communities is not well understood. In a new study, researchers use cheese rinds to demonstrate that fungal antibiotics can influence how microbiomes develop. The study is published in mBio, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
“My lab is interested in how ...
Broad climate change concern in Florida linked with recent extreme weather
2023-05-10
An increasing number of Floridians agree that human actions are causing climate change, including a record number of Florida Republicans, according to a new survey from Florida Atlantic University. This finding reinforces the trend observed in the prior seven Florida Climate Resilience Surveys, conducted by FAU’s Center for Environmental Studies within the Charles E. Schmidt College of Science.
Three main messages emerge from this latest poll. First, climate change is no longer an effective partisan wedge issue. Virtually all respondents (90 percent) ...
Niraula wins 2023 Endocrine Images Art Competition
2023-05-10
WASHINGTON—Anzela Niraula, Ph.D., of the University of Washington in Seattle, won the Endocrine Society's 2023 Endocrine Images Art Competition for her image of the microglia mandala.
This contest celebrates the beauty of endocrine science, and entries were judged based on aesthetic value and significance to endocrine research.
Niraula’s image of the microglia won the grand prize this year out of more than 25 entries. The image shows microglia and POMC neurons in close proximity within the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. Microglial regulation of POMC neurons holds significant implications ...
Looking to introduce a new brand extension? Be sure to leverage the brand equity of the parent brand as well as the extension fit
2023-05-10
Researchers from University of International Business and Economics, University of Groningen, University of Cologne, and University of Chinese Academy of Sciences published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the drivers of brand extension success.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “A Meta-Analysis of Brand Extension Success: The Effects of Parent Brand Equity and Extension Fit” and is authored by Chenming Peng, Tammo H.A. Bijmolt, ...
Why buses can’t get wheelchair users to most areas of cities
2023-05-10
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Imagine you could travel to only 1% of the city where you live – areas that were easily accessible to other residents.
That’s the situation for manual wheelchair users traveling by public buses in Columbus, a first-of-its-kind study finds. The situation for those with powered wheelchairs is only somewhat better – the study found they have access to about 25% of the areas available to the general bus ridership.
But the main problem isn’t with the bus system itself – the key obstacle is with the sidewalks and other infrastructure that wheelchair users need to get from ...
Historic $100 million gift to Brigham and Women’s Hospital to establish Institute of Immunology and Inflammation of the Brigham, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Harvard Medical School
2023-05-10
Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, today announces a historic $100 million gift from eminent biotechnology entrepreneur Gene Lay, MS, DVM, founder and CEO of BioLegend, Inc., through the Laygend Foundation. The landmark gift—the largest in the Brigham’s history—will establish The Gene Lay Institute of Immunology and Inflammation of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), also a founding member of Mass General Brigham, and Harvard Medical School (HMS). Vijay Kuchroo, DVM, PhD, an immunologist and principal investigator at the Brigham, will serve as inaugural director of the institute, which will be ...
Oxygen therapy improves heart function in patients with long COVID
2023-05-10
Barcelona, Spain – 10 May 2023: A small randomised trial in patients with post-COVID syndrome has found that hyperbaric oxygen therapy promotes restoration of the heart’s ability to contract properly. The research is presented at EACVI 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The study suggests that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be beneficial in patients with long COVID,” said study author Professor Marina Leitman of the Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University and Shamir Medical Centre, Be'er Ya'akov, Israel. “We used a sensitive measure of cardiac function which is ...
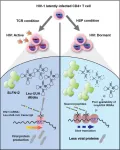
One step closer to eliminating latency, the real challenge in combating HIV
2023-05-10
An international study led by MELIS-UPF researchers from the Infection Biology and Molecular Virology laboratories has identified and characterized Schlafen 12 (SLFN 12) as a novel HIV restriction factor. SLFN 12 shuts down viral protein production and helps virus-infected cells to escape from anti-HIV therapy and immune responses. These findings pave the way for improving therapeutic strategies that aim to cure HIV infections.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infections, if left untreated, lead to the gradual destruction of the immune system, AIDS, in its final stages. Worldwide, some 650,000 ...
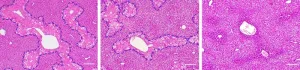
Delivery of antioxidants to liver mitochondria
2023-05-10
A new drug delivery system delivers an antioxidant directly to mitochondria in the liver, mitigating the effects of oxidative stress.
Mitochondria are microscopic organelles found within cells, and are well-known as the “powerhouse of the cell.” They are by far the largest producer of the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which provides energy to many processes in living cells. The process by which mitochondria synthesize ATP generates a large amount of reactive oxygen species (ROS), chemical groups that are highly reactive.
In a healthy cell, the ROS are controlled by the mitochondria; however, when this balance is lost, the excess ROS damages the mitochondria ...
[1] ... [1922]
[1923]
[1924]
[1925]
[1926]
[1927]
[1928]
[1929]
1930
[1931]
[1932]
[1933]
[1934]
[1935]
[1936]
[1937]
[1938]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.