Lessons from blockbusters to help teams adapt
2023-05-23
AMES, IA – We all like to think of ourselves as rational human beings. If there’s a drastic change in our lives or at work, we can evaluate our options and make the best choice. But James Summers, an expert in team management and adaptation at Iowa State University, says our ability to process information breaks down when we experience heightened negative emotions.
Fear and anxiety can lead to withdrawal and avoidance, both of which hinder a group’s ability to coordinate and overcome challenges. Because of this, many researchers ...
Flavonol-rich foods like apples and blackberries can lower chances of developing frailty
2023-05-23
Eating plant-based foods that contain dietary compounds called flavonols can lower your chances of developing frailty.
Foods like apples and blackberries that contain flavonoids called quercetin may be the most important for frailty prevention.
Approximately 10% to 15% of older adults experience frailty, a geriatric syndrome that leads to a greater risk of falls, fractures, disability, hospitalization, and mortality. Current dietary recommendations for frailty prevention primarily focus on protein intake. However there are many other foods that may have health benefits
“There ...
Researchers want to use ‘biochar’ to combat climate change
2023-05-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new review of research suggests that the nature-based technology biochar – a carbon-rich material – could be an important tool to use in agriculture to help mitigate climate change.
Made by pyrolysis, a process that involves heating organic material in a low-oxygen environment, biochar – a charcoal-like, porous substance – has long been utilized for crop production as a soil amendment or carbon sequestration agent. In recent years, researchers have seen a resurgence of heightened interest in the technology due to its unique physical structure and its various agricultural ...
Researchers build bee robot that can twist
2023-05-23
PULLMAN, Wash. – A robotic bee that can fly fully in all directions has been developed by Washington State University researchers.
With four wings made out of carbon fiber and mylar as well as four light-weight actuators to control each wing, the Bee++ prototype is the first to fly stably in all directions. That includes the tricky twisting motion known as yaw, with the Bee++ fully achieving the six degrees of free movement that a typical flying insect displays.
Led by Néstor O. Pérez-Arancibia, Flaherty associate professor in WSU’s School of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, the researchers ...
How the COVID-19 pandemic impacted social cohesion
2023-05-23
Did the pandemic bring societies together or increase the drifting apart? That was one of the central questions posed by the scientists. "The empirical knowledge gained in this special issue deepens our understanding of the social consequences of the pandemic," says Dr. Mandi Larsen, a sociologist at Constructor University, "a well-founded scientific basis is also important in order to be able to better counteract future pandemics in socio-political terms." Together with her expert colleagues Dr. Georgi ...
Are we truly “inattentionally blind”? New study revisits “invisible gorilla” experiment for new insights
2023-05-23
We are quite good at spotting unexpected objects while focused on another activity if they are moving fast, reveals a new study by a team of New York University researchers. Their findings cast doubt on a long-standing view that our ability to see the unexpected is necessarily impaired when our attention is already directed elsewhere.
“For decades, it’s been thought that when we’re intently focused on something relevant, like driving or playing a game, we fail to spot something that unexpectedly enters our field of vision, even if it is clearly visible and moving,” says Pascal Wallisch, a clinical associate professor at New York University’s ...
Putting the brakes on accelerated aging of bone, muscle from HIV infection, treatment
2023-05-23
AUGUSTA, Ga. (May 23, 2023) – Antiretroviral cocktails can make human immunodeficiency virus, or HIV, undetectable and untransmittable, but both the virus and its treatment can also accelerate aging of bone and muscle.
Now Medical College of Georgia scientists are looking at drugs already being studied in clinical trials for cancer to help put the brakes on these classic indicators of aging that can lead to falls, fractures and early frailty.
“These drugs are doing what they are supposed to be doing: ...
Viewers actually 'binge-watch' TV with a lot of self-control
2023-05-23
If viewers sometimes feel guilty about binge-watching television programing, they really shouldn’t. Though its name implies impulsive behavior, binge-watching TV is a common activity planned out by viewers, suggests new research from the University of California San Diego’s Rady School of Management and School of Global Policy and Strategy.
The study, in collaboration with the Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon University and Fox School of Business at Temple University, reveals that viewers prefer to binge-watch ...
Prescribed burns encourage foul-smelling invaders
2023-05-23
Though prescribed burns reduce wildfire threats and even improve habitat for some animals, new research shows these fires also spread stinknet, an aptly named weed currently invading superblooms across the Southwestern U.S.
Stinknet, also called globe chamomile, is native to South Africa, but is commonly seen in photos of California’s colorful superblooms. “Not all flowering plants are indicative of a healthy ecosystem,” said Loralee Larios, UC Riverside assistant botany professor and study co-author. “This one isn’t.”
In addition ...
Investigation reveals “shocking” epidemic of sexual assault in the NHS
2023-05-23
A joint investigation published today by The BMJ and The Guardian finds that NHS trusts recorded more than 35,000 cases of rape, sexual assault, harassment, stalking, and abusive remarks, between 2017 and 2022. The findings, which show that NHS trusts are failing to protect staff and patients, have led to calls for an independent inquiry.
The data, based on responses to Freedom of Information (FOI) requests from 212 NHS trusts and 37 police forces in England, show that a total of 35,606 sexual safety incidents were recorded ...
3 undergraduate researchers from Argonne selected for National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program
2023-05-23
Argonne supports students’ ongoing engagement with the lab and scientific research by helping them secure a graduate fellowship.
Three students who have completed their participation in the Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships (SULI) Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internships Program at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory were accepted into the National Science Foundation’s (NSF) Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP). Their achievements highlight the important role Argonne plays in students’ continued engagement in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (science, technology, ...
UC San Diego first to test cancer drugs in space using private astronaut mission
2023-05-23
On May 21, 2023, scientists at University of California San Diego Sanford Stem Cell Institute launched several new nanobioreactor experiments onto the International Space Station (ISS) via the second Axiom Space Private Astronaut Mission, Axiom Mission 2 (Ax-2). The latest experiments expand their research on human stem cell aging, inflammation and cancer in low Earth orbit.
Increasing evidence shows that microgravity conditions can accelerate aging, inflammation and immune dysfunction in human stem cells. Understanding this process is not only helpful for keeping astronauts healthy — it could also teach us how to better treat ...
Research favors testing and voluntary isolation over closures in disease outbreaks
2023-05-23
Regular diagnostic testing and self-isolation can be more effective than school and business closures when it comes to combating infectious disease outbreaks such as COVID-19, according to a new study by University of Wyoming researchers.
The findings appear today (Monday) in Scientific Reports, an online, open access journal from the publishers of Nature.
UW Department of Economics faculty members Stephen Newbold, David Finnoff, Jason Shogren and Linda Thunstrom, along with recent Ph.D. graduate Madison Ashworth, developed an epidemiological and economic model to compare the effectiveness of physical distancing mandates with policies encouraging regular testing and ...
Researchers examine cooling power plants with brackish groundwater
2023-05-23
A new analysis led by a University of Wyoming researcher shows that brackish or salty groundwater has the potential to replace fresh water to cool coal- and natural gas-fired power plants and strengthen resilience in the energy infrastructure, although there’s a cost associated with doing so.
With freshwater supplies threatened due to drought, climate change and rapid socioeconomic growth, water competition is increasing between the electric power sector and other sectors. While transitioning to a low-carbon energy future, decarbonization of fossil fuel-fired power plants by carbon capture and storage would significantly ...
In 2050, over 800 million people globally estimated to be living with back pain
2023-05-23
Analysis of over 30 years of data has shown the number of cases of low back pain is growing, with modelling suggesting by 2050, 843 million people will be affected by the condition largely due to population increases and ageing of populations.
The continued lack of a consistent approach on back pain treatment, and limited treatment options have researchers concerned that this will lead to a healthcare crisis, as low back pain is the leading cause of disability in the world.
In Australia, there will be a nearly 50 percent increase ...
Psychology: Unidentified aerial phenomena observations reported by almost one fifth of academic survey respondents
2023-05-23
19% of respondents to a survey of academics report that they or someone they know have witnessed unidentified aerial phenomena (UAP) — observations of the sky that cannot be identified as aircraft or as known natural phenomena — and 37% report some degree of interest in conducting research into UAP. The findings, which are based on a survey of 1,460 US academics, are published in Humanities and Social Science Communications and highlight that many academics consider the evaluation of UAP to be worthy of academic scrutiny.
Marissa Yingling, Charlton Yingling and Bethany Bell surveyed professors, ...
Modular builds may help construction industry weather a perfect storm
2023-05-23
Rising material prices, labour shortages, interest rate hikes and rainy weather have created a perfect storm for the construction industry in the past 12 months, sending many builders to the wall.
Of all these factors, weather is the one that most people would cite as being beyond human control. However, a new study out of the UK and Australia suggests this may not be the case.
Engineers from Aston University, Birmingham, and the University of South Australia (UniSA) have calculated the potential cost savings for ...
Survey: Nearly 7 in 10 parents believe social media image editing apps and filters have a negative influence on their children’s body image
2023-05-23
COLUMBUS, Ohio (May 23, 2023) — With children more plugged in to social media than ever before, a wave of new image editing apps and filters along with trends related to appearance have parents concerned about damage to body image. According to a new national survey conducted online by The Harris Poll on behalf of The On Our Sleeves Movement For Children’s Mental Health, 69% of parents of children younger than 18 think social media image editing apps and filters have a negative influence on their child(ren)’s body image. In ...
Support for extremism among military veterans is similar to U.S. public
2023-05-23
Support among military veterans for extremist groups and extremist ideals appears similar to or less than levels seen among the U.S. public in general, despite fears that it could be higher, according to a new RAND Corporation report.
Surveying a nationally representative group of military veterans, researchers found that support for extremist groups such the Proud Boys and Antifa was generally lower than rates derived from previous representative surveys of the general U.S. population.
Assessing support among veterans for extremist beliefs, researchers found results that were more mixed. Support for QAnon was lower than the public at large, while support for political ...
Texas A&M team studying effects of crypto mining on Texas power grid
2023-05-22
Cryptocurrency transactions may be costing more than just transaction fees. The electricity used for these transactions is more than what some countries, like Argentina and Australia, use in an entire year.
Published estimates of the total global electricity usage for cryptocurrency assets such as Bitcoin are between 120 and 240 billion kilowatt-hours per year, according to the White House Office of Science and Technology. The United States leads these numbers.
Finance and business experts have debated the ramifications of cryptocurrency and mining, but ...
Grant funds study of cannabis effects on HIV-infected brain tissue
2023-05-22
Weill Cornell Medicine has been awarded a five-year, $11.6 million grant from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) of the National Institutes of Health to study the effects cannabis, including marijuana and compounds derived from it, may have on the brains of those living with HIV.
“We know that the virus may cause changes within the brain, but it’s not clear yet how the use of cannabis might interact with the infection,” said principal investigator Dr. Lishomwa Ndhlovu, a professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Cannabis ...
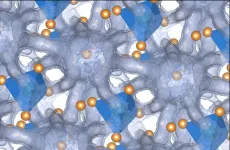
Flexing crystalline structures provide path to a solid energy future
2023-05-22
A team of researchers at Duke University and their collaborators have uncovered the atomic mechanisms that make a class of compounds called argyrodites attractive candidates for both solid-state battery electrolytes and thermoelectric energy converters.
The discoveries—and the machine learning approach used to make them—could help usher in a new era of energy storage for applications such as household battery walls and fast-charging electric vehicles.
The results appeared online May 18 in the journal Nature Materials.
“This is a puzzle that has not been cracked before because of how big and complex each building block of the material is,” said Olivier ...
California declares May 17 NEC Awareness Day
2023-05-22
Sacramento, California – The Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Society is grateful to announce that California has declared May 17th as NEC Awareness Day with ACR 69. This resolution reflects the tireless dedication and advocacy by the NEC Society, its founder, Jennifer Canvasser (Davis, CA), and Assemblymember Cecilia Aguiar-Curry, who represents the 4th California Assembly District.
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that affects medically fragile infants in their first ...
Sexing chicken eggs by scent
2023-05-22
Fertilized chicken eggs can be sexed by “sniffing” volatile chemicals emitted through the shell, according to new work by researchers at the University of California, Davis, and Sensit Ventures Inc., a startup company in Davis. The work is published May 22 in PLOS ONE.
The study shows that it is feasible to sort eggs by sex, early in incubation, based on volatile organic chemicals, said Professor Cristina Davis, associate vice chancellor for interdisciplinary research and strategic initiatives at UC Davis and co-author on the paper.
Hatcheries for laying hens sort chicks by sex a day after hatching, with male chicks being culled immediately. If hatcheries ...
Midwives provide better birth experiences marked by respect, autonomy
2023-05-22
People giving birth report more positive experiences when cared for by midwives in both hospitals and in community settings than by physicians, according to a new study published in the journal Reproductive Health. Additionally, those receiving midwifery care at home or at birth centers reported better experiences than those in hospital settings.
The majority of U.S. births (88%) are attended by physicians, while midwives attend 12% of births. Most births occur in the hospital, with less than 2% of all births occurring in community settings, including homes and freestanding birth centers. Most community births are attended by midwives.
Measures of ...
[1] ... [1914]
[1915]
[1916]
[1917]
[1918]
[1919]
[1920]
[1921]
1922
[1923]
[1924]
[1925]
[1926]
[1927]
[1928]
[1929]
[1930]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.