'Love hormone' guides young songbirds in choice of 'voice coach'
2023-05-15
Oxytocin, the so-called “love hormone,” plays a key role in the process of how a young zebra finch learns to sing by imitating its elders, suggests a new study by neuroscientists at Emory University. Scientific Reports published the findings, which add to the understanding of the neurochemistry of social learning.
“We found that the oxytocin system is involved from an early age in male zebra finches learning song,” says Natalie Pilgeram, first author of the study and an Emory PhD candidate in psychology. “It’s basic science that may lead to insights into the ...
Researchers find compound that combats multidrug-resistant bacteria in less than one hour
2023-05-15
Resistance to antibiotics is a problem that alarms the medical and scientific community. Bacteria resistant to three different classes of antibiotics, known as multi-drug resistant (MDR) bacteria, are far from rare. Some are even resistant to all currently available treatments and are known as pan-drug resistant (PDR). They are associated with dangerous infections and listed by the World Health Organization (WHO) as priority pathogens for drug development with maximum urgency.
An article published in a special issue of the journal Antibiotics highlights a compound with antibacterial activity that presented promising ...
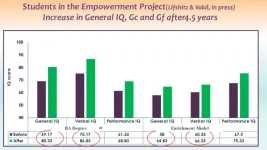
Postsecondary university education improves intelligence of adult students with intellectual disability
2023-05-15
Post-secondary education (PSE) has a potential for improving the IQ of adults with mild intellectual disability (ID), according to a new Bar-Ilan University study.
The study examined the impact of PSE on students with mild ID who study in a university-based program, known as the Empowerment Project, at the Bar-Ilan University Faculty of Education.
The study sample included 24 participants, divided into 12 students with ID who participate in the Empowerment Project and 12 adults with ID with the same background, who did not participate. The results were published in the European Journal of Special Needs Education.
The findings revealed significant IQ improvement ...
With formic acid towards CO2 neutrality
2023-05-15
New synthetic metabolic pathways for fixation of carbon dioxide could not only help to reduce the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere, but also replace conventional chemical manufacturing processes for pharmaceuticals and active ingredients with carbon-neutral, biological processes. A new study demonstrates a process that can turn carbon dioxide into a valuable material for the biochemical industry via formic acid.
In view of rising greenhouse gas emissions, carbon capture, the sequestration of carbon dioxide from large emission sources, is an ...
Astronomers observe the first radiation belt seen outside of our solar system
2023-05-15
Astronomers have described the first radiation belt observed outside our solar system, using a coordinated array of 39 radio dishes from Hawaii to Germany to obtain high-resolution images. The images of persistent, intense radio emissions from an ultracool dwarf reveal the presence of a cloud of high-energy electrons trapped in the object’s powerful magnetic field, forming a double-lobed structure analogous to radio images of Jupiter’s radiation belts.
“We are actually imaging the magnetosphere of our target by observing the radio-emitting ...
New study reveals widespread presence of environmental DNA in the sky, including allergens and pathogens
2023-05-15
Recently published in PeerJ Life and Environment, researchers successfully use aircraft surveys with novel instrumentation to capture airborne nucleic acids and probe biodiversity in the atmosphere, uncovering surprising findings.
[Clemson, May 2023] - A groundbreaking research article titled "Aircraft Surveys for Air eDNA: Probing Biodiversity in the Sky" unveils a revolutionary approach to studying genetic material in the atmosphere. Scientists have developed a durable and sterilizable probe and supporting system to capture air environmental nucleic acids (eDNA) with full-flow filtration and a high-integrity chamber.
Using this innovative probe, ...
Tetris reveals how people respond to unfair AI
2023-05-15
ITHACA, N.Y. – A Cornell University-led experiment in which two people play a modified version of Tetris revealed that players who get fewer turns perceived the other player as less likable, regardless of whether a person or an algorithm allocated the turns.
Most studies on algorithmic fairness focus on the algorithm or the decision itself, but researchers sought to explore the relationships among the people affected by the decisions.
“We are starting to see a lot of situations in which AI makes decisions on how resources should be distributed among people,” ...
Distinct types of cerebellar neurons control motor and social behaviors
2023-05-15
The cerebellum, a major part of the hindbrain in all vertebrates, is important for motor coordination, language acquisition, and regulating social and emotional behaviors. A study led by Dr. Roy Sillitoe, professor of Pathology and Neuroscience at Baylor College of Medicine and investigator at the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute (Duncan NRI) at Texas Children’s Hospital, shows two distinct types of cerebellar neurons differentially regulate motor and non-motor behaviors during development and in adulthood.
The study, published in Nature Communications, provides the first in ...
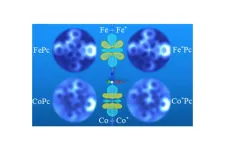
Seeing electron orbital signatures
2023-05-15
No one will ever be able to see a purely mathematical construct such as a perfect sphere. But now, scientists using supercomputer simulations and atomic resolution microscopes have imaged the signatures of electron orbitals, which are defined by mathematical equations of quantum mechanics and predict where an atom’s electron is most likely to be.
Scientists at UT Austin, Princeton University, and ExxonMobil have directly observed the signatures of electron orbitals in two different transition-metal atoms, iron (Fe) and cobalt ...
Commercial investors shift perspective of coastal properties in face of climate change
2023-05-15
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Investors in commercial real estate are rethinking the values of coastal properties exposed to flood risk — even in northern U.S. locales that haven’t suffered flood damage, according to researchers. This shift in perspective has implications for investors and developers alike as they determine the value of coastal properties amid a changing climate.
Eva Steiner, associate professor of real estate and King Family Early Career Professor in Real Estate in the Penn State Smeal College of Business, and her co-authors published these findings recently in Real Estate Economics.
Steiner and ...
Luo to receive NSF funding for collaborative research: catholyte molecular design for non-aqueous mg-organic hybrid redox flow batteries
2023-05-15
Chao Luo, Assistant Professor, Chemistry and Biochemistry, is set to receive funding from the National Science Foundation for the project: "Collaborative Research: Catholyte Molecular Design For Non-Aqueous Mg-Organic Hybrid Redox Flow Batteries."
Luo is proposing a new organic molecule structure design concept for redox flow batteries, which are promising for grid-scale energy storage. The research outcomes will afford low-cost, abundant, sustainable, and high-performance organic catholyte materials for non-aqueous Mg-organic hybrid redox flow batteries.
His goal is to design, synthesize, and characterize core-shell ...
Huneke wins grant to research lesbians in the Third Reich
2023-05-15
Samuel Clowes Huneke, Assistant Professor, History and Art History, has been awarded a Sharon Abramson Research Grant from the Holocaust Educational Foundation of Northwestern University. The award will enable him to complete research for his forthcoming book on lesbians in Nazi Germany.
For many decades after the end of World War II, the fates of queer women were ignored. Because female homosexuality had not been criminalized explicitly, historians long argued that lesbians were not persecuted by the Nazi regime.
In contrast, Huneke’s book, which is under advanced contract with Aevo-University of Toronto Press, argues that queer women under Nazism faced ...
Porous crystals made from plant extracts purify water from pharmaceutical pollutants
2023-05-15
Researchers from Stockholm University have developed porous crystals made from pomegranate extract to capture and degrade pharmaceutical molecules found in local municipal wastewater. The research is published in the scientific journal Nature Water.
Pharmaceutical compounds affect the human body to improve our health, but they can also have unintentional adverse effects for the wellbeing of wildlife. Hence wastewater treatment plants are facing the challenge of removing emerging organic contaminants (EOCs) such as active pharmaceutical ingredients, and therefore ...
Butterfly tree of life reveals an origin in North America
2023-05-15
About 100 million years ago, a group of trendsetting moths started flying during the day rather than at night, taking advantage of nectar-rich flowers that had co-evolved with bees. This single event led to the evolution of all butterflies.
Scientists have known the precise timing of this event since 2019, when a large-scale analysis of DNA discounted an earlier hypothesis that pressure from bats prompted the evolution of butterflies after the extinction of dinosaurs.
Now, scientists have discovered where the first butterflies originated ...
From molecular to whole-brain scale in a simple animal, study reveals serotonin’s effects
2023-05-15
Because serotonin is one of the primary chemicals the brain uses to influence mood and behavior, it is also the most common target of psychiatric drugs. To improve those drugs and to invent better ones, scientists need to know much more about how the molecule affects brain cells and circuits both in health and amid disease. In a new study, researchers at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT working in a simple animal model present a comprehensive accounting of how serotonin affects behavior from the scale of individual molecules all the way to the animal’s whole brain.
“There have been major challenges ...
Assessment of sociodemographics and inflation-related stress
2023-05-15
About The Study: This analysis of U.S. Census Bureau survey data found that rising inflation has become a significant source of stress, especially among women and those who were socioeconomically more vulnerable.
Authors: Cary Wu, Ph.D., of York University in Toronto, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13431)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Population-based estimates for the prevalence of multiple sclerosis in the US
2023-05-15
About The Study: In this national population-based cohort study of multiple sclerosis (MS) prevalence, researchers found that the distribution of MS in the United States has become more racially and ethnically diverse. White individuals continued to have the highest prevalence of MS followed by Black individuals, individuals from other races, and Hispanic individuals.
Authors: Mitchell T. Wallin, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Maryland School of Medicine in Washington, D.C., is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1135)
Editor’s ...
Risk of Parkinson disease among service members at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune
2023-05-15
About The Study: This study of 340,000 service members found that the risk of Parkinson disease was 70% higher in veterans who were stationed at Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, North Carolina, during 1975-1985 when the water supply was contaminated with the solvent trichloroethylene and other volatile organic compounds. The findings suggest that exposure to trichloroethylene in water may increase the risk of Parkinson disease; millions worldwide have been and continue to be exposed to this ubiquitous environmental contaminant.
Authors: Samuel M. Goldman, ...
New study using novel approach for glioblastoma treatment shows promising results, extending survival
2023-05-15
TORONTO - A new international study published in Nature Medicine and presented as a late-breaking abstract at the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (AANS) annual conference, shows great promise for patients with glioblastoma.
Drs. Farshad Nassiri and Gelareh Zadeh, neurosurgeons at the University Health Network (UHN) in Toronto, published the results of a Phase 1/2 clinical trial investigating the safety and effectiveness of a novel therapy which combines the injection of an oncolytic virus – a virus that targets and kills ...
Finding ‘vault’: Unravelling the mysteries of p62-bodies and the cellular recycling pathway
2023-05-15
Our body functioning is delicately balanced between the synthesis and breakdown of various cellular components. When these cellular components grow old or get damaged, they are digested by a process called “autophagy”—literally, “self-eating.” This process not only helps in the elimination of toxic wastes, but also helps to deliver building blocks for the synthesis of new cellular macromolecules. Thus, autophagy serves as the body's cellular cleaning and recycling system.
Researchers have long been studying the ...
Comprehensive analysis of single plant cells provides new insights into natural product biosynthesis
2023-05-15
Plants are impressive in their diversity, but especially in the variety of metabolites they produce. Many plant natural products are highly complex molecules, such as the alkaloids vincristine and vinblastine, which are produced by the Madagascar periwinkle Catharanthus roseus. These two substances are already indispensable in cancer therapy.
Researchers are very interested in finding out which individual biosynthetic steps are required to form the complex molecules. "Currently, these compounds are still obtained in very small quantities from the plant's leaf extract. We can learn from the plant how this compound is produced and use this knowledge ...
Dementia study reveals how toxic proteins spread through brain
2023-05-15
Fresh insights into the spread of damaging proteins that build up in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease could hold the key to stopping the condition progressing, a study says.
Researchers have discovered that synapses, which send essential signals through the brain, are also transporting toxic proteins known as tau around the brain.
Large clumps of the protein tau – called tangles – form in brain cells and are one of the defining features of Alzheimer’s disease. As these tangles spread through the brain during the disease there is a decline in ...
Combined delivery of engineered virus with immunotherapy is safe and improves outcomes in subset of patients with glioblastoma
2023-05-15
HOUSTON ― Intratumoral delivery of an engineered oncolytic virus (DNX-2401) targeting glioblastoma (GBM) cells combined with subsequent immunotherapy was safe and improved survival outcomes in a subset of patients with recurrent GBM, according to results from a multi-institutional Phase I/II clinical trial co-led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and the University of Toronto.
The study, published today in Nature Medicine, met its primary safety endpoint and demonstrated the combination was well tolerated overall with no dose-limiting toxicities. The study did not meet its primary efficacy endpoint of objective response rate, but ...
Mass General Brigham investigators identify new genetic variant protective against Alzheimer's disease
2023-05-15
A single patient can spark new research questions and provide answers about a disease. And when a new case is identified, investigators can make connections between them that can lead to even more powerful and persuasive ideas about cause and treatment. In a publication today in Nature Medicine, an international team led by investigators from two Mass General Brigham hospitals — Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Mass Eye and Ear — reports on a new case of a patient with a genetic predisposition for developing early-onset Alzheimer’s disease who remained cognitively intact until his late 60s. Through clinical assessments ...
Out of this world control on Ice Age cycles
2023-05-15
A research team, composed of climatologists and an astronomer, have used an improved computer model to reproduce the cycle of ice ages (glacial periods) 1.6 to 1.2 million years ago. The results show that the glacial cycle was driven primarily by astronomical forces in quite a different way than it works in the modern age. These results will help us to better understand the past, present, and future of ice sheets and the Earth’s climate.
Earth’s orbit around the Sun and its spin axis orientation change slowly over time, due to the pull of gravity from the Sun, the Moon, and other planets. These astronomical forces affect the environment on Earth due to changes in ...
[1] ... [1918]
[1919]
[1920]
[1921]
[1922]
[1923]
[1924]
[1925]
1926
[1927]
[1928]
[1929]
[1930]
[1931]
[1932]
[1933]
[1934]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.