Clinically relevant deficiency of the “bonding hormone” oxytocin demonstrated
2023-05-14
The hormone oxytocin is important for social interaction and to control emotions. A deficiency of this hormone has previously been assumed in various diseases such as autism, but has never been proven. Now, for the first time, researchers from the University of Basel and the University Hospital of Basel have succeeded in demonstrating a deficiency of oxytocin in patients with a deficiency of vasopressin caused by a disease of the pituitary gland. This finding could be key to developing new therapeutic approaches.
The hormones oxytocin and vasopressin are produced in the same area of the brain ...
Addiction scientists seek to better understand cocaine use disorder: ‘Stimulants are coming back’
2023-05-14
Nearly 2 percent of the U.S. population reported cocaine use in 2020, and the highly addictive substance was involved in nearly one in five overdose deaths, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
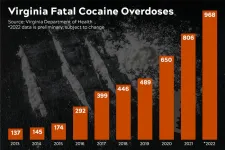
In Virginia, the number of cocaine-related overdoses has been increasing since 2013, with 968 fatal overdoses in 2022, according to preliminary data from the Virginia Department of Health, a 20 percent increase over 2021. Of those, four in five included fentanyl — prescription, illicit or analog — a driving force behind the fatalities.
Researchers at the ...
University of Kentucky physicians push for standard-of-care opioid treatment for incarcerated patients
2023-05-13
In a recently published commentary, UK HealthCare physicians call for standard-of-care treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) among patients who are incarcerated.
The viewpoint article by Anna-Maria South, M.D., Laura Fanucchi, M.D., and Michelle Lofwall, M.D., published in JAMA April 24 highlights the barriers to initiating medication for opioid use disorder (MOUD) among people who are incarcerated.
For patients with opioid use disorder, medications such as buprenorphine and methadone are considered by the medical community as standard of care treatments, as they alleviate withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings and pain, ...
Fear of childbirth exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic
2023-05-13
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated fear of childbirth among pregnant people in the U.S., according to a new Dartmouth study.
The researchers were particularly interested in understanding, from a U.S. context, which factors predict childbirth fear and how the pandemic has affected this fear and birth outcomes. The findings are published in Evolution, Medicine, and Public Health.
"Our results showed really high rates of childbirth fear in our sample," says first author Zaneta Thayer '08, an associate professor of anthropology at Dartmouth. "Since there's no pre-pandemic U.S. data, we cannot compare our data to that context but we know that ...
Restoring control to a particular brain region may help to prevent return to use of opioids
2023-05-13
A team of neuroscientists at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) has identified changes in the activity of brain cells known as pyramidal neurons, which contribute to drug seeking in a preclinical model of opioid use disorder. After access to heroin was stopped, these neurons became more excitable. The activity of these neurons was restored to normal by blocking the enzyme protein kinase A (PKA). Inhibiting this enzyme also reduced opioid-seeking behavior. Jacqueline McGinty, Ph.D., professor of neuroscience, and Saurabh Kokane, Ph.D., a postdoctoral scholar in McGinty’s laboratory, recently published their team’s findings in the Journal of Neuroscience.
The risk ...
Stress hormone during pregnancy may improve early language development in children
2023-05-13
High levels of the stress hormone cortisol during the third trimester of pregnancy may improve speech and language skills in the first 3 years of a child’s life, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings help researchers further understand the role cortisol plays in both fetal and child development.
Language development during early childhood can indicate how well a baby’s nervous system was developed in the womb. Prenatal exposure to cortisol – a steroid hormone that helps the body respond to ...
Steroids linked to long-lasting heart disease risk and worse quality of life
2023-05-13
Anabolic steroids not only can cause serious side effects during use, such as heart failure and depression, but can continue being harmful years after stopping, according to two studies presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. These studies, supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, were carried out by researchers from the Copenhagen University Hospital Rigshospitalet who investigated the impact of anabolic steroids in former users.
Anabolic steroids – synthetic hormones ...
Low levels of vitamin D linked to long COVID
2023-05-13
Long COVID risk has been found to increase with low levels of vitamin D, according to research presented at the 25th European Congress of Endocrinology in Istanbul. The findings suggest that individuals should have their vitamin D levels checked after COVID-19.
Also known as post COVID-19 syndrome, long COVID is a new condition in which the effects of COVID-19 last for more than 12 weeks after contracting the initial infection. Studies have shown that it affects 50-70% of patients previously hospitalised for COVID-19, yet very little is known about the condition. One risk factor for worse outcomes for hospitalised COVID-19 patients, such as intubation and mechanical ventilation ...
Accelerated delivery of transcranial magnetic stimulation is safe and effective
2023-05-12
May 12, 2023 — Accelerated schedules for repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) can be offered to patients experiencing treatment-resistant major depressive disorder (MDD), a group of clinician–researchers and neuroscientists have concluded. The group cautions that such treatment should be proposed only after detailed discussion with patients about acceleration being an alternate form of rTMS scheduling, with documentation of informed consent.
The recommendations are published in a ...
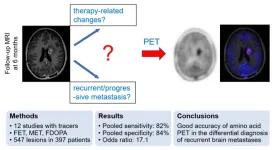
Amino acid PET successfully differentiates recurrent brain metastases, reducing invasive procedures and overtreatment
2023-05-12
Reston, VA—A newly published meta-analysis indicates that amino acid PET can accurately differentiate recurrent or progressive brain metastases from treatment-related changes. A specificity of 84 percent suggests that it may reduce the number of invasive procedures and overtreatment in patients who in fact experience treatment-related changes. This research was published in the May issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
Brain metastases occur in 20 to 40 percent of all cancer patients and are most likely ...
Is it too late to change your mind? Study reveals ‘developmental window’ for thinking styles
2023-05-12
Key takeaways
Researchers studied the way different generations in Romania determined the truth of information following the country’s transition from authoritarianism to democracy.
Those who were born and raised after the transition were more likely than older cohorts to compare and evaluate different perspectives before deciding who is right.
The factors associated with the youngest generation’s style of thinking were greater exposure to formal education and social media.
While people change and learn throughout life, experts recognize ...
TVT 2023 late-breaking science announced
2023-05-12
NEW YORK – May 12, 2023 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) announced that TVT: The Structural Heart Summit will feature 15 Late-Breaking Clinical Science studies. An annual meeting featuring cutting-edge research and techniques for structural heart interventions, TVT will take place June 7-10, 2023, at the Phoenix Convention Center – West in Phoenix, Arizona.
TVT has become the epicenter of innovation and collaboration in the structural heart arena over its 16-year history. The meeting brings together world-renowned experts and master operators to help translate novel discoveries into practical therapies for patients with valvular heart disease.
TVT’s ...
UArizona Engineering alum returns to lead School of Mining and Mineral Resources
2023-05-12
Misael Cabrera has been selected through a nationwide search as the inaugural director of the School of Mining and Mineral Resources. The school was created in 2021 and is jointly housed in the College of Engineering and the College of Science, with strong partnerships to additional colleges and centers.
“Our role is to deliver talent and technology through research, but also to change the top-of-mind association with mining. We can create real solutions that both industry and our planet need,” said Cabrera.
Cabrera, who began the position in April, most ...
Researchers track antimicrobial resistance in E. coli isolated from swine
2023-05-12
The spread of drug-resistant microbes has become a global health concern that threatens our ability to treat infections. The widespread use of antimicrobials in livestock, such as swine farms, exacerbates this problem. Therefore, we need surveillance systems to monitor these microbes to support the public health authorities. To this end, researchers have tracked the antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from swine.
Antimicrobials are essential for preventing and treating infections in humans and animals. According to the US Food and Drug Administration, 70% of all antibiotic ...
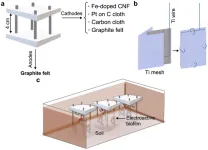
Carbon-based cathodes impact biofilm composition and performance in soil microbial fuel cells
2023-05-12
In the context of increasing energy demands and environmental concerns, renewable energy solutions are crucial for achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Microbial electrochemical technologies, such as SMFCs, are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, making them an attractive option for green energy systems. SMFCs utilize endogenous microorganisms present in soil to convert organic matter into electricity, offering a sustainable energy source and a self-powered in situ bioremediation strategy for contaminated soils.
Cathode materials play a significant role in the performance of microbial fuel cells. In this study, researchers compared the performance ...
Healthy teeth thanks to the "washing machine effect”
2023-05-12
Ruminants like cows have developed an unusual way of digesting their food: they ingest plants, give them a rough chewing and then swallow the half-chewed mash before regurgitating it repeatedly and continuing to chew. This has clear advantages, as a research team including the University of Göttingen has shown: the regurgitated mushy food contains much less hard grit, sand and dust than the food that they first ingested. This protects the teeth from being ground down during the chewing process. This ...
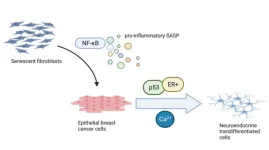
The senescence-associated secretory phenotype induces neuroendocrine transdifferentiation
2023-05-12
“We recently unveiled a new interesting role for SASP: its ability to induce neuroendocrine transdifferentiation (NED) in breast cancer epithelial cells [3].”
BUFFALO, NY- May 12, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 8, entitled, “The senescence-associated secretory phenotype induces neuroendocrine transdifferentiation.”
In this editorial, researchers Anda Huna, Nadine Martin and David Bernard from the Université de Lyon discuss the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). SASP, ...
Steckel selected as a Southern Weed Science Society Fellow
2023-05-12
Larry Steckel, row crop weed specialist and professor in the Department of Plant Sciences at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, has been named a Fellow of the Southern Weed Science Society (SWSS).
The award was given to honor Steckel’s years of research and contributions to weed prevention in row crop agriculture. Steckel was among only a small group of esteemed researchers to receive the honor, presented to him during the annual meeting of the SWSS.
Steckel says he is proud to be named a Fellow, and that he knows the research and extension work conducted by weed specialists across the ...
Manufacturing and metrology considerations are key when designing with freeform optics
2023-05-12
Manufacturing and metrology considerations are key when designing with freeform optics
Close communication between optics designers and manufacturers can help prevent problems
Québec City, Canada -- Although optical components such as lenses are traditionally spherical in shape, freeform optical components, which have little to no symmetry around the optical axis, are becoming more common. Freeform optical components are attractive because they can be designed to behave in ways traditional optics cannot, offering optical design flexibility ...
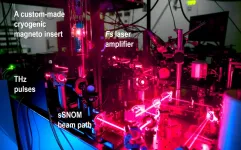
Ultralow temperature terahertz microscope capabilities enable better quantum technology
2023-05-12
A team of scientists from the Department of Energy’s Ames National Laboratory have developed a way to collect terahertz imaging data on materials under extreme magnetic and cryogenic conditions. They accomplished their work with a new scanning probe microscope. This microscope was recently developed at Ames Lab. The team used the ultralow temperature terahertz microscope to take measurements on superconductors and topological semimetals. These materials were were exposed to high magnetic fields and temperatures below liquid helium (below 4.2 ...
New study puts a definitive age on Saturn’s rings—they’re really young
2023-05-12
A new study led by physicist Sascha Kempf at the University of Colorado Boulder has delivered the strongest evidence yet that Saturn’s rings are remarkably young—potentially answering a question that has boggled scientists for well over a century.
The research, to be published May 12 in the journal Science Advances, pegs the age of Saturn’s rings at no more than 400 million years old. That makes the rings much younger than Saturn itself, which is about 4.5 billion years old.
“In ...
Researchers identify a brain marker indicating future suicide risk
2023-05-12
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE, May 12, 2023
Contact: Gina DiGravio, 617-358-7838, ginad@bu.edu
Researchers Identify a Brain Marker Indicating Future Suicide Risk
Changing the connectivity in this brain circuit with stimulation or pharmacotherapies could represent new treatments to reduce suicide risk.
(Boston)—Identifying people at high risk for suicide is critical for applying lifesaving interventions and treatments. However, it is very difficult to identify who is at greatest risk and only modest improvements has been made in identifying high risk people over the last 50 years. One novel way to identify people at high risk of suicide is by investigating and identifying brain markers.
VA ...
Researchers use 3D models to investigate bacteria movement
2023-05-12
The spiral-shaped bacteria Helicobacter pylori are common and troublesome.
More than 13 percent of Americans have an H. pylori infection, although rates vary with age, race and socioeconomic status. The microorganism uses its corkscrew-like tail to power forward through viscous fluids such as stomach mucus. When it arrives at the epithelium of the stomach wall, it can cause everything from ulcers to cancer.
In a new study published by Physical Review Letters, FAMU-FSU College of Engineering researchers created a 3D model of this bacteria to better understand its movement, hoping to crack the code governing the organism’s motility ...
Researchers at Purdue discover superconductive images are actually 3D and disorder-driven fractals
2023-05-12
Meeting the world’s energy demands is reaching a critical point. Powering the technological age has caused issues globally. It is increasingly important to create superconductors that can operate at ambient pressure and temperature. This would go a long way toward solving the energy crisis.
Advancements with superconductivity hinge on advances in quantum materials. When electrons inside of quantum materials undergo a phase transition, the electrons can form intricate patterns, such as fractals. A fractal is a never-ending pattern. When zooming in on a fractal, the image looks the same. Commonly seen fractals can be a tree or frost on a windowpane ...
Save the phages to protect Big Blue
2023-05-12
The plastic era has begun, and for sure, it will last for decades or even longer. Polymer-based materials are almost everywhere, reaching even the deepest regions of the oceans, and their global production is larger than recycling, leading to the generation of tremendous amounts of water pollution with microplastics. These tiny polymer particles not only release chemicals but also reduce the number of bacteriophages. Recently, researchers from the Institute of Physical Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences, led by Prof. Jan Paczesny, explored ...
[1] ... [1920]
[1921]
[1922]
[1923]
[1924]
[1925]
[1926]
[1927]
1928
[1929]
[1930]
[1931]
[1932]
[1933]
[1934]
[1935]
[1936]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.