DGIST and Seoul National University signed MOU to develop open innovation business model
2023-05-12
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology (DGIST; President Kuk Young) and Seoul National University (President Ryu Hong-lim) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on Wednesday, April 26 to develop an open innovation business model. Under this MOU, Senior Researcher Yun Jin-hyo at the Division of Electronics & Information Systems, DGIST provides consulting services required to develop an open business model to students in the Engineering Project Management Program at the Graduate School of Engineering Practice, Seoul National University. The first seminar was held on the day of the MOU.
□ Senior Researcher ...
Portugal participates in the development of a first-class instrument for the largest telescope in the world
2023-05-12
A research team from the University of Lisbon and University of Oporto (Portugal) participate in the development of METIS (Mid-infrared ELT Imager and Spectrograph). This powerful instrument will equip the largest telescope in the world - the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) - under construction by the European Southern Observatory (ESO) in Armazones, Chile.
At this critical acceptance stage of the complete and final METIS design, ESO is presenting an illustrative film demonstrating the exceptional capabilities of the instrument. The presentation will take place on May 12, at 4:00pm (CEST).
METIS will detect ...
Prevalence of UTI, bacteremia, and meningitis among febrile infants with SARS-CoV-2
2023-05-12
About The Study: Among 14,400 febrile infants ages 8 to 60 days, the prevalence of urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteremia, and bacterial meningitis was lower for infants who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, particularly infants ages 29 to 60 days and those with normal inflammatory markers. These findings may help inform management of certain febrile infants who test positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Authors: Paul L. Aronson, M.D., M.H.S., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13354)
Editor’s ...
Gender diversity and brain morphology among adolescents
2023-05-12
About The Study: The findings of this study of 2,165 adolescents from the Netherlands general population suggest that global brain volumetric measures did not differ between adolescents who reported gender diversity and those who did not. However, these findings further suggest that gender diversity in the general population correlates with specific brain morphologic features in the inferior temporal gyrus among youths who are assigned male at birth. Replication of these findings is necessary to elucidate ...
Association of hospital adoption of probiotics with outcomes among neonates with very low birth weight
2023-05-12
About The Study: In this study of 307,000 neonates with very low birth weight, adoption of routine use of probiotics in neonatal intensive care units increased slowly from 2012 to 2019 and was associated with lower necrotizing enterocolitis risk but not with sepsis or mortality rates.
Authors: Leila Agha, Ph.D., of Harvard Medical School in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0960)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
A look inside stem cells helps create personalized regenerative medicine
2023-05-12
Organelles – the bits and pieces of RNA and protein within a cell – play important roles in human health and disease, such as maintaining homeostasis, regulating growth and aging, and generating energy. Organelle diversity in cells not only exists between cell types but also individual cells. Studying these differences helps researchers better understand cell function, leading to improved therapeutics to treat various diseases.
In two papers out of the lab of Ahmet F. Coskun, a Bernie Marcus Early Career professor in the Coulter Department of Biomedical Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology and Emory University, researchers examined a specific ...
The beginning is the end
2023-05-12
All cells in an organism contain identical DNA sequence. What determines the identity and function of individual cells and tissues, is the set of genes that will be active in a given place, at a given time. These active genes are transcribed from the DNA template into distinct messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and will encode the proteins the cell needs to function.
At specific places called promoters, a complex molecular machinery starts transcribing DNA sequences into mRNA. Interestingly, most genes contain multiple possible sites where transcription ...
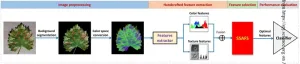
New artificial intelligence algorithm for more accurate plant disease detection
2023-05-12
Every year, plant diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, and fungi contribute to major economic losses. The prompt detection of these diseases is necessary to curb their spread and mitigate agricultural damage, but represents a major challenge, especially in areas of high-scale production. Smart agriculture systems use camera surveillance equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) models to detect features of plant diseases, which often manifest as changes in leaf morphology and appearance.
However, conventional methods ...
Visualizing PET's degradation by bacterial enzymes
2023-05-12
The rigidity, transparency and hardness of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) make it one of the most valuable plastics for the manufacture of plastic bottles, packaging and other single-use products. However, these characteristics make it highly persistent in the environment, to the point that a plastic PET bottle may take several hundred years to degrade in the ocean.
At the molecular level, PET, and all plastics, have a polymeric structure made up of tens of thousands of repetitions of small subunits called monomers. In the last decades, the degradation ...
Study highlights best practices in buffelgrass control
2023-05-12
WESTMINSTER, Colorado – 9 May, 2023 – Buffelgrass is a highly invasive perennial found in arid regions around the globe. It is known to reduce the biodiversity of native ecosystems and to increase the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
A team of researchers recently took a close look at efforts to control buffelgrass in Arizona’s Saguaro National Park, located in the Sonoran Desert. An article featured in volume 16, issue 1 of the journal Invasive Plant Science and Management describes what that investigation can tell us about effective control strategies. ...
Scientists discover a deadly brain cancer’s hidden weakness
2023-05-12
The difficult-to-treat brain cancer glioblastoma steals a person’s mental faculties as it spreads, yet the tumor’s insidious ability to infiltrate neighboring networks in the brain could also prove its undoing.
Scientists at UC San Francisco have discovered that neural activity in these deadly tumors can restructure connections in surrounding brain tissue, causing the cognitive decline associated with the disease, and that the drug gabapentin, commonly used to prevent seizures, could block this growth-causing ...
Researchers discover a way to improve nonviral gene editing as well as a new type of DNA repair
2023-05-12
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Gene editing is a powerful method for both research and therapy. Since the advent of the Nobel Prize-winning CRISPR/Cas9 technology, a quick and accurate tool for genome editing discovered in 2012, scientists have been working to explore its capabilities and boost its performance.
Researchers in UC Santa Barbara biologist Chris Richardson’s lab have added to that growing toolbox, with a method that increases the efficiency of CRISPR/Cas9 editing without the use of viral material to deliver the genetic template used to edit the target genetic sequence. According to their new paper ...
Vast majority of tweets about obesity are negative, study finds
2023-05-12
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress on Obesity (ECO, Dublin, 17-20 May). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
New research to be presented at next week’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Dublin, Ireland (17-20 May), has found that tweets about obesity are predominantly negative.
The analysis, by researchers in Switzerland and the UK, also found that Twitter activity spiked around the time of significant political events.
These included comments about Donald Trump’s weight when he was US president and ...
USC research identifies biomarker that may predict treatment response to chemoimmunotherapy
2023-05-12
Cutting-edge cancer treatments like immunotherapy are offering new hope for patients, often in combination with more common approaches such as chemotherapy. But determining the best treatment combination isn't always straightforward. Many patients spend valuable time on expensive therapies with serious side effects that aren’t effective against their cancer.
Now, a new discovery is poised to help. Researchers from USC Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center have identified a biomarker that indicates which patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) will respond well to chemoimmunotherapy. The biomarker, ...
Cervical cancer screening doubles when under-screened women are mailed testing kits
2023-05-12
CHAPEL HILL, NC -- Researchers at the UNC Gillings School of Global Public Health and UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center found mailing human papillomavirus (HPV) self-collection tests and offering assistance to book in-clinic screening appointments to under-screened, low-income women improved cervical cancer screening nearly two-fold compared to scheduling assistance alone. Scheduling assistance primarily consisted of helping to book an appointment for in-person screening at a clinic, regardless of whether an at-home test was offered or returned, or whether the HPV test was negative or positive.
The findings from the randomized ...
THE LANCET PUB. HEALTH: Mailing at-home HPV sampling kits nearly doubles cervical screening uptake among hard-to-reach populations, US clinical trial suggests
2023-05-12
Peer-reviewed / Randomised Controlled Trial / People
Clinical trial with 665 under-screened women in North Carolina (USA) investigated use of high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV) self-collection kits to increase cervical cancer screening uptake.
Screening uptake among participants sent self-collection kits and given support to attend an in-person appointment was almost double (72%) the cervical cancer screening uptake in those only given appointment support alone (37%).
More than three quarters (78%) of these underserved participants ...
International Nurses Day: World’s oldest children’s nursing organization recognizes outstanding contributions to the care of children and young people
2023-05-12
At a recent event to celebrate the Association’s 85th Anniversary, the Association of British Paediatric Nurses awarded Honorary Fellowships to eight children’s nurses in recognition of their outstanding contribution to the nursing care of children and young people.
The 2023 Honorary Fellows
Ann Bisbrown Lee for services to children’s nursing and for many years’ service to the Association of British Paediatric Nurses, especially in leading marketing and conference activities.
Professor Steven Campbell for services to children’s nurse education and to the Association ...
Stress-management interventions may help individual healthcare workers for at least a year
2023-05-12
Interventions aimed at reducing work-related stress for individual healthcare workers may lead to improvements in how people cope with stress up to a year later. Findings from a Cochrane review of the latest available evidence build on the conclusions of a previous review in 2015 that found low-quality evidence that interventions, such as cognitive behavioural training (CBT), mental and physical relaxation, were better than none.
The researchers included 117 studies of the effects of different interventions on stress alleviation in the current review, of which 89 studies were new. These 89 studies were published between 2013 and ...
Research pinpoints the time of year and hour when people have the strongest suicidal thoughts
2023-05-12
New research has identified the month when people have the strongest suicidal thoughts, and that these thoughts occur a few months before the peak of suicide behaviours in spring/early summer. It also showed the daily peak in suicidal thought is between 4-5 am.
Most people assume suicide rates will be highest in winter, yet spring/early summer is when suicidal behaviours peak and this finding has baffled researchers since first identified.
Research from the University of Nottingham’s School of Psychology, led in collaboration with the University of Amsterdam and Harvard University, ...
AI study finds that patients with Parkinson’s disease speak differently to healthy patients
2023-05-12
Using artificial intelligence (AI) to process natural language, a research group evaluated the characteristics of speech among patients with Parkinson’s disease (PD). AI analysis of their data determined that these patients spoke using more verbs and fewer nouns and fillers. The study was led by Professor Masahisa Katsuno and Dr. Katsunori Yokoi, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, in collaboration with Aichi Prefectural University and Toyohashi University of Technology. They published their results ...
Astronomers reveal the largest cosmic explosion ever seen
2023-05-12
A team of astronomers led by the University of Southampton have uncovered the largest cosmic explosion ever witnessed.
The explosion is more than ten times brighter than any known supernova (exploding star) and three times brighter than the brightest tidal disruption event, where a star falls into a supermassive black hole.
The explosion, known as AT2021lwx, has currently lasted over three years, compared to most supernovae which are only visibly bright for a few months. It took place nearly 8 billion light years away, when the universe was around 6 billion years old, and is still being detected by a network of telescopes.
The researchers believe that the explosion is ...
Scientists find fire records inside sand dunes
2023-05-12
A previously unrecognised sedimentary archive in sand dunes could unlock a repository of fire records, a discovery that could expand fire histories across the globe.
The research, conducted by Dr Nicholas Patton during his PhD at The University of Queensland, has solved a persistent problem facing historians investigating changing fire patterns.
“Knowing how the frequency and intensity of wildfires has changed over time offers scientists a glimpse into Earth’s past landscapes, as well as an understanding of future climate change impacts,” Dr Patton said.
“To reconstruct fire records, researchers usually rely heavily ...
Brain-belly connection: gut health may influence likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s
2023-05-11
Could changing your diet play a role in slowing or even preventing the development of dementia? We’re one step closer to finding out, thanks to a new UNLV study that bolsters the long-suspected link between gut health and Alzheimer’s disease.
The analysis — led by a team of researchers with the Nevada Institute of Personalized Medicine (NIPM) at UNLV and published this spring in the Nature journal Scientific Reports — examined data from dozens of past studies into the belly-brain connection. The results? There’s a strong link between particular kinds of gut bacteria and Alzheimer’s disease.
Between 500 and 1,000 species of bacteria ...
New research from UMass Amherst links changes in land use to water quality and quantity
2023-05-11
AMHERST, Mass. – Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst recently published a study in the journal PLOS Water that focuses on the Sudbury-Assabet and Concord watershed in eastern Massachusetts, and which links hydrological changes, including floods, drought and runoff, to changing patterns of land use.
“We all live in a watershed” says Timothy Randhir, professor of environmental conservation at UMass Amherst and the paper’s senior author. “We’re constantly modifying our landscape, turning what were once forests into ...
UC Irvine study shows traffic-related air pollution in Irvine weakens brain function
2023-05-11
Irvine, Calif., May 11, 2023 – Researchers from the University of California, Irvine have found that exposure to traffic-related air pollution in Irvine led to memory loss and cognitive decline and triggered neurological pathways associated with the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
“The link between air pollution and Alzheimer’s disease is concerning, as the prevalence of toxicants in ambient air is not just on the rise globally, but also hitting close to home here in Irvine,” said corresponding ...
[1] ... [1916]
[1917]
[1918]
[1919]
[1920]
[1921]
[1922]
[1923]
1924
[1925]
[1926]
[1927]
[1928]
[1929]
[1930]
[1931]
[1932]
... [8818]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.