Dirty air linked with premature death in patients with heart failure
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: Heart failure patients are at increased risk of dying from their condition on polluted days and up to two days afterwards, according to research presented today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The findings indicate that reducing air pollution has the potential to prevent worsening heart failure,” said study author Dr. Lukasz Kuzma of the Medical University of Bialystok, Poland. “Protecting ...
Eu3+-Bi3+ codoping double perovskites for single-component white-light-emitting diodes
2023-05-22
They published their work on May. 15 in Energy Material Advances.
"With lead-halide perovskites reaching a mature research stage approaching product marketing, concerns remain about the materials' stability and the toxicity of lead-based salts." said paper author Hongwei Song, professor at College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University. Double perovskites with Cs2AgInCl6 composition, often doped with various elements, have been in the spotlight owing to their intriguing optical properties, namely, ...
ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium celebrates 10th annual meeting at Automate 2023
2023-05-22
San Antonio, Texas – May 22 ,2023 – The ROS-Industrial Americas Consortium, a project dedicated to advancing open-source robotics for manufacturing and industry, will celebrate its 10th anniversary on May 25 at its annual meeting in Detroit.
The event will correspond with the Automate 2023 show, the largest automation showcase in North America, creating an exciting atmosphere for ROS-Industrial members to reflect on the organization’s history while also setting the stage for innovation in the years to come.
The ROS-Industrial open-source project began as a collaboration among Yaskawa Motoman Robotics, Southwest Research Institute ...
ETRI lays the groundwork for convenient and safe drone flight
2023-05-22
The lack of a single communication standard among drone makers has made it difficult for information to be shared between drones, but a Korean research team has found a solution.
The Korea Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) announced that four contributions related to the ‘Unmanned Aircraft Area Network’ were established as international standards at the International Organization for Standardization (ISO*) meeting in Vienna, Austria.
* ISO/IEC JTC1/SC6(communication and information exchange between systems)
The technology ...
The diagnosis of heart failure is more often missed than made especially for women
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: The diagnosis of heart failure is usually missed, denying patients treatments that could improve wellbeing and reduce mortality. That’s the finding from a late breaking science presentation today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“For patients with heart failure, lifestyle advice, medicines and devices can improve symptoms, reduce morbidity and prolong life but this requires someone ...
Are you prone to feeling guilty? You may be less likely to take a bribe
2023-05-22
Bribery is among the most recognizable forms of corruption, and new research is shedding light on personality traits that could deter this behavior. Guilt-prone people are less likely to accept bribes, particularly when the act would cause obvious harm to other people.
The research, published in Social Psychological and Personality Science, contributes to a growing body of literature on individual differences in corrupt behaviors.
“Our results have important implications for current world events, particularly in the realm of politics and governance where corruption and bribery are major concerns,” says author Prof. Xiaolin Zhou, of East China Normal University. “More ...
Compound from magnolia tree bark impedes SARS-CoV-2 replication in certain cells
2023-05-22
Washington, DC – A compound called honokiol, which is found in the bark of multiple species of magnolia tree, inhibits replication of SARS-CoV-2 virus in several types of cells, according to a team of researchers in the Netherlands. The research is published in Microbiology Spectrum, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The researchers found that Honokiol inhibits replication of SARS-CoV-2 in several cell types, causing production of infectious SARS-CoV-2 particles in treated cells to fall to around 1,000th of the previous level.
The compound also inhibited replication of other highly pathogenic human coronaviruses, including MERS- ...
Leadless pacemakers soon available for all patients
2023-05-22
Every year more than one million people receive a pacemaker. Until now, leadless versions were only available for 20% of these patients. However, thanks to an international consortium led by Amsterdam UMC, an improved version will soon be available for all patients. The results of this clinical trial are, today, published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Research from Amsterdam UMC has succeeded in further revolutionising the wireless pacemaker. The improved version can now be placed in both the atrium and the ventricle of ...
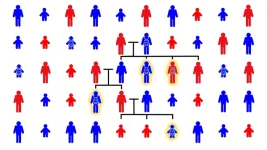
Siblings with autism share more of dad’s genome, not mom’s
2023-05-22
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) researchers have flipped the script on autism spectrum disorder (ASD) genetics.
Scientists long thought that siblings born with ASD share more of their mother’s genome than their father’s. But CSHL Associate Professor Ivan Iossifov and Professor Michael Wigler have now shown that, in many cases, it’s dad who might be playing a bigger genetic role.
Autism spectrum disorders cover a range of neurological and developmental conditions. They can affect how a person communicates, socializes, learns, and behaves. ASD may also manifest as repetitive behaviors ...
Women more likely to die after heart attack than men
2023-05-22
Prague, Czechia – 22 May 2023: Women are more than twice as likely to die after a heart attack than men, according to research presented today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Women of all ages who experience a myocardial infarction are at particularly high risk of a poor prognosis,” said study author Dr. Mariana Martinho of Hospital Garcia de Orta, Almada, Portugal. “These women need regular monitoring after their heart event, with strict control of blood pressure, ...
ASCO: Targeted therapy for early breast cancer, progress treating recurrent glioma, PSMA PET scan advances and more
2023-05-22
Physicians and scientists from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center will discuss the latest research and clinical trial results on combination therapies for breast cancer, a potential new treatment for patients with recurrent glioma, and advances in PSMA PET guided radiotherapy for patients with prostate cancer, among other topics, at the American Society of Clinical Oncology’s annual meeting.
At this year’s scientific forum, Dr. Dennis Slamon, chair of hematology-oncology and director of clinical ...
Cancer researchers join forces against deadliest brain tumors in children
2023-05-22
Virginia Tech researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC have joined a Children’s National Hospital effort to treat deadly brain tumors with ultrahigh frequency sound waves.
The scientists are studying how to use an emerging technology called focused ultrasound to fight diffuse midline glioma (DMG), one of the most lethal childhood brain cancers with a nearly 100 percent rate of mortality within five years of diagnosis.
A multi-institutional team led by Javad Nazarian, a principal investigator with Children’s National Hospital, will study how to use focused ultrasound to create ...
Eruption of Tonga underwater volcano found to disrupt satellite signals halfway around the world
2023-05-22
An international team has used satellite- and ground-based ionospheric observations to demonstrate that an air pressure wave triggered by volcanic eruptions could produce an equatorial plasma bubble (EPB) in the ionosphere, severely disrupting satellite-based communications. Their findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The ionosphere is the region of the Earth's upper atmosphere where molecules and atoms are ionized by solar radiation, creating positively charged ions. The area with the highest concentration of ionized particles is called the F-region, an area 150 to 800 km above the Earth's surface. The F-region plays ...
Adverse pregnancy outcomes increase stroke risk
2023-05-22
Investigators from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai found that women who experience an adverse pregnancy outcome—such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia or preterm birth—have a higher risk of developing stroke in their lifetime, and at a younger age.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Stroke, also found that compared to women with one uncomplicated pregnancy, a woman who had two or more pregnancies impacted by an adverse pregnancy outcome had a twofold higher increase of stroke.
“We understand from past studies in the U.S. that women have a greater risk of experiencing a stroke and a disproportionate ...
Earlier snowpack melt in the West could bring summer water scarcity
2023-05-22
Snow is melting earlier, and more rain is falling instead of snow in the mountain ranges of the Western U.S. and Canada, leading to a leaner snowpack that could impact agriculture, wildfire risk and municipal water supplies come summer, according to a new study from the University of Colorado Boulder.
Published in Nature Communications Earth & Environment, the study documents more than 60 years of change in snowpack water storage across Western North America. It found that from 1950 to 2013, snowpack water storage ...
What’s the relationship between cancer survivors’ tobacco use, symptom burden, and motivation to quit smoking?
2023-05-22
Study’s findings may help inform tobacco cessation support efforts.
In a recent study, current smoking and vaping were associated with a higher burden of symptoms among adult cancer survivors, but these symptoms were not related to survivors’ desire to quit smoking. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Continued smoking after a cancer diagnosis lowers survival rates, increases the likelihood of additional cancers, and decreases the effectiveness ...
Tokyo Tech, Tohoku University, Fujitsu, and RIKEN start collaboration to develop distributed training of Large Language Models
2023-05-22
Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), Tohoku University, Fujitsu Limited, and RIKEN today announced that they will embark on the research and development of a distributed training of Large Language Models (LLM) [1]on supercomputer Fugaku in May 2023, within the scope of the initiatives for use of Fugaku defined by Japanese policy.
LLMs are AI models for deep learning that serve as the core of generative AI including ChatGPT[2]. The four organizations aim to improve the environment for creating LLMs that can be widely used by academia and companies, contribute to improving the research capabilities of AI in Japan, and increase the value of utilizing Fugaku in both ...
Nitrate: healthy heart or cancer risk? Meet nutrition’s Jekyll and Hyde
2023-05-22
Despite our understanding of nutrition expanding remarkably in recent times, few aspects of our diet continue to confuse and divide the experts like nitrate.
For a long time nitrate has been viewed warily, with previous research showing it could potentially be linked to causing cancer.
However, subsequent research has revealed dietary nitrate also has various cardiovascular health benefits, which could help reduce the risk of related conditions such as heart disease, dementia and diabetes.
So, how can one dietary compound have such contrasting potential risks and benefits?
Edith Cowan University’s (ECU) Nutrition and Health ...
Can charismatic robots help teams be more creative?
2023-05-22
Increasingly, social robots are being used for support in educational contexts. But does the sound of a social robot affect how well they perform, especially when dealing with teams of humans? Teamwork is a key factor in human creativity, boosting collaboration and new ideas. Danish scientists set out to understand whether robots using a voice designed to sound charismatic would be more successful as team creativity facilitators.
“We had a robot instruct teams of students in a creativity task. The robot ...
Stop eradication of small mammals to protect vital ecosystems, say scientists
2023-05-22
A new article published in the Journal of Animal Ecology suggests that current measures to protect grasslands in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau are damaging the ecosystem and should be stopped.
The existing policy, introduced in 2000, calls for the eradication of small burrowing mammals. These include the mountain-dwelling herbivores, the plateau pika, and another small rodent, the zokor. Both are keystone species and are known as ecosystem engineers due to their modification of and impact on the environment.
The ...
Study linking mucus plugs and COPD mortality could help save lives
2023-05-21
A retrospective analysis of patient data from the COPDGene study suggests that targeting mucus plugs could help prevent deaths from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease—the fourth leading cause of death in the United States
Many patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experience airway-clogging mucus plugs, an accumulation of mucus in the lungs that can affect quality of life and lung functioning. A new study led by researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding ...
Sacubitril/valsartan shows benefit in heart failure with ejection fraction above 40%
2023-05-21
Prague, Czechia – 21 May 2023: Sacubitril/valsartan leads to greater reduction in plasma NT-proBNP levels compared to valsartan alone after stabilisation for worsening heart failure in patients with an ejection fraction (EF) above 40%, according to late breaking science presented today at Heart Failure 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC),1 and published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Principal investigator Dr. Robert Mentz of Duke University Medical Center, Durham, US said: “These data add to the evidence supporting a potential treatment benefit of sacubitril/valsartan ...
New device gently moves esophagus, making heart ablations safer, study found
2023-05-21
A new device invented with the help of an electrophysiologist at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center makes a heart procedure safer for patients suffering from atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common irregular heart rhythm.
AFib affects millions of people worldwide and greatly increases their risk of stroke and heart failure. To treat AFib, doctors use cardiac ablation to help restore the heart’s rhythm. Heat or cold energy delivered through a catheter destroys the heart tissue causing rapid and irregular heartbeats. ...
Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions names George D. Dangas, MD, MSCAI, President for 2023-24
2023-05-21
PHOENIX (May 20, 2023) – George D. Dangas, MD, PhD, MSCAI, Professor of Medicine (Cardiology and Surgery), and Director of Cardiovascular Innovation at the Zena and Michael A. Weiner Cardiovascular Institute at the Icahn School of Medicine of Mount Sinai in New York City, and Chief of Cardiology at Mount Sinai Queens assumed the office of president of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) today during the closing ceremonies at the SCAI 2023 Scientific Sessions in Phoenix, AZ.
Dr. Dangas is an authoritative voice in the performance of nonsurgical cardiovascular and valve interventions using both established ...
SCAI announces 2023-24 SCAI-WIN CHIP Fellowship Recipient
2023-05-21
PHOENIX (May 20, 2023) – Njambi Mathenge, MD, MPH, an interventional cardiology fellow at the Massachusetts General Hospital has been selected as the recipient of the SCAI-Women in Innovations (SCAI-WIN) CHIP Fellowship, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions announced today.
The $115,000 fellowship opportunity was made possible by support from Abiomed (founding supporter), Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Shockwave Medical, Inc., and is offered to interventional cardiology (IC) fellows or practicing interventional cardiologists interested in ...
[1] ... [1917]
[1918]
[1919]
[1920]
[1921]
[1922]
[1923]
[1924]
1925
[1926]
[1927]
[1928]
[1929]
[1930]
[1931]
[1932]
[1933]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.