Administering opioids to pregnant mice alters behavior and gene expression in offspring
2021-07-26
Mice exposed to the opioid oxycodone before birth experience permanent changes in behavior and gene expression. The new research published in eNeuro highlights a need to develop safer types of painkillers for pregnant women.
Opioids like oxycodone are prescribed to pregnant women to treat pain, but the drugs may affect the fetus, too. Opioids can pass through the placenta, binding to receptors in the fetal brain, which can lead to opioid withdrawal in newborn babies. The long-term consequences of prenatal opioid exposure haven't been fully studied, however.
To explore this, Martin et al. administered oxycodone to female mice every day for the two weeks prior ...
Brain's 'memory center' needed to recognize image sequences but not single sights
2021-07-26
A new MIT study of how a mammalian brain remembers what it sees shows that while individual images are stored in the visual cortex, the ability to recognize a sequence of sights critically depends on guidance from the hippocampus, a deeper structure strongly associated with memory but shrouded in mystery about exactly how.
By suggesting that the hippocampus isn't needed for basic storage of images so much as identifying the chronological relationship they may have, the new research published in Current Biology can bring neuroscientists closer to understanding how the brain coordinates long-term visual memory across key regions.
"This offers the ...
Safety of second dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines after first-dose allergic reactions
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the safety of the second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna COVID-19 vaccines in patients who experienced an allergic reaction to the first dose.
Authors: Kimberly G. Blumenthal, M.D., M.Sc., of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3779)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. ...
Changes in disparities in access to care, health after Medicare eligibility
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: The association between Medicare eligibility at age 65 and changes in racial and ethnic disparities in access to care and self-reported health was evaluated in this study.
Authors: Jacob Wallace, Ph.D., of the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3922)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and ...
Use of high-risk medications among lonely older adults
2021-07-26
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to investigate the relationship between loneliness and high-risk medication use in adults older than age 65.
Authors: Ashwin A. Kotwal, M.D., M.S., of the University of California, San Francisco School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.3775)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding and support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
65+ and lonely? Don't talk to your doctor about another prescription
2021-07-26
Lonely, older adults are nearly twice as likely to use opioids to ease pain and two-and-a-half times more likely to use sedatives and anti-anxiety medications, putting themselves at risk for drug dependency, impaired attention, falls and other accidents, and further cognitive impairment, according to a study by researchers at UC San Francisco.
The study found that just over half of 6,000 respondents in a nationally representative survey of seniors living independently were not lonely, while 40 percent were moderately lonely, and 7 percent were highly lonely.
The proportion of seniors ...
Exosome formulation developed to deliver antibodies for choroidal neovascularization therapy
2021-07-26
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital and the University of Queensland have developed a new formulation based on regulatory T-cell exosomes (rEXS) to deliver vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibodies for choroidal neovascularization therapy.
The study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering on July 26.
Ocular neovascularization is often associated with age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy and other ocular diseases, which can cause severe vision loss.
The present treatment for ocular neovascular disease in clinic is intravitreal injection of VEGF antibodies (aV) to block the activity of VEGF ...
Second COVID-19 mRNA vaccine dose found safe following allergic reactions to first dose
2021-07-26
BOSTON - In a multi-hospital analysis of individuals who experienced an allergic reaction to their first mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, all patients who went on to receive a second dose tolerated it without complications. The research, which was led by allergists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and is published in JAMA Internal Medicine, indicates that a first dose reaction to COVID-19 vaccination should not keep people from getting a second dose.
Allergic reactions after mRNA COVID-19 vaccinations have been reported to be as high as 2%, with anaphylaxis--a life-threatening whole-body allergic reaction--occurring in up to 2.5 per 10,000 people. ...
Plant root-associated bacteria preferentially colonize their native host-plant roots
2021-07-26
Plants, including crops such as rice and wheat, obtain their essential mineral nutrients and water through their roots, making them an important interface between plants and the soil environment. The roots of land plants associate with a wide range of microbes - including bacteria - that are recruited from the surrounding soil and assemble into structured communities known as the root microbiota. These microbial communities are sustained by the plant host, which provides them with nutrients, primarily in the form of organic carbon compounds secreted by the root. In turn, these commensal bacteria mediate multiple processes ...
Rare inherited variants in previously unsuspected genes may confer significant risk for autism
2021-07-26
New York, NY (July 26, 2021) - Researchers have identified a rare class of genetic differences transmitted from parents without autism to their affected children with autism and determined that they are most prominent in "multiplex" families with more than one family member on the spectrum. These findings are reported in Recent ultra-rare inherited variants implicate new autism candidate risk genes, END ...
International experts call for a unified public health response to NAFLD and NASH epidemic
2021-07-26
Bethesda, MD (July 26, 2021) -- There is an urgent need to develop and implement effective screening, diagnosis and treatment strategies for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), common liver conditions with a rising burden in the U.S. and globally. This is particularly important for the most at-risk patients, those with diabetes and obesity.
As a critical first step, the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) -- in collaboration with seven professional associations -- convened an international conference of 32 experts to develop a multidisciplinary action plan to improve care for the growing population of patients with NAFLD ...
International collaboration of scientists rewrite the rulebook of flowering plant genetics
2021-07-26
How do you study a group of organisms with over 300,000 species, dispersed across all seven continents, and with up to 50 times as much DNA content as the human genome?
This is the question posed to biologists studying the evolutionary history of flowering plants, called angiosperms, whose rapid diversification was so convoluted a problem that Darwin referred to it as the 'abominable mystery.'
This month, both the American Journal of Botany (AJB) and Applications in Plant Sciences (APPS) are devoting their July issues to what has recently become a turning point in the way scientists study the relationships among flowering plants. Dubbed Angiosperms353, the initiative combines ...
Improving air quality reduces dementia risk, multiple studies suggest
2021-07-26
DENVER, JULY 26, 2021 -- Improving air quality may improve cognitive function and reduce dementia risk, according to several studies reported today at the END ...
Misplaced trust: When trust in science fosters pseudoscience
2021-07-26
The Covid-19 pandemic and the politicization of health-prevention measures such as vaccination and mask-wearing have highlighted the need for people to accept and trust science.
But trusting science isn't enough.
A new study finds that people who trust science are more likely to believe and disseminate false claims containing scientific references than people who do not trust science. Reminding people of the value of critical evaluation reduces belief in false claims, but reminding them of the value of trusting science does not.
"We conclude that ...
Two types of blood pressure meds prevent heart events equally, but side effects differ
2021-07-26
DALLAS, July 26, 2021 -- People who are just beginning treatment for high blood pressure can benefit equally from two different classes of medicine - angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) - yet ARBs may be less likely to cause medication side effects, according to an analysis of real-world data published today in Hypertension, an American Heart Association journal.
While the class of blood pressure-lowering medicines called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors may be prescribed more commonly, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) work just as well and may cause fewer side effects. Currently, ACE inhibitors are prescribed more commonly than ARBs as a first-time blood pressure ...
New statement provides path to include ethnicity, ancestry, race in genomic research
2021-07-26
DALLAS, July 26, 2021 -- Genomic studies have produced advances in how to calculate and reduce heart-disease risk, however, the benefits don't necessarily apply to people from historically marginalized racial and ethnic groups and Indigenous populations. Efforts must be made to eliminate barriers to increase their participation in genomic research, according to a new scientific statement from the American Heart Association, published today in the Association's journal Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine.
"Profound breakthroughs in genetic and genomic science are rapidly improving our ability to prevent, detect and treat cardiovascular ...
Among effective antihypertensive drugs, less popular choice is slightly safer
2021-07-26
NEW YORK, NY (July 26, 2021)--Two types of drugs that are recommended as a first treatment for patients with high blood pressure were found equally effective in improving cardiovascular outcomes, but the more popular type causes slightly more side effects, finds a multinational observational study led by researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
The study, which analyzed claims and electronic health data from millions of patients worldwide, is the largest to compare the safety and efficacy of angiotensin-converting ...
Juicy past of favorite Okinawan fruit revealed
2021-07-26
Citrus fruits from the mandarin family have important commercial value but how their diversity arose has been something of a mystery
Researchers analyzed the genomes of the East Asian varieties and found a second center of diversity in the Ryukyu Islands along with the previously known center in the mountains of southern China
They discovered a new citrus species native to Okinawa that arose about two million years ago when the Ryukyu archipelago became disconnected from mainland Asia
Other citrus from Okinawa and mainland Japan, including shiikuwasha and tachibana, are hybrids of this newly discovered wild species with different mainland Asian varieties
This research may have commercial implications and ...
Anticipate a resurgence of respiratory viruses in young children
2021-07-26
Canada should anticipate a resurgence of a childhood respiratory virus as COVID-19 physical distancing measures are relaxed, authors warn in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Cases of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) have risen sharply in Australia and, more recently, the United States as COVID-19 case counts have waned and pandemic public health measures have been relaxed. Respiratory syncytial virus affects the lower respiratory tract and can cause serious illness and death. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, about 2.7 million children worldwide were infected with RSV each year, and it was the fourth most common cause of death in young children.
"The off-season resurgence in seasonal respiratory viruses now potentially poses a threat to vulnerable infants," ...
Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
2021-07-26
A new "return to campus" survey led by The Ohio State University's Office of the Chief Wellness Officer finds rising rates of anxiety, depression, burnout and the use of unhealthy coping mechanisms among students navigating through a year affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, similar to other data on college students throughout the U.S.
Ohio State conducted surveys in August 2020 and April 2021 of randomly-selected students to assess changes in mental health, coping strategies, healthy lifestyle behaviors and needs over time. Among the 1,072 Ohio State students who responded:
Students who screened positive for anxiety:
August 2020: 39%
April 2021: 42.6%
Students who screened positive for depression:
August 2020: 24.1%
April 2021: 28.3%
Students who screened ...
Goal-setting and positive parent-child relationships reduce risk of youth vaping
2021-07-26
PITTSBURGH, July 26, 2021 - Adolescents who set goals for their future and those with strong parental support are less likely to use e-cigarettes and other tobacco products, according to a study by UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine physician-scientists.
The research, published today in the journal Pediatrics, suggests that strategies to prevent youth vaping may be different from what works to dissuade youth from smoking cigarettes.
"The use of e-cigarettes by young people is at epidemic proportions, with 27% of youth ...
New research identifies cancer types with little survival improvements in adolescents and young adul
2021-07-26
Survival rates for adolescents and young adults diagnosed with cancer have varied considerably depending on cancer type. A new study indicates that survival for multiple cancer types in such patients has improved in recent years, but some patients diagnosed with common cancer types still show limited survival improvements. The results are published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, investigators at the National Cancer Institute analyzed survival trends related to cancers with the highest mortality rates in adolescents and young adults. Relying on information from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) cancer ...
Oncotarget: Replication-stress sensitivity in breast cancer cells
2021-07-26
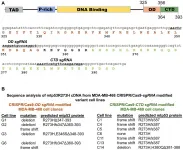
Oncotarget published "Frame-shift mediated reduction of gain-of-function p53 R273H and deletion of the R273H C-terminus in breast cancer cells result in replication-stress sensitivity" which reported that these authors recently documented that gain-of-function mutant p53 R273H in triple negative breast cancer cells interacts with replicating DNA and PARP1. The missense R273H GOF mtp53 has a mutated central DNA binding domain that renders it unable to bind specifically to DNA, but maintains the capacity to interact tightly with chromatin.
Both the C-terminal domain ...
Oncotarget: TERT and its binding protein: overexpression of GABPA/B in gliomas
2021-07-26
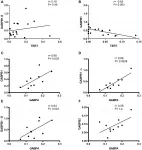
Oncotarget published "TERT and its binding protein: overexpression of GABPA/B in high grade gliomas" which reported that all GA-binding proteins progress through the glioma grades and have the highest expression levels in secondary glioblastomas.
In secondary glioblastomas after chemotherapy, GABPB1 and GABPB1-L are expressed on a lower level than without treatment.
Between primary and secondary glioblastomas with and without chemotherapy, TERT is elevated in the former while GABPB1 is increased in the secondary glioblastomas.
GABPA and GABPB1, GABPB1-L and GABPB1-S positively correlate in primary glioblastomas.
This ...
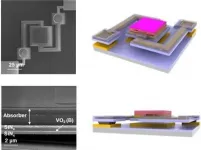
Development of a novel technology to check body temperature with smartphone camera
2021-07-26
Thermal-imaging sensors that detect and capture images of the heat signatures of human bodies and other objects have recently sprung into use in thermostats to check facial temperatures in a contactless attempt to screen for COVID-19 at several building entrances. Under these circumstances, the smartphone industry is actively considering the incorporation of such sensors as portable features to create the add-on function of measuring temperature in real time. Additionally, the application of such technology to autonomous vehicles may facilitate safer autonomous driving.
A research team lead by Dr. ...
[1] ... [2090]
[2091]
[2092]
[2093]
[2094]
[2095]
[2096]
[2097]
2098
[2099]
[2100]
[2101]
[2102]
[2103]
[2104]
[2105]
[2106]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.